Peering deeply into the cosmos, NASA’s James Webb House Telescope is giving scientists their first detailed glimpse of supernovae from a time when our universe used to be only a small fraction of its present age. A crew the usage of Webb information has known 10 instances extra supernovae within the early universe than have been up to now identified. A number of the newfound exploding stars are essentially the most far-off examples in their sort, together with the ones used to measure the universe’s growth price.
“Webb is a supernova discovery system,” stated Christa DeCoursey, a third-year graduate scholar on the Steward Observatory and the College of Arizona in Tucson. “The sheer collection of detections plus the good distances to those supernovae are the 2 most fun results from our survey.”
DeCoursey offered those findings in a press convention on the 244th assembly of the American Astronomical Society in Madison, Wisconsin.
‘A Supernova Discovery System’
To make those discoveries, the crew analyzed imaging information bought as a part of the JWST Complex Deep Extragalactic Survey (JADES) program. Webb is perfect for locating extraordinarily far-off supernovae as a result of their gentle is stretched into longer wavelengths — a phenomenon referred to as cosmological redshift.
Previous to Webb’s release, just a handful of supernovae were discovered above a redshift of two, which corresponds to when the universe used to be simplest 3.3 billion years previous — simply 25% of its present age. The JADES pattern comprises many supernovae that exploded even additional previously, when the universe used to be lower than 2 billion years previous.
Prior to now, researchers used NASA’s Hubble House Telescope to view supernovae from when the universe used to be within the “younger grownup” level. With JADES, scientists are seeing supernovae when the universe used to be in its “youth” or “pre-teens.” Sooner or later, they hope to appear again to the “infant” or “toddler” segment of the universe.
To find the supernovae, the crew when compared a couple of photographs taken as much as 12 months aside and seemed for resources that disappeared or gave the impression in the ones photographs. Those items that adjust in seen brightness through the years are known as transients, and supernovae are a kind of temporary. In all, the JADES Brief Survey Pattern crew exposed about 80 supernovae in a patch of sky simplest concerning the thickness of a grain of rice held at arm’s duration.
“That is in reality our first pattern of what the high-redshift universe looks as if for temporary science,” stated teammate Justin Pierel, a NASA Einstein Fellow on the House Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Maryland. “We’re seeking to establish whether or not far-off supernovae are basically other from or very just like what we see within the within sight universe.”
Pierel and different STScI researchers supplied knowledgeable research to resolve which transients have been in truth supernovae and which have been no longer, as a result of regularly they seemed very identical.
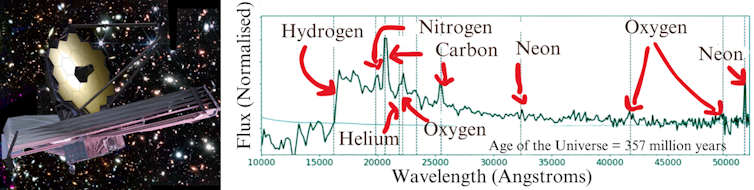
The crew known a variety of high-redshift supernovae, together with the farthest one ever spectroscopically showed, at a redshift of three.6. Its progenitor famous person exploded when the universe used to be only one.8 billion years previous. This is a so-called core-collapse supernova, an explosion of a large famous person.
Uncovering Far away Sort Ia Supernovae
Of explicit pastime to astrophysicists are Sort Ia supernovae. Those exploding stars are so predictably vivid that they’re used to measure far away cosmic distances and lend a hand scientists to calculate the universe’s growth price. The crew known no less than one Sort Ia supernova at a redshift of two.9. The sunshine from this explosion started touring to us 11.5 billion years in the past when the universe used to be simply 2.3 billion years previous. The former distance file for a spectroscopically showed Sort Ia supernova used to be a redshift of one.95, when the universe used to be 3.4 billion years previous.
Scientists are keen to research Sort Ia supernovae at excessive redshifts to look if all of them have the similar intrinsic brightness, without reference to distance. That is significantly necessary, as a result of if their brightness varies with redshift, they wouldn’t be dependable markers for measuring the growth price of the universe.
Pierel analyzed this Sort Ia supernova discovered at redshift 2.9 to resolve if its intrinsic brightness used to be other than anticipated. Whilst that is simply the primary such object, the effects point out no proof that Sort Ia brightness adjustments with redshift. Extra information is wanted, however for now, Sort Ia supernova-based theories concerning the universe’s growth price and its final destiny stay intact. Pierel additionally offered his findings on the 244th assembly of the American Astronomical Society.
Taking a look Towards the Long run
The early universe used to be an overly other position with excessive environments. Scientists be expecting to look historical supernovae that come from stars that include a ways fewer heavy chemical parts than stars like our Solar. Evaluating those supernovae with the ones within the native universe will lend a hand astrophysicists perceive famous person formation and supernova explosion mechanisms at those early instances.
“We’re necessarily opening a brand new window at the temporary universe,” stated STScI Fellow Matthew Siebert, who’s main the spectroscopic research of the JADES supernovae. “Traditionally, every time we’ve got executed that, we’ve got discovered extraordinarily thrilling issues — issues that we did not be expecting.”
“As a result of Webb is so delicate, it is discovering supernovae and different transients nearly all over it’s pointed,” stated JADES crew member Eiichi Egami, a analysis professor on the College of Arizona in Tucson. “That is the primary important step towards extra intensive surveys of supernovae with Webb.”
The James Webb House Telescope is the sector’s premier house science observatory. Webb is fixing mysteries in our sun device, taking a look past to far-off worlds round different stars, and probing the mysterious constructions and origins of our universe and our position in it. Webb is a global program led through NASA with its companions, ESA (Eu House Company) and CSA (Canadian House Company).
NASA's Webb Opens New Window on Supernova Science










_Gd6attm.jpg?width=690&quality=80&format=jpg&auto=webp)

