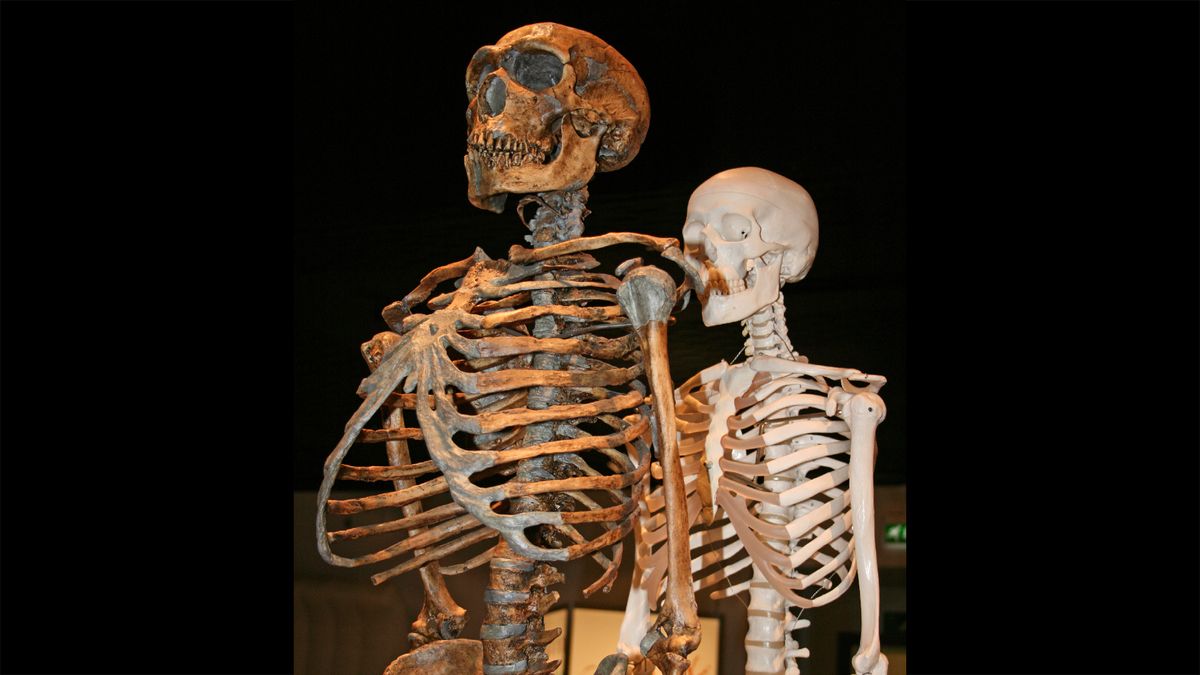
Neanderthal genes noticed in fashionable people will have entered our DNA thru an period of interbreeding beginning about 47,000 years in the past that lasted just about 7,000 years, new analysis unearths.Neanderthals had been a few of the closest extinct relations of contemporary people (Homo sapiens), with the ancestors of each lineages diverging about 500,000 years in the past. Greater than a decade in the past, scientists printed that Neanderthals interbred with the ancestors of contemporary people who migrated out of Africa. As of late, the genomes of contemporary human populations out of doors Africa comprise about 1% to two% of Neanderthal DNA.Researchers are nonetheless undecided about when and the place Neanderthal DNA made its means into the trendy human genome. As an example, did Neanderthals and fashionable people intermingle at one explicit position and time out of doors Africa, or did they interbreed at many puts and instances?To resolve this thriller, researchers analyzed greater than 300 fashionable human genomes spanning the previous 45,000 years. Those incorporated samples from 59 people who lived between 2,200 and 45,000 years in the past and 275 various present-day fashionable people. The scientists posted their findings at the BioRxiv preprint database. (Because the find out about is these days underneath evaluation for doable newsletter in a systematic magazine, the find out about’s authors declined to remark.)The scientists concerned about how a lot Neanderthal DNA they may see in those fashionable human samples. By means of evaluating how the extent of Neanderthal ancestry numerous in fashionable human DNA throughout other places and instances, they may estimate when Neanderthals and fashionable people interbred, and for the way lengthy.Comparable: ‘Extra Neanderthal than human’: How your well being would possibly rely on DNA from our long-lost ancestorsThe perfect clarification for many Neanderthal DNA noticed within the fashionable human genome was once a unmarried main duration of interbreeding about 47,000 years in the past that lasted about 6,800 years, the researchers discovered. Get the arena’s most attractive discoveries delivered directly in your inbox.As fashionable people began leaving Africa a minimum of 194,000 years in the past, a most likely position for them to stumble upon Neanderthals was once western Asia, the place Africa connects with Eurasia, Chris Stringer, a paleoanthropologist on the Herbal Historical past Museum in London who was once no longer concerned within the new find out about, informed Are living Science. Fashionable people bearing Neanderthal ancestry will have then dispersed around the globe, he famous.The scientists additionally investigated how Neanderthal DNA endured within the fashionable human genome over the years. The longer a piece of Neanderthal DNA lasted, the much more likely it bestowed some more or less evolutionary get advantages to trendy people. Conversely, Neanderthal DNA that were given weeded out temporarily most likely conferred some form of evolutionary drawback. The researchers discovered the Neanderthal genes that lasted are related to pores and skin colour, metabolism and the immune machine, most likely offering some more or less fast get advantages to trendy people as they encountered new evolutionary pressures out of doors Africa.Given the velocity at which maximum Neanderthal DNA was once eradicated from the trendy human genome, the find out about estimated that after the newly known duration of interbreeding ended, greater than 5% of the trendy human genome was once Neanderthal in foundation. In different phrases, “about one in 20 oldsters in our ancestral inhabitants was once a Neanderthal,” Fernando Villanea, a inhabitants geneticist on the College of Colorado Boulder who didn’t participate on this find out about, informed Are living Science.Rajiv McCoy, a inhabitants geneticist at Johns Hopkins College in Baltimore who didn’t take part on this new paintings, informed Are living Science that interbreeding between Neanderthals and fashionable people will have additionally taken position at different instances, however that those didn’t depart any lasting strains within the fashionable human gene pool. As an example, a contemporary human jaw from about 37,000 to 42,000 years in the past present in Romania in 2002 possesses Neanderthal DNA no longer noticed in different fashionable human genomes, which would possibly replicate an interbreeding tournament “that didn’t give a contribution to recent human variety,” in line with McCoy.Stringer famous that prior analysis instructed that the interbreeding that offered Neanderthal DNA into the trendy human genome came about between 50,000 and 60,000 years in the past. The brand new estimate of 47,000 years in the past “has implications for Homo sapiens dispersals out of doors of Africa, as a result of all extant [living] populations out of doors of Africa — Chinese language, Local American citizens, Indonesians, Local Australians and so forth — raise the indicators of this tournament, which due to this fact constrains when their ancestors started to disperse, to not up to more or less 47,000 years in the past,” Stringer mentioned.Then again, “there may be archaeological proof of human career in northern Australia about 65,000 years in the past,” Stringer mentioned. “So both that proof is mistaken; the populations had been Homo sapiens however they went extinct or had been swamped by means of a later dispersal; or the inhabitants was once no longer, in truth, Homo sapiens.” The latter risk “turns out a lot much less most likely given the complicated habits implied by means of the proof, however could be an enormous bombshell, in fact.”Apparently, the change of DNA seems to were a technique — which means fashionable human DNA turns out to have no longer entered Neanderthal genomes. “There’s little proof of gene go with the flow within the opposite route at the moment — this is, Homo sapiens to Neanderthal,” Stringer famous. “Perhaps it did occur however we’ve not but detected it. Or most likely it didn’t occur, with implications for the habits of the 2 populations.” Or most likely such hybrids had been much less a success for some reason why, he famous — for example, most likely they had been much less wholesome, or much less fertile.