The kilonova explosion that resulted when two neutron stars slammed into each and every different a thousand million light-years away became out to be manufacturing unit for uncommon heavy components.It is the first time the James Webb Area Telescope has probed such an tournament; and, within the aftermath of a colossal gamma-ray burst that emerged on 7 March 2023, the telescope’s information published proof of tellurium – an extraordinary steel too heavy to be solid within the hearts of stars by way of the method of fusion.There used to be additionally an offer of different metals, corresponding to tungsten and selenium. The invention, researchers say, confirms neutron big name mergers as a supply of heavy components, a very powerful piece of ways our Universe makes subject material and spreads it throughout house.”There are just a mere handful of recognized kilonovas, and that is the primary time we’ve been ready to have a look at the aftermath of a kilonova with the James Webb Area Telescope,” says astrophysicist Andrew Levan of Radboud College, who led the research.He provides, “Simply over 150 years since Dmitri Mendeleev wrote down the periodic desk of components, we at the moment are in the end able to start out filling in the ones closing blanks of working out the place the whole lot used to be made.”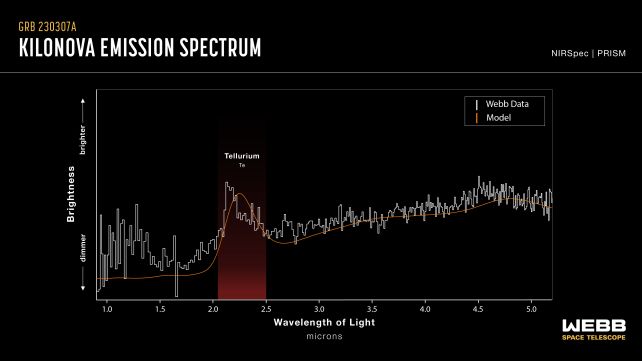 The spectrum noticed by way of JWST, with the signature of tellurium. (NASA, ESA, CSA, J. Olmsted/STScI)Stars are beautiful glorious issues, in reality. They take the hydrogen that makes up maximum of Universe’s visual topic, and spoil its atoms in combination, over and over again, to make heavier components: hydrogen into helium, after which the ones heavier atoms into even heavier ones, the entire approach as much as iron.That is the place stars’ fusion engines run out of oomph, regardless that. The fusion of iron into heavier components calls for a better power expenditure than it releases, surroundings the big name on a trail to head kaboom beneath the load of its personal gravity.However this full of life blast too can generate a chain of nuclear reactions wherein atomic nuclei collide with free neutrons to synthesize even heavier components.The reactions wish to occur temporarily sufficient that radioactive decay does not have an opportunity to happen sooner than extra neutrons are added to the nucleus. This implies it must occur the place there are a large number of unfastened neutrons floating about – like inside a supernova or kilonova. This actual nucleosynthesis task is referred to as the speedy neutron seize task, or r-process.When two neutron stars had been noticed colliding for the primary time in 2017, the aftermath showed that kilonovae produce r-process components. Scientists detected the presence of strontium, the thirty eighth part at the periodic desk.
The spectrum noticed by way of JWST, with the signature of tellurium. (NASA, ESA, CSA, J. Olmsted/STScI)Stars are beautiful glorious issues, in reality. They take the hydrogen that makes up maximum of Universe’s visual topic, and spoil its atoms in combination, over and over again, to make heavier components: hydrogen into helium, after which the ones heavier atoms into even heavier ones, the entire approach as much as iron.That is the place stars’ fusion engines run out of oomph, regardless that. The fusion of iron into heavier components calls for a better power expenditure than it releases, surroundings the big name on a trail to head kaboom beneath the load of its personal gravity.However this full of life blast too can generate a chain of nuclear reactions wherein atomic nuclei collide with free neutrons to synthesize even heavier components.The reactions wish to occur temporarily sufficient that radioactive decay does not have an opportunity to happen sooner than extra neutrons are added to the nucleus. This implies it must occur the place there are a large number of unfastened neutrons floating about – like inside a supernova or kilonova. This actual nucleosynthesis task is referred to as the speedy neutron seize task, or r-process.When two neutron stars had been noticed colliding for the primary time in 2017, the aftermath showed that kilonovae produce r-process components. Scientists detected the presence of strontium, the thirty eighth part at the periodic desk.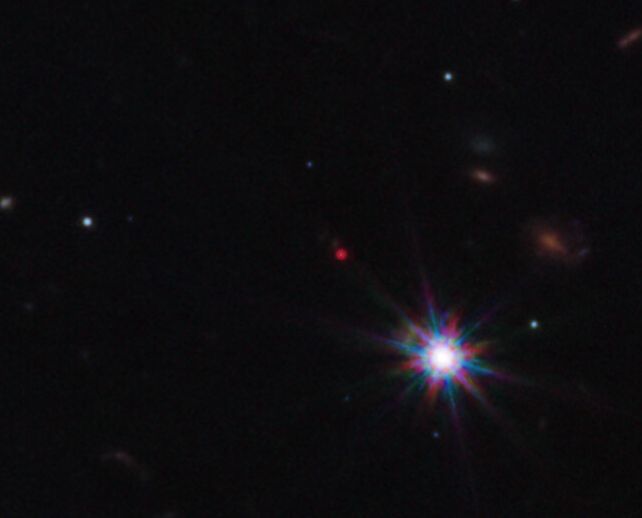 The pink dot in the course of the picture is the kilonova noticed by way of JWST. (NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, A. Levan/IMAPP, Warw, A. Pagan/STScI)When a gamma-ray burst, named GRB230307A, used to be stuck flaring in March of this 12 months, scientists in an instant tuned in for a better glance. GRB230307A used to be in reality impressive – probably the most brightest gamma-ray bursts ever noticed, 1,000 instances brighter than conventional and over 1,000,000 instances brighter than all the Milky Means Galaxy.It used to be additionally of an strangely lengthy length, at round 200 seconds. This lengthy length is considered a signature of a kilonova – supernova gamma-ray bursts are of a far shorter length. Multi-wavelength observations showed it: the profile of the aftermath of the burst used to be in line with a kilonova foundation.And because kilonovae are a recognized supply of r-process components, astronomers asked to check out the supply of the explosion with the infrared JWST.On 5 April, they became the telescope to the glow, which by way of then had a vital infrared element, and picked up spectra.This information published the presence of tellurium, the 52nd part at the periodic desk. That is beautiful hefty. That implies there are probably different r-process components within the increasing ejecta from the neutron big name collision, even though extra observations might be had to verify that.
The pink dot in the course of the picture is the kilonova noticed by way of JWST. (NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, A. Levan/IMAPP, Warw, A. Pagan/STScI)When a gamma-ray burst, named GRB230307A, used to be stuck flaring in March of this 12 months, scientists in an instant tuned in for a better glance. GRB230307A used to be in reality impressive – probably the most brightest gamma-ray bursts ever noticed, 1,000 instances brighter than conventional and over 1,000,000 instances brighter than all the Milky Means Galaxy.It used to be additionally of an strangely lengthy length, at round 200 seconds. This lengthy length is considered a signature of a kilonova – supernova gamma-ray bursts are of a far shorter length. Multi-wavelength observations showed it: the profile of the aftermath of the burst used to be in line with a kilonova foundation.And because kilonovae are a recognized supply of r-process components, astronomers asked to check out the supply of the explosion with the infrared JWST.On 5 April, they became the telescope to the glow, which by way of then had a vital infrared element, and picked up spectra.This information published the presence of tellurium, the 52nd part at the periodic desk. That is beautiful hefty. That implies there are probably different r-process components within the increasing ejecta from the neutron big name collision, even though extra observations might be had to verify that. The site of the explosion, approach out in intergalactic house. (NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, A. Levan/IMAPP, Warw, A. Pagan/STScI)And it is price noting that the explosion happened someplace in reality bizarre: in intergalactic house, 120,000 light-years from the closest galaxy. The researchers made up our minds that the galaxy used to be most certainly the place the 2 neutron stars had originated as customary, huge stars; when each and every went supernova a while prior to now, one at a time, the power of the explosions used to be sufficient of a kick to yeet them filter of the galaxy.There is much more to be realized from this attention-grabbing tournament, the researchers say.”Till not too long ago, we did not assume mergers may energy gamma-ray bursts for greater than two seconds,” says astronomer Ben Gompertz of the College of Birmingham in the United Kingdom.”Our subsequent process is to search out extra of those long-lived mergers and increase a greater working out of what drives them – and whether or not even heavier components are being created. This discovery has opened the door to a transformative working out of our universe and the way it works.”The analysis has been printed in Nature.
The site of the explosion, approach out in intergalactic house. (NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, A. Levan/IMAPP, Warw, A. Pagan/STScI)And it is price noting that the explosion happened someplace in reality bizarre: in intergalactic house, 120,000 light-years from the closest galaxy. The researchers made up our minds that the galaxy used to be most certainly the place the 2 neutron stars had originated as customary, huge stars; when each and every went supernova a while prior to now, one at a time, the power of the explosions used to be sufficient of a kick to yeet them filter of the galaxy.There is much more to be realized from this attention-grabbing tournament, the researchers say.”Till not too long ago, we did not assume mergers may energy gamma-ray bursts for greater than two seconds,” says astronomer Ben Gompertz of the College of Birmingham in the United Kingdom.”Our subsequent process is to search out extra of those long-lived mergers and increase a greater working out of what drives them – and whether or not even heavier components are being created. This discovery has opened the door to a transformative working out of our universe and the way it works.”The analysis has been printed in Nature.
Neutron Famous person Collision Stuck Forging Heavy Metals in a JWST First