A map of the crystal construction of the alloy made with electron backscatter diffraction in a scanning electron microscope. Each and every colour represents a piece of the crystal the place the repeating construction adjustments its 3-d orientation. Credit score: Berkeley LabResearchers have found out an unusual steel alloy that gained’t crack at excessive temperatures because of kinking, or bending, of crystals within the alloy on the atomic degree.A steel alloy composed of niobium, tantalum, titanium, and hafnium has surprised fabrics scientists with its spectacular power and toughness at each extraordinarily cold and warm temperatures, a mix of homes that gave the impression thus far to be just about inconceivable to reach. On this context, power is outlined as how a lot power a subject material can face up to prior to it’s completely deformed from its unique form, and toughness is its resistance to fracturing (cracking). The alloy’s resilience to bending and fracture throughout a huge vary of prerequisites may just open the door for a singular elegance of fabrics for next-generation engines that may perform at upper efficiencies.The staff, led via Robert Ritchie at Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and UC Berkeley, in collaboration with the teams led via professors Diran Apelian at UC Irvine and Enrique Lavernia at Texas A&M College, found out the alloy’s sudden homes after which found out how they stand up from interactions within the atomic construction. Their paintings is described in a learn about just lately revealed within the magazine Science.“The potency of changing warmth to electrical energy or thrust is made up our minds via the temperature at which gasoline is burned – the warmer, the easier. Alternatively, the working temperature is proscribed via the structural fabrics which should face up to it,” mentioned first writer David Prepare dinner, a Ph.D. scholar in Ritchie’s lab. “Now we have exhausted the facility to additional optimize the fabrics we these days use at excessive temperatures, and there’s a large want for novel metal fabrics. That’s what this alloy presentations promise in.”The alloy on this learn about is from a brand new elegance of metals referred to as refractory excessive or medium entropy alloys (RHEAs/RMEAs). Many of the metals we see in industrial or commercial programs are alloys made of 1 primary steel combined with small amounts of alternative components, however RHEAs and RMEAs are made via blending near-equal amounts of metal components with very excessive melting temperatures, which supplies them distinctive homes that scientists are nonetheless unraveling. Ritchie’s team has been investigating those alloys for a number of years on account of their possible for high-temperature programs.
A map of the crystal construction of the alloy made with electron backscatter diffraction in a scanning electron microscope. Each and every colour represents a piece of the crystal the place the repeating construction adjustments its 3-d orientation. Credit score: Berkeley LabResearchers have found out an unusual steel alloy that gained’t crack at excessive temperatures because of kinking, or bending, of crystals within the alloy on the atomic degree.A steel alloy composed of niobium, tantalum, titanium, and hafnium has surprised fabrics scientists with its spectacular power and toughness at each extraordinarily cold and warm temperatures, a mix of homes that gave the impression thus far to be just about inconceivable to reach. On this context, power is outlined as how a lot power a subject material can face up to prior to it’s completely deformed from its unique form, and toughness is its resistance to fracturing (cracking). The alloy’s resilience to bending and fracture throughout a huge vary of prerequisites may just open the door for a singular elegance of fabrics for next-generation engines that may perform at upper efficiencies.The staff, led via Robert Ritchie at Lawrence Berkeley Nationwide Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and UC Berkeley, in collaboration with the teams led via professors Diran Apelian at UC Irvine and Enrique Lavernia at Texas A&M College, found out the alloy’s sudden homes after which found out how they stand up from interactions within the atomic construction. Their paintings is described in a learn about just lately revealed within the magazine Science.“The potency of changing warmth to electrical energy or thrust is made up our minds via the temperature at which gasoline is burned – the warmer, the easier. Alternatively, the working temperature is proscribed via the structural fabrics which should face up to it,” mentioned first writer David Prepare dinner, a Ph.D. scholar in Ritchie’s lab. “Now we have exhausted the facility to additional optimize the fabrics we these days use at excessive temperatures, and there’s a large want for novel metal fabrics. That’s what this alloy presentations promise in.”The alloy on this learn about is from a brand new elegance of metals referred to as refractory excessive or medium entropy alloys (RHEAs/RMEAs). Many of the metals we see in industrial or commercial programs are alloys made of 1 primary steel combined with small amounts of alternative components, however RHEAs and RMEAs are made via blending near-equal amounts of metal components with very excessive melting temperatures, which supplies them distinctive homes that scientists are nonetheless unraveling. Ritchie’s team has been investigating those alloys for a number of years on account of their possible for high-temperature programs.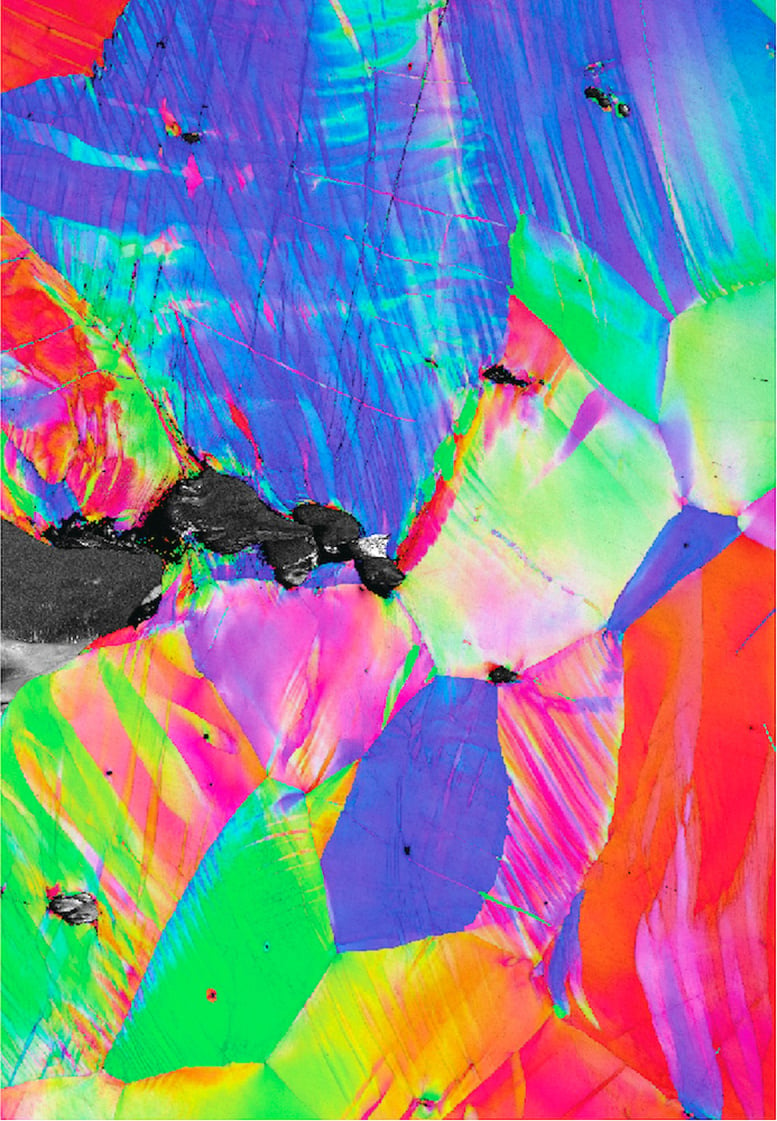 This subject material construction map presentations kink bands shaped close to a crack tip right through crack propagation (from left to proper) within the alloy at 25 C, room temperature. Made with a electron-backscatter diffraction detector in a scanning electron microscope. Credit score: Berkeley Lab“Our staff has carried out earlier paintings on RHEAs and RMEAs and we now have discovered that those fabrics are very robust, however in most cases possess extraordinarily low fracture toughness, which is why we have been surprised when this alloy displayed exceptionally excessive toughness,” mentioned co-corresponding writer Punit Kumar, a postdoctoral researcher within the team.Consistent with Prepare dinner, maximum RMEAs have a fracture toughness of not up to 10 MPa√m, which makes them one of the vital maximum brittle metals on file. The most efficient cryogenic steels, specifically engineered to withstand fracture, are about 20 occasions harder than those fabrics. But the niobium, tantalum, titanium, and hafnium (Nb45Ta25Ti15Hf15) RMEA alloy used to be ready to overcome even the cryogenic metal, clocking in at over 25 occasions harder than conventional RMEAs at room temperature.However engines don’t perform at room temperature. The scientists evaluated power and toughness at 5 temperatures overall: -196°C (the temperature of liquid nitrogen), 25°C (room temperature), 800°C, 950°C, and 1200°C. The final temperature is ready 1/5 the outside temperature of the solar.The staff discovered that the alloy had the best power within the chilly and become reasonably weaker because the temperature rose, however nonetheless boasted spectacular figures all over the big variety. The fracture toughness, which is calculated from how a lot power it takes to propagate an present crack in a subject material, used to be excessive in any respect temperatures.Unraveling the atomic arrangementsAlmost all metal alloys are crystalline, that means that the atoms within the subject material are organized in repeating devices. Alternatively, no crystal is best possible, all of them include defects. Essentially the most distinguished defect that strikes is named the dislocation, which is an unfinished airplane of atoms within the crystal. When power is implemented to a steel it reasons many dislocations to transport to deal with the form trade.As an example, while you bend a paper clip which is product of aluminum, the motion of dislocations within the paper clip contains the form trade. Alternatively, the motion of dislocations turns into tougher at decrease temperatures and because of this many fabrics turn into brittle at low temperatures as a result of dislocations can’t transfer. Because of this the metal hull of the Titanic fractured when it hit an iceberg. Parts with excessive melting temperatures and their alloys take this to the intense, with many last brittle as much as even 800°C. Alternatively, this RMEA greenbacks the fad, withstanding snapping even at temperatures as little as liquid nitrogen (-196°C).
This subject material construction map presentations kink bands shaped close to a crack tip right through crack propagation (from left to proper) within the alloy at 25 C, room temperature. Made with a electron-backscatter diffraction detector in a scanning electron microscope. Credit score: Berkeley Lab“Our staff has carried out earlier paintings on RHEAs and RMEAs and we now have discovered that those fabrics are very robust, however in most cases possess extraordinarily low fracture toughness, which is why we have been surprised when this alloy displayed exceptionally excessive toughness,” mentioned co-corresponding writer Punit Kumar, a postdoctoral researcher within the team.Consistent with Prepare dinner, maximum RMEAs have a fracture toughness of not up to 10 MPa√m, which makes them one of the vital maximum brittle metals on file. The most efficient cryogenic steels, specifically engineered to withstand fracture, are about 20 occasions harder than those fabrics. But the niobium, tantalum, titanium, and hafnium (Nb45Ta25Ti15Hf15) RMEA alloy used to be ready to overcome even the cryogenic metal, clocking in at over 25 occasions harder than conventional RMEAs at room temperature.However engines don’t perform at room temperature. The scientists evaluated power and toughness at 5 temperatures overall: -196°C (the temperature of liquid nitrogen), 25°C (room temperature), 800°C, 950°C, and 1200°C. The final temperature is ready 1/5 the outside temperature of the solar.The staff discovered that the alloy had the best power within the chilly and become reasonably weaker because the temperature rose, however nonetheless boasted spectacular figures all over the big variety. The fracture toughness, which is calculated from how a lot power it takes to propagate an present crack in a subject material, used to be excessive in any respect temperatures.Unraveling the atomic arrangementsAlmost all metal alloys are crystalline, that means that the atoms within the subject material are organized in repeating devices. Alternatively, no crystal is best possible, all of them include defects. Essentially the most distinguished defect that strikes is named the dislocation, which is an unfinished airplane of atoms within the crystal. When power is implemented to a steel it reasons many dislocations to transport to deal with the form trade.As an example, while you bend a paper clip which is product of aluminum, the motion of dislocations within the paper clip contains the form trade. Alternatively, the motion of dislocations turns into tougher at decrease temperatures and because of this many fabrics turn into brittle at low temperatures as a result of dislocations can’t transfer. Because of this the metal hull of the Titanic fractured when it hit an iceberg. Parts with excessive melting temperatures and their alloys take this to the intense, with many last brittle as much as even 800°C. Alternatively, this RMEA greenbacks the fad, withstanding snapping even at temperatures as little as liquid nitrogen (-196°C).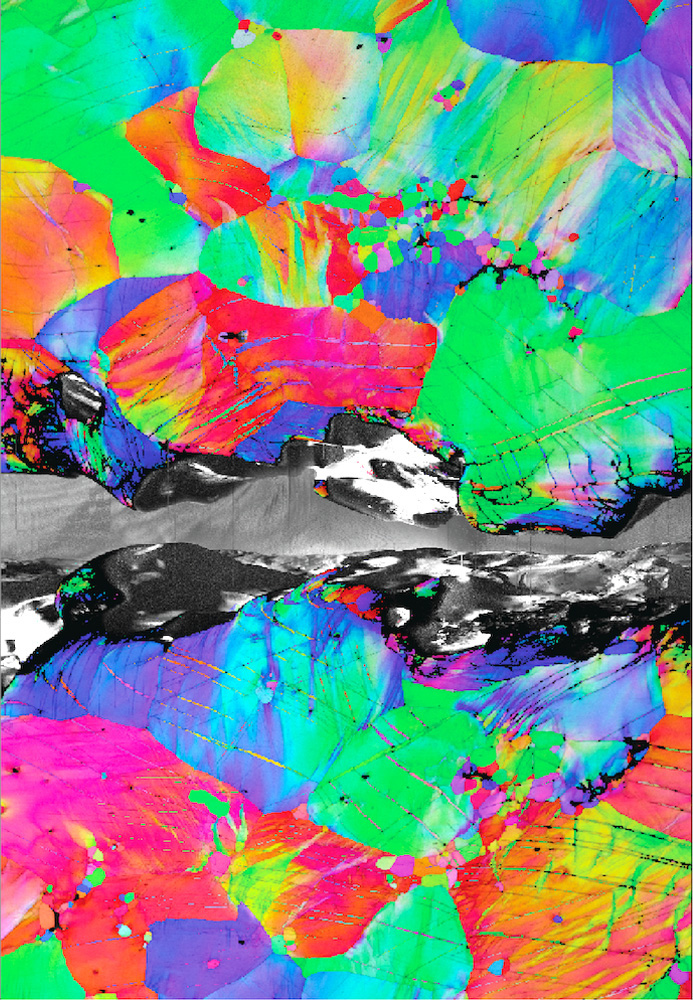 This map presentations kink bands shaped close to a crack tip right through crack propagation trying out (from left to proper) within the alloy at -196 C. Credit score: Berkeley LabTo perceive what used to be taking place within the outstanding steel, co-investigator Andrew Minor and his staff analyzed the wired samples, along unbent and uncracked regulate samples, the use of 4-dimensional scanning transmission electron microscopy (4D-STEM) and scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) on the Nationwide Middle for Electron Microscopy, a part of Berkeley Lab’s Molecular Foundry.The electron microscopy knowledge published that the alloy’s atypical toughness comes from an sudden aspect impact of an extraordinary defect referred to as a kink band. Kink bands shape in a crystal when an implemented power reasons strips of the crystal to cave in on themselves and swiftly bend. The path wherein the crystal bends in those strips will increase the power that dislocations really feel, inflicting them to transport extra simply. At the bulk degree, this phenomenon reasons the fabric to melt (that means that much less power must be implemented to the fabric as it’s deformed). The staff knew from previous analysis that kink bands shaped simply in RMEAs, however assumed that the softening impact would make the fabric much less tricky via making it more straightforward for a crack to unfold in the course of the lattice. However in fact, this isn’t the case.“We display, for the primary time, that within the presence of a pointy crack between atoms, kink bands in reality withstand the propagation of a crack via distributing harm clear of it, fighting fracture and resulting in extremely excessive fracture toughness,” mentioned Prepare dinner.The Nb45Ta25Ti15Hf15 alloy will wish to go through much more basic analysis and engineering trying out prior to the rest like a jet airplane turbine or SpaceX rocket nozzle is comprised of it, mentioned Ritchie, as a result of mechanical engineers rightfully require a deep figuring out of the way their fabrics carry out prior to they use them in the actual international. Alternatively, this learn about signifies that the steel has the prospective to construct the engines of the long run.Reference: “Kink bands advertise remarkable fracture resistance in a NbTaTiHf refractory medium-entropy alloy” via David H. Prepare dinner, Punit Kumar, Madelyn I. Payne, Calvin H. Belcher, Pedro Borges, Wenqing Wang, Flynn Walsh, Zehao Li, Arun Devaraj, Mingwei Zhang, Mark Asta, Andrew M. Minor, Enrique J. Lavernia, Diran Apelian and Robert O. Ritchie, 11 April 2024, Science.
This map presentations kink bands shaped close to a crack tip right through crack propagation trying out (from left to proper) within the alloy at -196 C. Credit score: Berkeley LabTo perceive what used to be taking place within the outstanding steel, co-investigator Andrew Minor and his staff analyzed the wired samples, along unbent and uncracked regulate samples, the use of 4-dimensional scanning transmission electron microscopy (4D-STEM) and scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) on the Nationwide Middle for Electron Microscopy, a part of Berkeley Lab’s Molecular Foundry.The electron microscopy knowledge published that the alloy’s atypical toughness comes from an sudden aspect impact of an extraordinary defect referred to as a kink band. Kink bands shape in a crystal when an implemented power reasons strips of the crystal to cave in on themselves and swiftly bend. The path wherein the crystal bends in those strips will increase the power that dislocations really feel, inflicting them to transport extra simply. At the bulk degree, this phenomenon reasons the fabric to melt (that means that much less power must be implemented to the fabric as it’s deformed). The staff knew from previous analysis that kink bands shaped simply in RMEAs, however assumed that the softening impact would make the fabric much less tricky via making it more straightforward for a crack to unfold in the course of the lattice. However in fact, this isn’t the case.“We display, for the primary time, that within the presence of a pointy crack between atoms, kink bands in reality withstand the propagation of a crack via distributing harm clear of it, fighting fracture and resulting in extremely excessive fracture toughness,” mentioned Prepare dinner.The Nb45Ta25Ti15Hf15 alloy will wish to go through much more basic analysis and engineering trying out prior to the rest like a jet airplane turbine or SpaceX rocket nozzle is comprised of it, mentioned Ritchie, as a result of mechanical engineers rightfully require a deep figuring out of the way their fabrics carry out prior to they use them in the actual international. Alternatively, this learn about signifies that the steel has the prospective to construct the engines of the long run.Reference: “Kink bands advertise remarkable fracture resistance in a NbTaTiHf refractory medium-entropy alloy” via David H. Prepare dinner, Punit Kumar, Madelyn I. Payne, Calvin H. Belcher, Pedro Borges, Wenqing Wang, Flynn Walsh, Zehao Li, Arun Devaraj, Mingwei Zhang, Mark Asta, Andrew M. Minor, Enrique J. Lavernia, Diran Apelian and Robert O. Ritchie, 11 April 2024, Science.
DOI: 10.1126/science.adn2428This analysis used to be performed via David H. Prepare dinner, Punit Kumar, Madelyn I. Payne, Calvin H. Belcher, Pedro Borges, Wenqing Wang, Flynn Walsh, Zehao Li, Arun Devaraj, Mingwei Zhang, Mark Asta, Andrew M. Minor, Enrique J. Lavernia, Diran Apelian, and Robert O. Ritchie, scientists at Berkeley Lab, UC Berkeley, Pacific Northwest Nationwide Laboratory, and UC Irvine, with investment from the Division of Power (DOE) Place of job of Science. Experimental and computational research used to be performed on the Molecular Foundry and the Nationwide Power Analysis Clinical Computing Middle – each are DOE Place of job of Science consumer amenities.
New Alloy Shocks Scientists With Its Just about Inconceivable Energy and Toughness