A world workforce of researchers has unveiled new insights into Earth’s earliest ecosystem and got here to a shocking consequence: existence may have begun flourishing inside of a couple of hundred million years of the planet’s formation.
The find out about, printed Friday within the magazine Nature Ecology & Evolution, specializes in our Final Common Commonplace Ancestor (LUCA), the hypothetical commonplace ancestor from which all fashionable mobile existence descends.
This comprises single-celled organisms akin to micro organism all of the approach up via timber, shellfish, dinosaurs, and people. LUCA is regarded as the basis of the tree of existence sooner than it branches into Micro organism, Archaea, and Eukarya.
The workforce when put next genes around the genomes of dwelling species, monitoring mutations that happened since they shared an ancestor in LUCA. Through aligning those genetic timelines with fossil data, they decided that LUCA existed round 4.2 billion years in the past, roughly 400 million years after Earth’s formation.
“We didn’t be expecting LUCA to be so outdated,” Dr. Sandra Álvarez-Carretero, from the College of Bristol’s College of Earth Sciences, mentioned in a commentary. “Then again, our effects are compatible with fashionable perspectives at the habitability of early Earth.”
Additional, the workforce modeled LUCA’s biology through inspecting the physiological traits of contemporary species and tracing them again to LUCA. “The evolutionary historical past of genes is sophisticated through their change between lineages,” explains lead writer Dr. Edmund Moody. “We need to use complicated evolutionary fashions to reconcile the evolutionary historical past of genes with the family tree of species.”
Tracing all of it again to LUCA
What’s outstanding about this find out about is how the genetic fingerprints of LUCA nonetheless exist on this huge variety of species which might, on its floor, glance irreconcilable.
“Some of the actual benefits this is making use of the gene-tree species-tree reconciliation technique to any such numerous dataset representing the principle domain names of existence Archaea and Micro organism,” mentioned find out about co-author Dr. Tom Williams from Bristol’s College of Organic Sciences. “This permits us to mention with some self assurance and assess that degree of self assurance on how LUCA lived.”
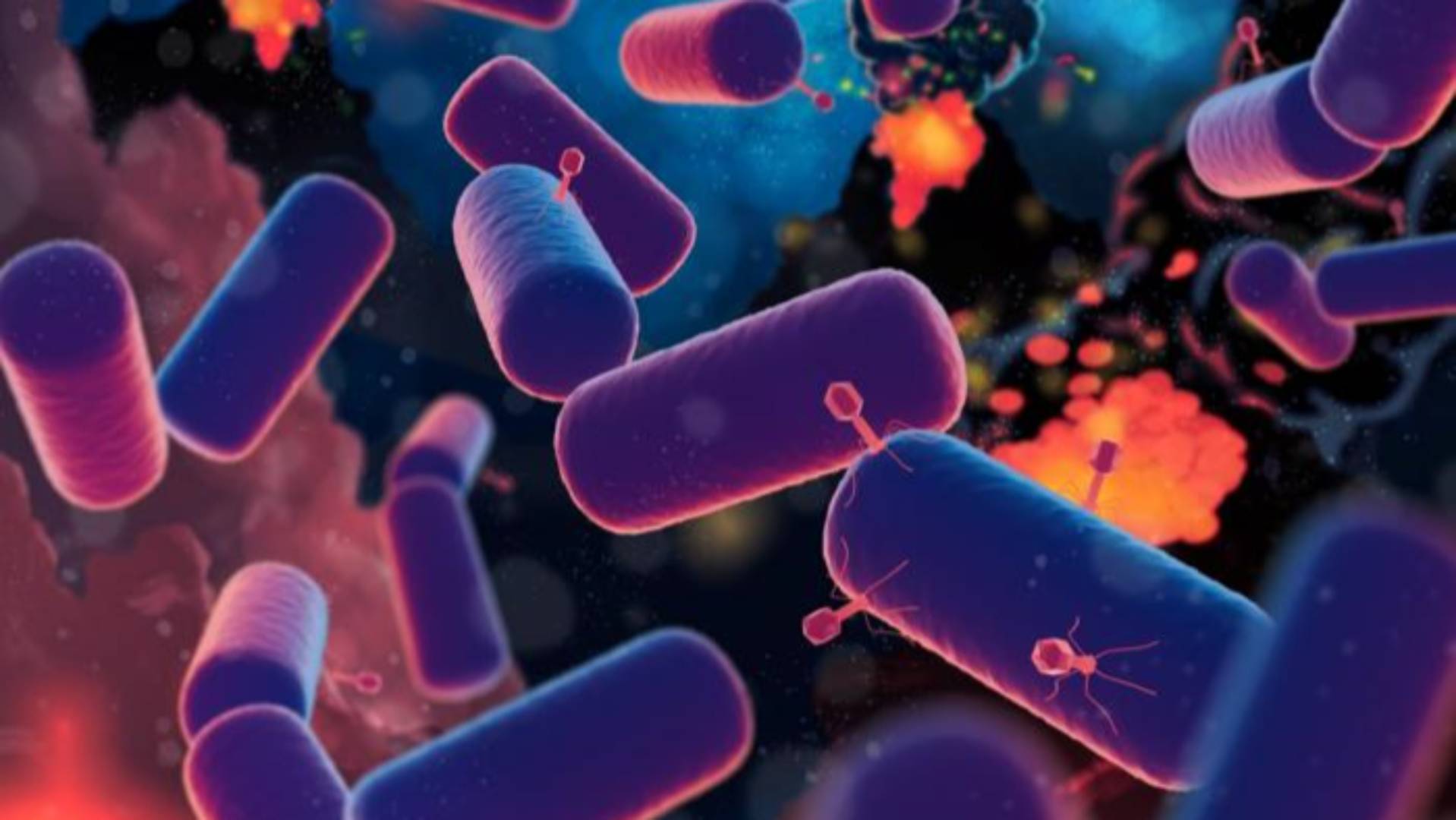
The find out about printed that LUCA used to be a posh organism, very similar to fashionable prokaryotes, and had an early immune machine, indicating an historic struggle with viruses. “It’s transparent LUCA used to be exploiting and converting its surroundings,” Co-author Tim Lenton, from the College of Exeter, mentioned. “It’s not likely to have lived on my own; its waste would had been meals for different microbes, making a recycling ecosystem.”NEWSLETTERThe Blueprint DailyStay up-to-date on engineering, tech, house, and science information with The Blueprint.ABOUT THE EDITORJohn Loeffler John is a creator and programmer dwelling in New York Town. He writes about computer systems, gadgetry, gaming, VR/AR, and comparable client applied sciences. You’ll be able to to find him on Twitter @thisdotjohn




![Galaxy S25 ‘Slender’ is almost definitely thicker than ‘iPhone 17 Air’ as leak finds 6.4mm design [Gallery] Galaxy S25 ‘Slender’ is almost definitely thicker than ‘iPhone 17 Air’ as leak finds 6.4mm design [Gallery]](https://9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2025/01/galaxy-s25-slim-4.jpg?quality=82&strip=all&w=1600)