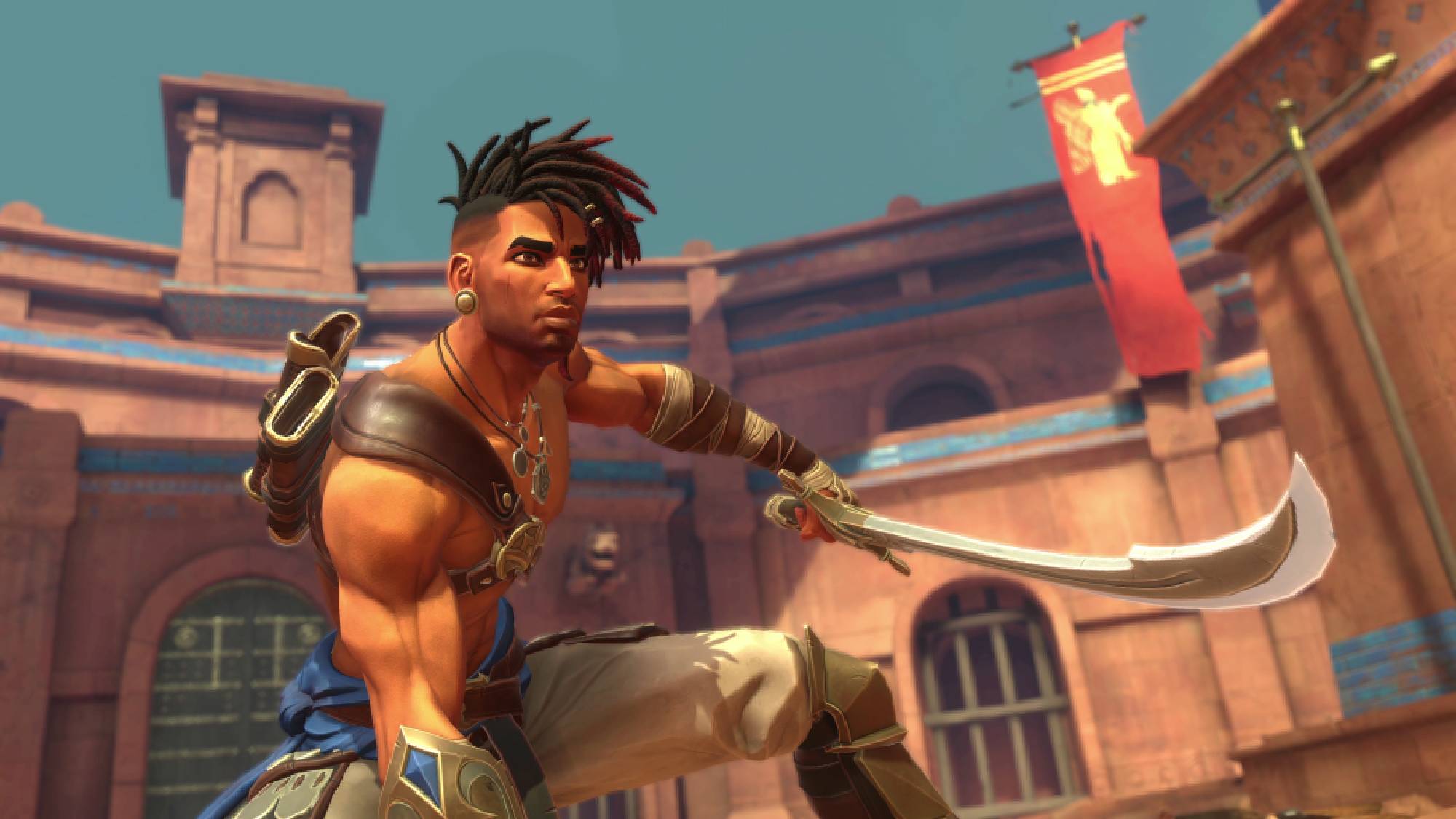
The simplified abstract diagram displays the relative variety of fossils prior to now 2 billion years. … [+] Easy eukaryotic cells ruled the primary part a thousand million years. Algae gave the impression round 1,200 million years in the past. The primary complicated animals like Charnia gave the impression round 500 million years in the past.Tang et al.2024/Science
A global crew of researchers revealed a high-resolution research of the worldwide variety of existence paperwork spanning 2 billion years in line with a world compilation of fossil information.
The fossil file of organisms with laborious portions (like bones and shells) displays how evolution and extinctions opened up during the last part a thousand million years. However existence on Earth arose a lot previous, a minimum of 3 to two billion years in the past. This early existence was once typically smaller and squishier, ruled via microbial communities, algae, sponges, worm-like creatures and jellyfish, leaving few lines to fossilize within the first position. Proterozoic fossils, relationship from 2,500 million to 539 million years in the past, come with frame imprints in effective sediments, stromatolites, hint fossils, chemical and isotopic stays.
A brand new learn about in line with to be had fossil information compiled a curve of existence’s variety spanning 2,000 million years, appearing how round 600 million years in the past a sequence of tremendous ice ages spurred a complete new generation for existence on Earth.
“That is probably the most complete and up-to-date research of this era thus far. And extra importantly, we’ve used a graphic correlation program that allowed us to reach better temporal decision,” explains Virginia Tech geobiologist Shuhai Xiao, coauthor of the learn about.
The analysis crew appeared particularly at information of historical marine eukaryotes — organisms whose cells include a nucleus. Early eukaryotes later developed into the multicellular organisms credited for ushering in a complete new generation for existence on Earth, together with animals, vegetation, and fungi.
The primary eukaryotes arose no later than 1.8 billion years in the past and step by step developed to a strong degree of variety from about 1,450 million to 720 million years in the past, a duration now and again referred via paleontologists because the “dull billion,” as species reputedly developed slower and lasted longer than those who got here later.
Between 720 million and 635 million years in the past, Earth plunged into a sequence of tremendous ice ages. Ice lined nearly all the planet, leaving at the back of glacial particles on the equator. When the ice in the end thawed, evolutionary process picked up, and issues weren’t so dull anymore. The primary complicated and big organisms seem within the fossil file in a while after, round 580 million years in the past.
“The ice ages had been a significant component that reset the evolutionary trail relating to variety and dynamics,” Xiao summarizes the learn about’s maximum intriguing conclusion. “We see fast turnover of eukaryotic species straight away after glaciation. That’s a big discovering.”
How precisely the glaciations boosted evolution isn’t but transparent. One speculation means that ice-shields eroded the continents and glaciers deposited nutrient-rich sediments within the oceans, offering a fertile surroundings for complicated existence to conform.
The learn about, “Quantifying the worldwide biodiversity of Proterozoic eukaryotes,” was once revealed within the magazine Science and may also be discovered on-line right here.
Further subject material and interviews supplied via Virginia Tech.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/rsp-tier-3-cerave-moisturizing-cream-hwortock-001-002-5cf5145cc2324820bdd1b68b96c01fa7.jpeg)




