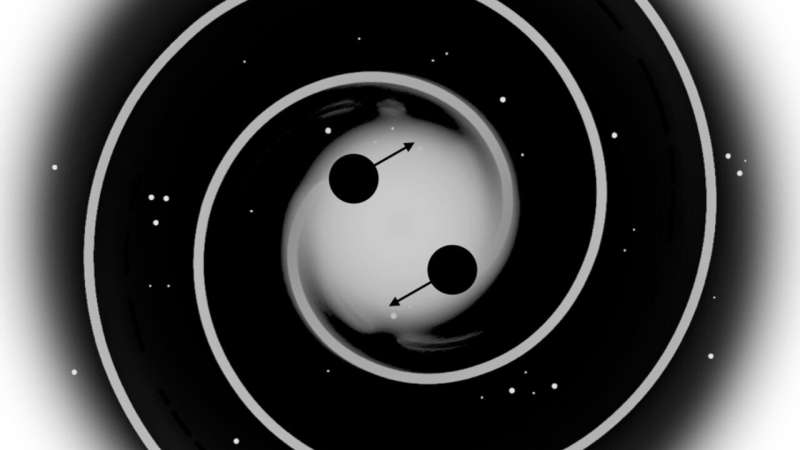
Illustrative illustration of a black hollow binary immersed in a depressing topic spike on the heart of a galaxy. Credit score: Authentic symbol: NASA science.nasa.gov/useful resource/spiral-galaxy-blue/. Changed by means of Alvarez, Cline, and Dewar.
In a brand new find out about, scientists from Canada have proposed a strategy to the general parsec downside of supermassive black hollow (SMBH) mergers the use of self-interacting darkish topic.
When two galaxies merge, fuel and dirt collide, resulting in superstar formation. Alternatively, the celebs themselves do not collide because of their huge distances. The SMBHs on the heart of the 2 galaxies additionally start to merge.
Alternatively, the merger of the black holes stalls when they’re 1 parsec (or 30.9 trillion kilometers) aside. This downside is referred to as the general parsec downside in astronomy and astrophysics.
The find out about, printed in Bodily Overview Letters (PRL), makes an attempt to unravel this downside and provide an explanation for the gravitational wave spectrum noticed in 2021 by means of the Pulsar Timing Array collaborations.
Phys.org spoke to the primary creator of the find out about, Dr. Gonzalo Alonso Alvarez, a postdoc on the College of Toronto.
Talking of the inducement in the back of the staff’s paintings, he stated, “What struck us probably the most when Pulsar Timing Array collaborations introduced proof for a gravitational wave spectrum is that there was once room to check new particle physics eventualities, in particular darkish topic self-interactions, even inside of the usual astrophysical clarification of supermassive black hollow mergers.”
Why forestall at 1 parsec?
When SMBHs from two merging galaxies are separated by means of 1 parsec, two counteracting issues are at play.
Originally, massive items like an SMBH reason ripples in spacetime, resulting in the formation of gravitational waves that trip all the way through spacetime. Those gravitational waves lift power clear of the supply. When two SMBHs merge, the gravitational waves lift power clear of the merger, inflicting the black holes to spiral inwards extra unexpectedly.
The second one is a frictional power referred to as dynamical friction. When large items like black holes trip thru a medium (like mud and stars), they have got a path of disturbed fluid referred to as the wake. For instance, when a boat strikes thru water, it leaves a turbulent path of water in the back of it; that is its wake.
The debris drawn to the SMBH by way of gravity could cause a drag power, which is dynamical friction. This friction opposes the movement of the huge object, forcing it to decelerate. With regards to two SMBHs merging, this may lead them to forestall shifting in opposition to every different.
“Earlier calculations have discovered that this procedure stalls when the black holes are round 1 parsec clear of every different, a state of affairs on occasion known as the general parsec downside,” defined Dr. Alvarez.
That is the place dynamical friction comes into play. This may both oppose or lend a hand with the merging of the 2 SMBHs.
Self-interacting darkish topic
The researchers suggest {that a} type of darkish topic could be the strategy to this downside.
“On this paper, we display that together with the in the past overpassed impact of darkish topic can assist black holes conquer this ultimate parsec of separation and merge, thus emitting a gravitational wave sign that fits the only noticed by means of Pulsar Timing Arrays,” stated Dr. Alvarez.
In a galaxy, darkish topic is predominantly provide within the galactic halo, the area surrounding the visual galaxy. However, it is usually provide close to the galactic core, the place the SMBH is provide. Due to this fact, the character of darkish topic may play a the most important function within the merger of SMBHs.
Self-interacting darkish topic (SIDM) is a hypothetical type of darkish topic through which darkish topic debris have interaction with every different by way of a brand new unknown power.
In galaxies containing SIDM, the interactions between the darkish topic debris can have an effect on the density (distribution) and pace of the darkish topic, resulting in a extra environment friendly funneling of topic and effort towards the SMBH, which might doubtlessly conquer the dynamical friction.
A mild steadiness
To discover the function of SIDM within the SMBH merger, the researchers carried out detailed calculations of darkish topic density profiles round SMBHs for SIDM and chilly darkish topic (much less interacting).
In addition they modeled dynamical friction results on SMBH orbits, calculated power switch between the SMBH and darkish topic, and performed simulations of gravitational wave spectra underneath other darkish topic eventualities.
They then when compared those effects with observational knowledge from the pulsar timing arrays.
The researchers discovered that the interplay cross-section of darkish topic debris should be inside of an optimum vary. A bigger cross-sectional space, because of this extra common interactions, reasons darkish topic debris to engage and scatter, knocking down the density profile close to the SMBHs.
This relief in density decreases the dynamical friction vital for the SMBHs to merge.
“However, sufficiently common darkish topic self-interactions are had to save you this profile from being dispersed by means of the black hollow movement,” defined Dr. Alvarez.
The best cross-section vary lets in sufficient interactions to steer the SMBHs’ motion with out dispersing the darkish topic an excessive amount of, thereby keeping up enough dynamical friction to help the merging procedure.
The researchers discovered this price to be between 2.5 and 25 cm2/g. Which means for each gram of darkish topic, the efficient space over which the debris have interaction must be between 2.5 and 25 sq. centimeters.
Speed-dependent interactions
The researchers additionally discovered that the rate of the SIDM debris should be optimum. This pace is in flip influenced by means of the unknown power service or mediator’s mass, which facilitates the interplay between SIDM debris.
If the mediator is heavy, it might imply that darkish topic debris most effective have interaction considerably when they’re shifting slowly relative to one another. Conversely, if the mediator is gentle, interactions may happen at upper velocities.
“Apparently, this pace dependence is theoretically well-motivated. It’s exactly what one unearths if the particle that acts because the power service for the darkish topic self-interactions has a mass this is more or less 1 p.c of the darkish topic particle mass,” stated Dr. Alvarez.
The researchers estimated this price to be between 300 and 600 km/s.
“Those velocity-dependent self-interactions depart an imprint at the gravitational wave spectrum as a result of when the black holes are a fragment of a parsec clear of every different, an important fraction of the orbital power is misplaced to darkish topic friction fairly than gravitational wave emission, thus rather suppressing the gravitational wave sign at some frequencies in comparison to others,” added Dr. Alvarez.
Implications and long term paintings
The researchers’ type of SIDM debris predicted that the gravitational waves can be weaker or much less intense at low frequencies. This prediction matched what has been noticed in exact knowledge.
In addition they confirmed that SIDM with a velocity-dependent cross-section can clear up the general parsec downside and continue to exist the merger procedure.
Talking of the have an effect on in their paintings, Dr. Alvarez stated, “We discover the evolution of the black hollow’s orbit to be very delicate to the microphysics of darkish topic, which means that we will be able to use the gravitational wave emission of SMBH binaries to constrain darkish topic fashions. This gives a brand new window for probing the darkish topic nature within the innermost areas of galaxies that had been in the past now not observationally obtainable.”
The staff may be refining their type and growing numerical simulations to substantiate the consequences discovered on this paper. Those simulations will supply a greater working out of ways darkish topic profiles react to the power injected by means of merging black holes.
Additional info:
Gonzalo Alonso-Álvarez et al, Self-Interacting Darkish Topic Solves the Ultimate Parsec Downside of Supermassive Black Hollow Mergers, Bodily Overview Letters (2024). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.133.021401.
© 2024 Science X Community
Quotation:
New find out about makes use of self-interacting darkish topic to unravel the general parsec downside (2024, July 30)
retrieved 30 July 2024
from
This file is matter to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal find out about or analysis, no
phase is also reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is equipped for info functions most effective.