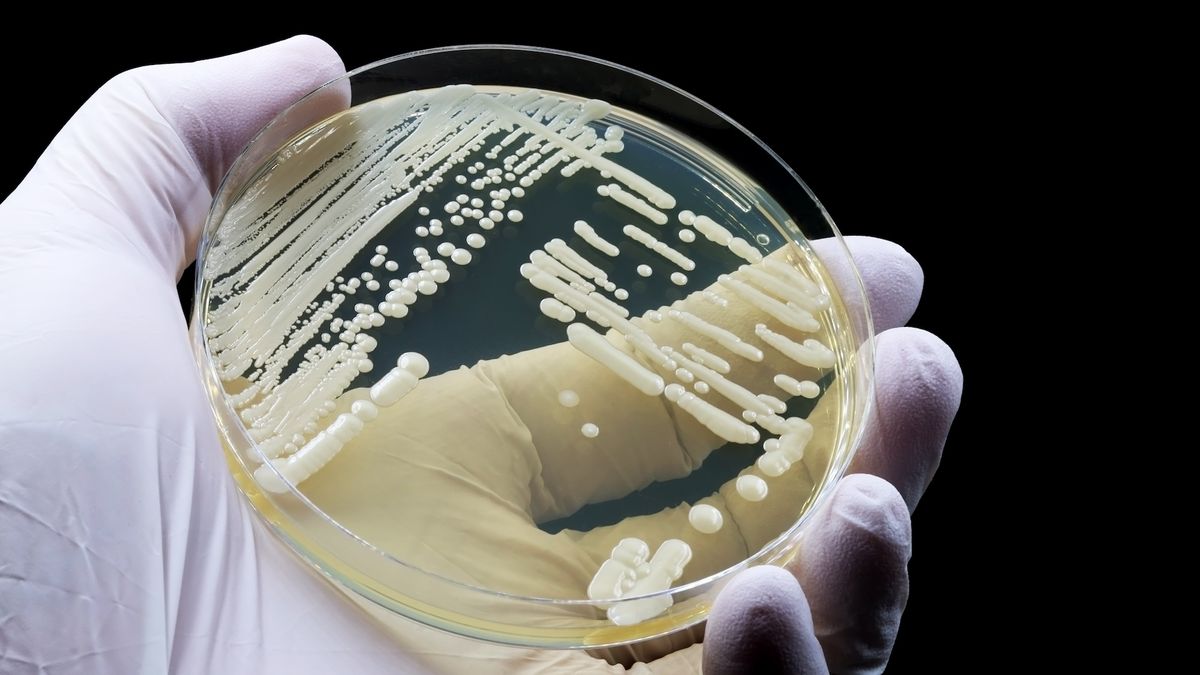
Scientists in China have came upon a up to now unknown fungal pathogen that may infect people. The fungus, referred to as Rhodosporidiobolus fluvialis, used to be present in scientific samples from two unconnected sanatorium sufferers. In experiments, the researchers discovered that the yeast used to be immune to a number of first-line antifungal medicine at upper temperatures — round that of the human frame. This temperature additionally gave upward thrust to “hypervirulent mutants” able to inflicting more-severe illness in lab mice. The findings “strengthen the concept international warming can advertise the evolution of recent fungal pathogens,” the researchers in the back of the invention wrote in a file revealed June 19 within the magazine Nature Microbiology.The scientists made this discovery after analyzing fungi sampled from sufferers in 96 hospitals throughout China between 2009 and 2019. In all, 27,100 lines of fungi have been amassed and analyzed; of those, best R. fluvialis had by no means been noticed in people ahead of.Similar: Uncommon fungal STI noticed in US for the first timeR. fluvialis used to be exposed within the blood of 2 unconnected sufferers who, along with being inflamed with the yeast, had severe underlying well being prerequisites. One affected person used to be a 61-year-old who died in an extensive care unit (ICU) in Nanjing in 2013, and the opposite used to be an 85-year-old who died in 2016 after being handled in an ICU in Tianjin. The file does not notice whether or not the fungal an infection immediately contributed to those sufferers’ deaths or if they simply took place to be inflamed on the time.As a part of their therapies, the sufferers got commonplace antifungal medicine, together with fluconazole and caspofungin. Lab research by way of the staff later discovered that R. fluvialis is immune to each those medicine. Get the sector’s most attractive discoveries delivered immediately for your inbox.”This can be a outstanding and in point of fact surprising discovering, which bodes badly for the long run,” David Denning, a professor of infectious illnesses on the College of Manchester within the U.Okay. who used to be no longer concerned within the analysis, informed Science. Invasive fungal infections, which assault tissues deep within the frame, most commonly have an effect on other people whose immune methods are weakened, because of HIV an infection or on account of taking immunosuppressant medicine, for instance. Particularly, the 61-year-old inflamed with R. fluvialis have been immunosuppressed, and the 85-year-old had diabetes, which is able to obstruct immune serve as. Alternatively, emerging international temperatures have pushed fungi to conform and lengthen their geographical levels, making some much more likely to come back into touch with people. Thus, new pathogens have emerged, together with the drug-resistant Candida auris, which has been recognized in additional than 40 nations since its discovery in 2009. In the meantime, the improvement of recent antifungal medicine has in large part stalled, leaving few choices to struggle resistant infections.Similar: Superbugs are on the upward thrust. How are we able to save you antibiotics from changing into out of date?Within the new learn about, researchers sickened immunocompromised mice with R. fluvialis and located that one of the fungal cells abruptly developed to develop extra aggressively. The staff then regarded on the fungus in lab dishes saved round human frame temperature — 98.6 levels Fahrenheit (37 levels Celsius). At that temperature, the yeast mutated 21 instances quicker than it did at room temperature, round 77 F (25 C). The warmth additionally made R. fluvialis much more likely to develop into drug resistant. When uncovered to the antifungal drug amphotericin B, the yeast evolved resistance extra briefly at frame temperature than it did at room temperature. If yeasts like R. fluvialis are much more likely to develop into virulent and drug resistant at prime temperatures, international warming may just probably power the evolution of recent, bad fungal pathogens, the staff wrote within the paper. However as for R. fluvialis, in particular, some scientists argue towards leaping to worrisome conclusions. Matthew Fisher, a professor of fungal illness epidemiology at Imperial School London who used to be no longer concerned within the analysis, informed Science the yeast should not but be noticed as a big, rising risk.”My roughly first feeling here’s that there are unsurveyed environments in China the place those yeasts stay, and that those two sufferers were unfortunate sufficient to be uncovered,” he informed Science. Briefly, there is not proof of R. fluvialis spreading extensively throughout the populace, regardless of its relating to options.Ever marvel why some other people construct muscle extra simply than others or why freckles pop out within the solar? Ship us your questions on how the human frame works to neighborhood@livescience.com with the topic line “Well being Table Q,” and you may even see your query spoke back at the site!