Schematic illustration of the evolution of the Labrador Sea, Baffin Bay and Davis Strait throughout the Paleogene. Abbreviations: Pre-Ungava Turn out to be Margin (Pre-UTM), Davis Strait proto-microcontinent (DSPM), Ungava Fracture Zone (UFZ). Credit score: Longley et al. 2024.
Plate tectonics are the motive force at the back of Earth’s continental configurations, with the lithosphere (oceanic and continental crusts and higher mantle) transferring because of convection processes happening within the softer underlying asthenospheric mantle. Many earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and mountain formations are direct penalties of the actions of those globe-spanning plates, specifically at their margins.
One such plate boundary happens between Canada and Greenland, which has shaped the Davis Strait seaway connecting two ocean basins, the Labrador Sea and Baffin Bay. The tectonic evolution of the Davis Strait is dated to ~33–61 million years in the past (Ma) all through the Paleogene, all through which one specifically peculiar characteristic shaped—a thicker than commonplace (19–24 km) fragment of continental crust within the ocean.
That is now deemed to be a newly-recognized, incompletely rifted and submerged microcontinent offshore of west Greenland: the Davis Strait proto-microcontinent.
Figuring out the mechanism and reason why for this crustal anomaly is the point of interest of latest analysis, printed in Gondwana Analysis. Doctoral researcher Luke Longley and Dr. Jordan Phethean (College of Derby, UK) along Dr. Christian Schiffer (Uppsala College, Sweden) have generated a reconstruction of the plate tectonic actions spanning ~30 million years that resulted within the proto-microcontinent’s formation. They outline proto-microcontinents as “areas of fairly thick continental lithosphere separated from main continents by way of a zone of thinner continental lithosphere.”
Dr. Phethean explains why this actual location is so essential for this analysis and why having a look at previous microcontinent formation is important for lately. “The well-defined adjustments in plate movement that happen within the Labrador Sea and Baffin Bay, that have fairly restricted exterior headaches affecting them, make this house a perfect herbal laboratory for learning microcontinent formation.
“Rifting and microcontinent formation are completely ongoing phenomena—with each earthquake we could be operating against the following microcontinent separation. The purpose of our paintings is to know their formation effectively sufficient to are expecting that very long term evolution.”
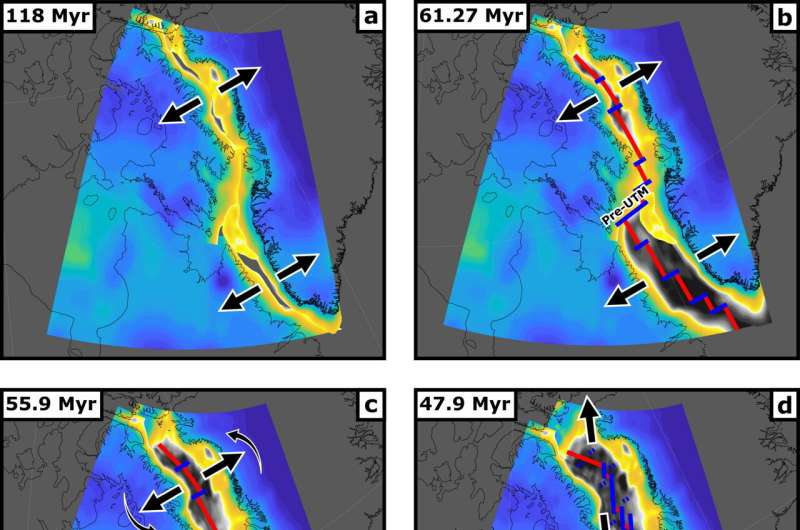
Style of plate tectonic evolution between Canada and Greenland, figuring out the location of the Davis Strait proto-microcontinent (DSPM), in addition to indicating the positioning of turn into faults alongside the Mid-Atlantic mid-ocean ridge and continental crust thicknesses. Credit score: Longley et al. 2024.
To discover this additional, the analysis workforce used maps derived from gravity and seismic mirrored image information to spot the orientation and age of faults touching on rifting, the mid-ocean ridge (the place Greenland rifted except the North American plate), and related turn into faults (the place two tectonic plates slide previous every different).
The scientists known preliminary rifting between Canada and Greenland started ~118 Ma all through the Decrease Cretaceous, with seafloor spreading setting out within the Labrador Sea and Baffin Bay at ~61 Ma.
Therefore, the duration ~49–58 Ma is famous as being key to the formation of this proto-microcontinent, with the orientation of seafloor spreading between Canada and Greenland changing from northeast-southwest alongside the Pre-Ungava Turn out to be Margin, to north-south, rifting off the Davis Immediately proto-microcontinent. By means of ~33 Ma, ocean spreading ceased as Greenland collided with Ellesmere Island, and then Greenland joined the North American plate.
On this fashion, the Davis Strait proto-microcontinent is known primarily based upon crustal thicknesses, the place the microcontinent seems within the vary of nineteen–24 km-thick thinned continental crust, surrounded by way of two slender bands of skinny (15–17 km) continental crust that separate it from mainland Greenland and Baffin Island.
This analysis has applicability to different microcontinents globally to know their calving from continental crust, together with the Jan Mayen microcontinent northeast of Iceland, East Tasman Upward push southeast of Tasmania, and the Gulden Draak Knoll, offshore western Australia.
Dr. Phethean notes, “Higher wisdom of ways those microcontinents shape permits researchers to know how plate tectonics operates on Earth, with helpful implications for the mitigation of plate tectonic hazards and finding new sources.”
Additional information:
Luke Longley et al, The Davis Strait proto-microcontinent: The function of plate tectonic reorganization in continental cleaving, Gondwana Analysis (2024). DOI: 10.1016/j.gr.2024.05.001
© 2024 Science X Community
Quotation:
New incompletely rifted microcontinent known between Greenland and Canada (2024, July 10)
retrieved 10 July 2024
from
This record is matter to copyright. With the exception of any honest dealing for the aim of personal find out about or analysis, no
phase could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions handiest.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-2235491023-3d9cea1d65dc4d40884c5f134d512f81.jpg)







