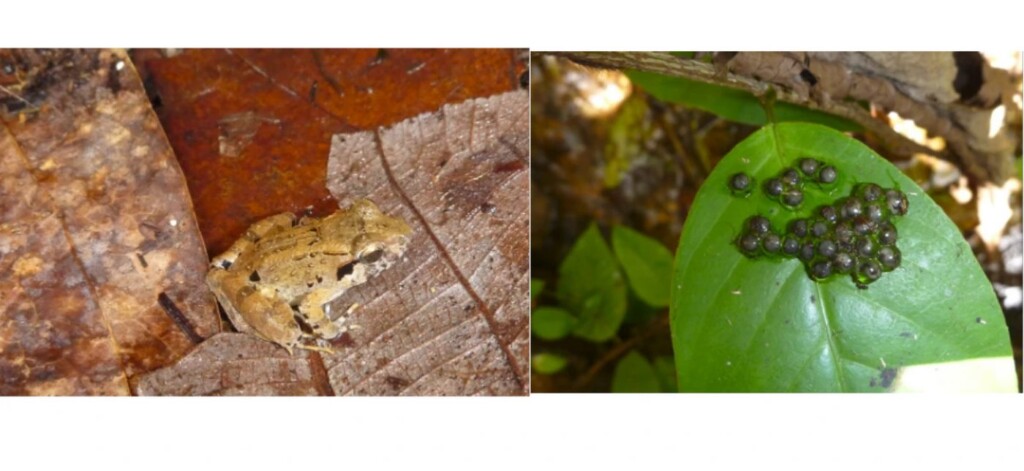
Left the brand new species of fanged frog, Limnonectes phyllofolia. Proper the frog’s eggs, laid on a leaf – picture credit score, Sean Reilly.
Left the brand new species of fanged frog, Limnonectes phyllofolia. Proper the frog’s eggs, laid on a leaf – picture credit score, Sean Reilly.
In a brand new find out about, printed within the magazine PLOS ONE, researchers have described a brand new species of fanged frog: the smallest one ever came upon.
Normally, frogs’ enamel aren’t anything else to write down house about—they seem like pointy little pinpricks lining the higher jaw. However one crew of stream-dwelling frogs in Southeast Asia has a peculiar adaptation: two bony “fangs” jutting out in their decrease jawbone.
There are over 70 species of those Dracula frogs, they usually use those fangs to fight with every different over territory and pals, and occasionally, extremely, even to seek tough-shelled prey like massive centipedes and crabs.
In collaboration with the Bogor Zoology Museum, a workforce from the McGuire Lab at Berkeley discovered the frogs on Sulawesi, a rugged, mountainous island that makes up a part of Indonesia.
“It’s an enormous island with an unlimited community of mountains, volcanoes, lowland rainforest, and cloud forests up within the mountains. The presence of a majority of these other habitats imply that the magnitude of biodiversity throughout many vegetation and animals we discover there may be unreal—rivaling puts just like the Amazon,” mentioned Jeff Frederick, a postdoctoral researcher on the Box Museum in Chicago and the find out about’s lead creator.
“This new species is tiny in comparison to different fanged frogs at the island the place it was once discovered, concerning the dimension of 1 / 4,” says Frederick.
“Many frogs on this genus are massive, weighing as much as two kilos. On the huge finish, this new species weighs about the similar as a dime.”
Whilst trekking in the course of the jungle, participants of the joint US-Indonesia amphibian and reptile analysis workforce spotted one thing sudden at the leaves of tree saplings and moss-covered boulders: nests of frog eggs.
Frogs are amphibians, they usually lay eggs which are encapsulated by means of jelly, relatively than a difficult, protecting shell. To stay their eggs from drying out, maximum amphibians lay their eggs in water. To the analysis workforce’s marvel, they stored recognizing the terrestrial egg plenty on leaves and mossy boulders a number of toes above the bottom. In a while after, they started to peer the small, brown frogs themselves.
“Most often after we’re searching for frogs, we’re scanning the margins of circulation banks or wading via streams to identify them without delay within the water,” Frederick says. “After again and again tracking the nests although, the workforce began to search out attending frogs sitting on leaves hugging their little nests.”
SCIENTISTS DISCOVER 30 NEW FROGS: 32 Species of Harlequin Frogs Have been Present in Ecuador That We Concept Have been Extinct
This shut touch with their eggs permits the frog folks to coat the eggs with compounds that stay them wet and unfastened from bacterial and fungal contamination.
Nearer exam of the amphibian folks published no longer best that they have been tiny participants of the fanged frog circle of relatives, entire with slightly visual fangs, however that the frogs taking care of the clutches of eggs have been all male.
“Male egg-guarding conduct isn’t completely unknown throughout all frogs, however it’s relatively unusual,” says Frederick.
MORE NEW SPECIES: Newly-Known Species of Clear ‘Glass’ Frogs Unveiled in Superb Pictures From Ecuador
Frederick and his colleagues hypothesize that the frogs’ peculiar reproductive behaviors may additionally relate to their smaller-than-usual fangs. One of the vital frogs’ family members have larger fangs, which lend a hand them push back pageant for spots alongside the river to put their eggs within the water. Since those frogs developed a approach to lay their eggs clear of the water, they’ll have misplaced the will for such giant enforcing fangs. (The medical title for the brand new species is Limnonectes phyllofolia; phyllofolia way “leaf-nester.”)
“It’s interesting that on each and every next expedition to Sulawesi, we’re nonetheless finding new and numerous reproductive modes,” says Frederick. “Our findings additionally underscore the significance of retaining those very particular tropical habitats. Lots of the animals that are living in puts like Sulawesi are relatively distinctive, and habitat destruction is an ever-looming conservation factor for retaining the hyper-diversity of species we discover there. Finding out about animals like those frogs which are discovered nowhere else on Earth is helping make the case for safeguarding those treasured ecosystems.”
SHARE This Little Protector With Your Pals On Social Media…
‘New Species’ of Frog With Fangs Hunts Crabs Even Despite the fact that it’s No Larger Than a Quarter