A brand new find out about has pinpointed mind neurons that separate the feeling of fullness from nausea in weight problems medicine, paving the best way for therapies that suppress urge for food with out inflicting adversarial results.Analysis suggests the potential of growing a brand new medicine that suppresses urge for food with out inflicting nausea.The following bankruptcy within the tale of headline-making widespread weight problems medicine may just center of attention on working out the bodily sensation of fullness after consuming in comparison to the mind’s legislation of nausea. Researchers on the Monell Chemical Senses Middle have recognized a gaggle of neurons within the mind that organize meals intake with out inducing nausea in animal fashions, distinguishing the recommended sides of those medicine from their unwanted effects.The find out about, printed within the magazine Nature, describes two distinct neural circuits that govern other results of the similar drug. The medicine studied are amongst among the best weight-loss medicine to be had – referred to as long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP1R) agonists – which start up neurochemical responses by way of receptors expressed within the frame.One of the crucial efficient and widespread GLP1-based medicine – known as semaglutide and advertised as Ozempic and Wegovy – produces spectacular weight reduction leads to medical trials. Consistent with the International Well being Group, in 2022, 1 in 8 other people globally have been residing with weight problems, making the advance of gear like those of dire significance.
A brand new find out about has pinpointed mind neurons that separate the feeling of fullness from nausea in weight problems medicine, paving the best way for therapies that suppress urge for food with out inflicting adversarial results.Analysis suggests the potential of growing a brand new medicine that suppresses urge for food with out inflicting nausea.The following bankruptcy within the tale of headline-making widespread weight problems medicine may just center of attention on working out the bodily sensation of fullness after consuming in comparison to the mind’s legislation of nausea. Researchers on the Monell Chemical Senses Middle have recognized a gaggle of neurons within the mind that organize meals intake with out inducing nausea in animal fashions, distinguishing the recommended sides of those medicine from their unwanted effects.The find out about, printed within the magazine Nature, describes two distinct neural circuits that govern other results of the similar drug. The medicine studied are amongst among the best weight-loss medicine to be had – referred to as long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP1R) agonists – which start up neurochemical responses by way of receptors expressed within the frame.One of the crucial efficient and widespread GLP1-based medicine – known as semaglutide and advertised as Ozempic and Wegovy – produces spectacular weight reduction leads to medical trials. Consistent with the International Well being Group, in 2022, 1 in 8 other people globally have been residing with weight problems, making the advance of gear like those of dire significance.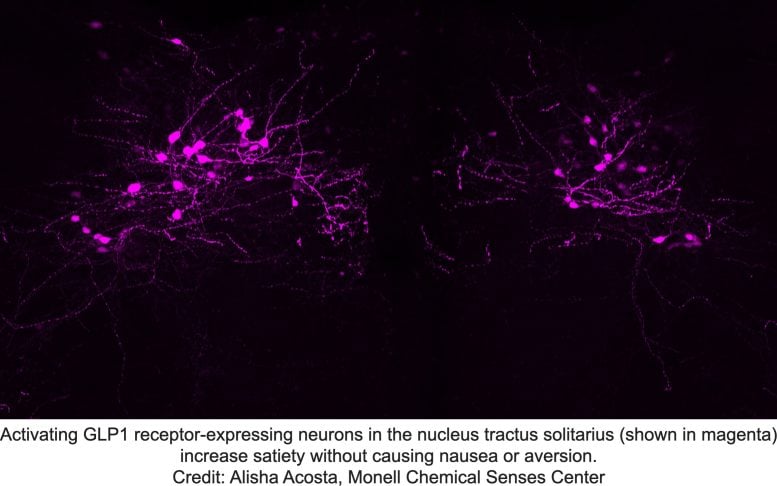 Activating GLP1 receptor-expressing neurons within the nucleus tractus solitarius (magenta) build up sateity with out inflicting nausea or aversion. Credit score: Alisha Acosta, Monell Chemical Senses CenterOvercoming Aspect Results in Weight problems Remedy“One of the crucial obstacles to drug therapies for weight problems is unwanted effects similar to nausea and vomiting,” mentioned senior creator Amber L. Alhadeff, PhD, Monell Assistant Member. “We didn’t have a good suggestion of whether or not those unsightly unwanted effects are comparable or essential for the weight-loss results.”To determine, the Monell crew investigated the mind circuits that hyperlink feeling complete after drinking a meal to these inflicting meals avoidance because of feeling nauseated. The researchers discovered that neurons within the hindbrain mediate each results of those weight problems medicine, and impulsively additionally came upon that the person neurons mediating satiety and nausea are other.Two-photon imaging of hindbrain GLP1R neurons in are living mice confirmed that almost all particular person neurons are tuned to react to stimuli which are both nutritive or aversive, however no longer each. What’s extra, the find out about published that GLP1R neurons in a single a part of the hindbrain known as the realm postrema reply extra to aversive stimuli, while GLP1R neurons in some other space known as the nucleus tractus solitarius lean towards nutritive stimuli.Subsequent, the crew one by one manipulated the 2 teams of GLP1R neurons to grasp their results on habits. They discovered that activating neurons within the nucleus tractus solitarius triggers satiety, with out a aversion habits; while, activating neurons within the space postrema cause a robust aversion response. Importantly, the weight problems medicine decreased meals consumption even if the aversion pathway used to be inhibited. Those unexpected findings spotlight the inhabitants of neurons within the nucleus tractus solitarius as a goal for long run weight problems medicine to cut back meals consumption with out making people really feel unwell.“Creating experimental weight problems medicine that selectively turn on this inhabitants might advertise weight reduction whilst heading off aversive unwanted effects,” mentioned Alhadeff. If truth be told, say the authors, the concept that of isolating healing and unwanted effects on the degree of neural circuits may just, in idea, be carried out to any drug with unwanted effects.Reference: “Dissociable hindbrain GLP1R circuits for satiety and aversion” through Kuei-Pin Huang, Alisha A. Acosta, Misgana Y. Ghidewon, Aaron D. McKnight, Milena S. Almeida, Nathaniel T. Nyema, Nicholas D. Hanchak, Nisha Patel, Yenoukoume S. Okay. Gbenou, Alice E. Adriaenssens, Kevin A. Bolding and Amber L. Alhadeff, 10 July 2024, Nature.
Activating GLP1 receptor-expressing neurons within the nucleus tractus solitarius (magenta) build up sateity with out inflicting nausea or aversion. Credit score: Alisha Acosta, Monell Chemical Senses CenterOvercoming Aspect Results in Weight problems Remedy“One of the crucial obstacles to drug therapies for weight problems is unwanted effects similar to nausea and vomiting,” mentioned senior creator Amber L. Alhadeff, PhD, Monell Assistant Member. “We didn’t have a good suggestion of whether or not those unsightly unwanted effects are comparable or essential for the weight-loss results.”To determine, the Monell crew investigated the mind circuits that hyperlink feeling complete after drinking a meal to these inflicting meals avoidance because of feeling nauseated. The researchers discovered that neurons within the hindbrain mediate each results of those weight problems medicine, and impulsively additionally came upon that the person neurons mediating satiety and nausea are other.Two-photon imaging of hindbrain GLP1R neurons in are living mice confirmed that almost all particular person neurons are tuned to react to stimuli which are both nutritive or aversive, however no longer each. What’s extra, the find out about published that GLP1R neurons in a single a part of the hindbrain known as the realm postrema reply extra to aversive stimuli, while GLP1R neurons in some other space known as the nucleus tractus solitarius lean towards nutritive stimuli.Subsequent, the crew one by one manipulated the 2 teams of GLP1R neurons to grasp their results on habits. They discovered that activating neurons within the nucleus tractus solitarius triggers satiety, with out a aversion habits; while, activating neurons within the space postrema cause a robust aversion response. Importantly, the weight problems medicine decreased meals consumption even if the aversion pathway used to be inhibited. Those unexpected findings spotlight the inhabitants of neurons within the nucleus tractus solitarius as a goal for long run weight problems medicine to cut back meals consumption with out making people really feel unwell.“Creating experimental weight problems medicine that selectively turn on this inhabitants might advertise weight reduction whilst heading off aversive unwanted effects,” mentioned Alhadeff. If truth be told, say the authors, the concept that of isolating healing and unwanted effects on the degree of neural circuits may just, in idea, be carried out to any drug with unwanted effects.Reference: “Dissociable hindbrain GLP1R circuits for satiety and aversion” through Kuei-Pin Huang, Alisha A. Acosta, Misgana Y. Ghidewon, Aaron D. McKnight, Milena S. Almeida, Nathaniel T. Nyema, Nicholas D. Hanchak, Nisha Patel, Yenoukoume S. Okay. Gbenou, Alice E. Adriaenssens, Kevin A. Bolding and Amber L. Alhadeff, 10 July 2024, Nature.
DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07685-6This paintings used to be supported through the Nationwide Institutes of Well being (R00DK119574 and DP2AT011965), the American Middle Affiliation, New York Stem Cellular Basis, Klingenstein Fund and Simons Basis, Pew Charitable Trusts, Nationwide Science Basis (Grant2236662), the Penn Institute for Diabetes, Weight problems, and Metabolism, and the Monell Chemical Senses Middle. The confocal microscope utilized in those research used to be bought with an NIH instrumentation grant (S10OD030354). Alhadeff is a New York Stem Cellular Basis Robertson investigator and a Pew biomedical pupil.
No Extra Nausea: New Discovery May Cut back the Aspect Results of Ozempic and Wegovy