New analysis unearths how our impulses to consume, even if we aren’t hungry, may well be prompted through a selected a part of the mind quite than the standard starvation pangs from our stomachs – a discovering which may be necessary sooner or later remedy of consuming problems.
In checks on mice, performed through a workforce led through researchers from the College of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), specific clusters of cells have been proven to force snacking habits. Those cells are in part of the mind that has been connected to panic responses, however to not consuming.
“This area we are finding out is known as the periaqueductal grey (PAG), and it’s within the brainstem, which could be very previous in evolutionary historical past,” says neuroscientist Avishek Adhikari, from UCLA. “As a result of that, it’s functionally an identical between people and mice.”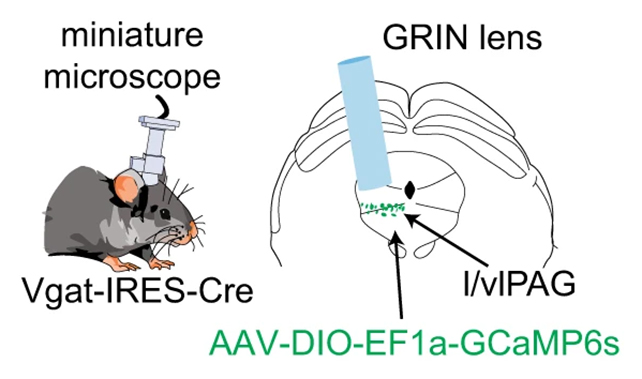 Mice have been monitored with customized microscopes. (Reis et al., Nature Communications, 2024)When the precise PAG cells have been intentionally activated in mice that had already eaten, they activate at the hunt for meals – each reside meals, and particularly fatty meals that did not rely as prey (the an identical of heading to the refrigerator for a late-night snack, or having a candy dessert).
Mice have been monitored with customized microscopes. (Reis et al., Nature Communications, 2024)When the precise PAG cells have been intentionally activated in mice that had already eaten, they activate at the hunt for meals – each reside meals, and particularly fatty meals that did not rely as prey (the an identical of heading to the refrigerator for a late-night snack, or having a candy dessert).
The animals have been so made up our minds when those particular PAG neurons have been grew to become on, they persevered tiny electrical shocks to get to their meals. As scientists know from earlier experiments, this is not one thing mice would most often do when they are no longer hungry.
And the stimulation additionally led to mice to be extra adventurous, chasing after ping pong balls and extra totally exploring their enclosures. When alerts from the similar mind neurons have been grew to become down, those behaviors have been reversed.
“The consequences counsel the next habits is expounded extra to in need of than to starvation,” says Adhikari. “Starvation is aversive, which means that mice normally keep away from feeling hungry if they may be able to. However they search out activation of those cells, suggesting that the circuit isn’t inflicting starvation.”
“As an alternative, we expect this circuit reasons the yearning of extremely rewarding, high-caloric meals. Those cells may cause the mouse to consume extra high-calorie meals even within the absence of starvation.”
This nonetheless must be verified in people in fact, however now we have the similar roughly neuron cellular construction in our personal brains, so it is most likely that one thing an identical is happening after we’re getting cravings for snacks that don’t seem to be specifically excellent for us. If the circuit is recognized in people, it would result in higher working out of consuming problems, and possible remedy goals.
The PAG mind circuit turns out so as to override the standard impulses we get about what to consume and when to consume it, specifically with regards to junk meals – and that’s the reason a very powerful discovering for any roughly long run analysis into consuming patterns and alternatives, which might be in fact basic behaviors in each residing organism.
“Even supposing our findings have been a marvel, it is sensible that food-seeking can be rooted in such an historic a part of the mind, since foraging is one thing all animals wish to do,” says Adhikari.The analysis has been revealed in Nature Communications.
Nonetheless Hungry After a Large Meal? The Cause May Be in The Mind