Octopuses generally tend to stay secrets and techniques, however we have simply learnt how they succeed in their abnormal dexterity.The positive regulate those almost-alien animals have over each and every in their 8 fingers is a minimum of in part all the way down to the segmentation of the anxious machine circuitry that governs it. This discovery via researchers on the College of Chicago is helping us perceive the extraordinary means cephalopods navigate the sector, and will also tell long run designs for delicate robots.
“If you’ll have a anxious machine that is controlling such dynamic motion, that is a great way to set it up,” says neurobiologist Clifton Ragsdale. “We expect it is a characteristic that in particular advanced in soft-bodied cephalopods with suckers to hold out those worm-like actions.”
The octopus anxious machine is likely one of the maximum ordinary on Earth. Not like in different clever animals, it is extremely dispensed, with an important percentage of its 500 million-odd neurons unfold right through the 8 fingers. In truth, extra neurons are living within the fingers than within the octopus’s head.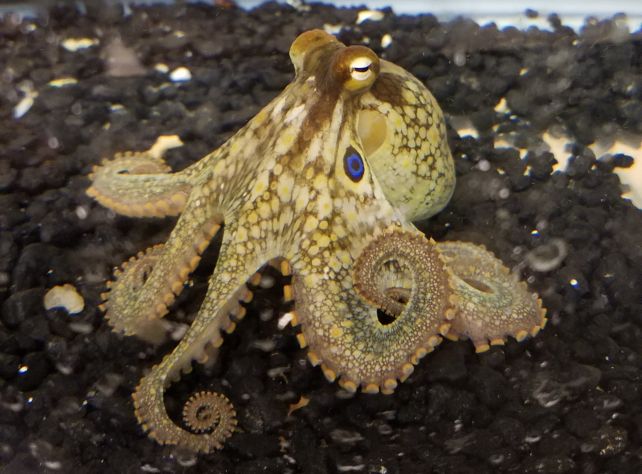 Octopus bimaculoides, the California two-spot octopus. (Cassady Olson)Their fingers are able to making selections independently and will also proceed to react to stimuli after being severed. Each and every has extra levels of freedom than we will depend, and any of its loads of suckers, ready to “style” the chemistry of the octopus’s setting, is in a position to exchange form independently.
Octopus bimaculoides, the California two-spot octopus. (Cassady Olson)Their fingers are able to making selections independently and will also proceed to react to stimuli after being severed. Each and every has extra levels of freedom than we will depend, and any of its loads of suckers, ready to “style” the chemistry of the octopus’s setting, is in a position to exchange form independently.
The neurons within the octopus’s fingers are concentrated alongside an axial nerve twine that undulates down the duration of each and every arm, with nodes targeted round each and every of the suckers. It kind of feels advanced and targeted, and a group led via neuroscientist Cassady Olsen sought after to check it intimately to look if they may be informed extra about the way it purposes.
After they put longitudinal slices of arm from the California two-spot octopus (Octopus bimaculoides) underneath the microscope, they discovered one thing that they’d by no means observed ahead of. Alongside the axial nerve twine, the neuronal cells are packed into segments, separated via gaps referred to as septa, wealthy with connective tissue, the place the nerves and veins go out to connect with muscle mass within sight.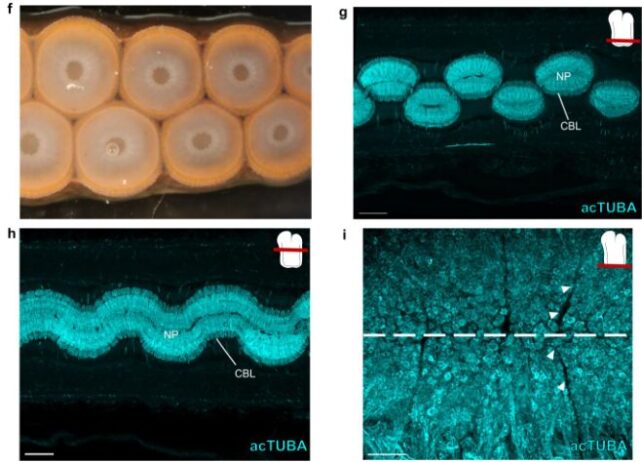 The structure of the octopus anxious machine, appearing (f) the arm, (g) the nerves of the suckers, (h) the axial nerve twine and (i) the neuronal segmentation. (Olson et al., Nat. Commun., 2025)Following those connections, the researchers discovered that nerves from more than one segments hook up with other muscle areas – suggesting that the segments paintings in combination to regulate the muscle mass with a prime level of precision.
The structure of the octopus anxious machine, appearing (f) the arm, (g) the nerves of the suckers, (h) the axial nerve twine and (i) the neuronal segmentation. (Olson et al., Nat. Commun., 2025)Following those connections, the researchers discovered that nerves from more than one segments hook up with other muscle areas – suggesting that the segments paintings in combination to regulate the muscle mass with a prime level of precision.
They discovered that the nerves for the suckers additionally attach by means of the septa, making a form of anxious spatial map of the suckers, and taking into consideration the positive, person regulate of each and every one because the octopus makes use of them to sense its setting thru touch-tasting.
“Eager about this from a modeling viewpoint, one of the best ways to arrange a regulate machine for this very lengthy, versatile arm could be to divide it into segments,” Olson says. “There must be some form of communique between the segments, which you’ll believe would lend a hand easy out the actions.”
Your next step used to be to take a look at to determine the connection between the segmentation of the axial nerve twine and its serve as via in search of identical structure in any other workforce of cephalopods: squids.
Those animals diverged from octopuses round 270 million years in the past, and their appendage association is somewhat other. Squids have 8 sucker-lined fingers too, but additionally two tentacles that haven’t any suckers alongside the stalk, with suckers at the golf equipment on the finish.
Squids and octopuses use their limbs in a different way: octopuses to discover, transfer around the seafloor, and manipulate gadgets, whilst squids use theirs in open water to take hold of and grasp prey. frameborder=”0″ permit=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>The researchers discovered that the structure of the axial nerve twine within the longfin inshore squid (Doryteuthis pealeii) is slightly other from that of octopuses. As well as, there used to be no segmentation within the suckerless stalks of the tentacles – however nerve segmentation used to be discovered within the suckered golf equipment.
The discovering suggests {that a} segmented anxious machine is said to the regulate of suckered appendages, and is the most important to positive, dextrous regulate. Squids most certainly do not want as many segments as a result of they do not use their suckers for exploration the best way octopuses do.
“Organisms with those sucker-laden appendages that experience worm-like actions want the correct of anxious machine,” Ragsdale says. “Other cephalopods have get a hold of a segmental construction, the main points of which range in line with the calls for in their environments and the pressures of loads of thousands and thousands of years of evolution.”The analysis has been revealed in Nature Communications.
Octopus Fingers Are Managed via a Apprehensive Device That is Like No Different