Herbal diamonds take billions of years to shape within the excessive pressures and temperatures deep underground. Artificial paperwork will also be produced a long way faster, however they normally nonetheless require some intense squishing for as much as a number of weeks.
A brand new approach in keeping with a mixture of liquid metals can come out a man-made diamond in an issue of mins, with out the will for an enormous squeeze.
Whilst prime temperatures have been nonetheless required, within the area of one,025°C or 1,877°F, a continual diamond movie was once shaped in 150 mins, and at 1 atm (or usual surroundings unit). That is the identical of the power we really feel at sea stage, and tens of hundreds of instances lower than the power usually required.
The group at the back of the leading edge manner, led via researchers from the Institute for Elementary Science in South Korea, is assured that the method will also be scaled as much as make an important distinction within the manufacturing of man-made diamonds.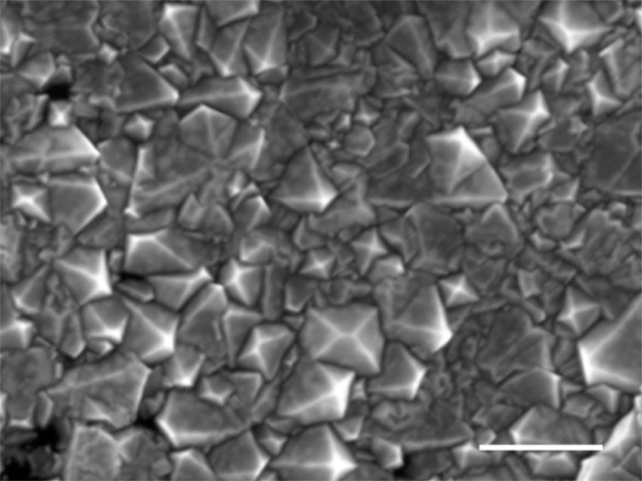 Scanning electron micrograph of a diamond movie grown in liquid steel. (Gong et al., Nature, 2024)Dissolving carbon into liquid steel for the manufacture of diamond is not completely new. Basic Electrical advanced a procedure 1/2 a century in the past the use of molten iron sulfide, as an example.
Scanning electron micrograph of a diamond movie grown in liquid steel. (Gong et al., Nature, 2024)Dissolving carbon into liquid steel for the manufacture of diamond is not completely new. Basic Electrical advanced a procedure 1/2 a century in the past the use of molten iron sulfide, as an example.
However those processes nonetheless required pressures of five–6 gigapascals and a diamond ‘seed’ for the carbon to grasp to.
“We came upon a approach to develop diamonds at 1 atm power and beneath a reasonable temperature via the use of a liquid steel alloy,” write the researchers of their revealed paper.
The aid in power was once accomplished the use of a moderately combined mix of liquid metals: gallium, iron, nickel, and silicon. A personalized vacuum machine was once constructed inside of a graphite casing to very impulsively warmth after which cool the steel whilst it was once uncovered to a mixture of methane and hydrogen.
Those stipulations reason carbon atoms from the methane to unfold into the melted steel, performing as seeds for the diamonds. After simply quarter-hour, small fragments of diamond crystals extruded from the liquid steel simply underneath the skin, whilst two-and-a-half hours of publicity produced a continual diamond movie.
Despite the fact that the focus of carbon forming the crystals reduced at a intensity of only some hundred nanometers, the researchers be expecting the method will also be progressed with a couple of tweaks.
“We advise that easy changes may just allow rising diamond over an overly huge house via the use of a bigger floor or interface, via configuring heating components to reach a far better attainable enlargement area and via distributing carbon to the diamond enlargement area in some new techniques,” write the researchers.
The ones changes are going to take time, and analysis into this procedure remains to be at its very early levels, however the authors of the brand new learn about assume that it has a number of attainable – and that different liquid metals might be integrated to get identical and even higher effects.
The method these days used to create maximum artificial diamonds – used for all kinds of business processes, electronics, or even quantum computer systems – takes a number of days and desires much more power. If this new methodology fulfills its attainable, making diamonds goes to transform so much quicker and so much more uncomplicated.
“The overall manner of the use of liquid metals may just boost up and advance the expansion of diamonds on quite a few surfaces, and in all probability facilitate the expansion of diamond on small diamond (seed) debris,” write the researchers.The analysis has been revealed in Nature.
Omit Billions of Years: Scientists Have Grown Diamonds in Simply 150 Mins














