A find out about of 26 years’ price of wolf behavioral information, and an research of the blood of 229 wolves, has proven that an infection with the parasite Toxoplasma gondii makes wolves 46 instances much more likely to develop into a pack chief.
The analysis presentations that the results of this parasite within the wild had been horrendously understudied – and its position in ecosystems and animal habits underestimated.
When you have a cat, you’ve got most probably heard of this parasite ahead of. The microscopic organism can most effective sexually reproduce within the our bodies of tom cats, however it might probably infect and thrive in just about all warm-blooded animals.
This contains people, the place it might probably purpose a most often symptomless (however nonetheless probably deadly) parasitic illness referred to as toxoplasmosis.
As soon as it is in some other host, particular person T. gondii parasites must give you the option to get their offspring again inside of a cat if it does not need to develop into an evolutionary dead-end. And it has a type of creepy manner of maximizing its possibilities.
Animals reminiscent of rats inflamed with the parasite get started taking extra dangers, and in some circumstances if truth be told develop into fatally drawn to the smell of tom cat urine, and thus much more likely to be killed by means of them.
For higher animals, reminiscent of chimpanzees, it method an higher threat of a run-in with a bigger cat, reminiscent of a leopard. Hyenas inflamed with T. gondii are also much more likely to be killed by means of lions.
Grey wolves (Canis lupus) within the Yellowstone Nationwide Park don’t seem to be precisely cat prey. However now and again their territory overlaps with that of cougars (Puma concolor), identified carriers of T. gondii, and the 2 species each prey at the elk (Cervus canadensis), bison (Bison bison), and mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus) that still may also be discovered there.
It is conceivable that wolves additionally develop into inflamed, most likely from every now and then consuming lifeless cougars, or drinking cougar poo.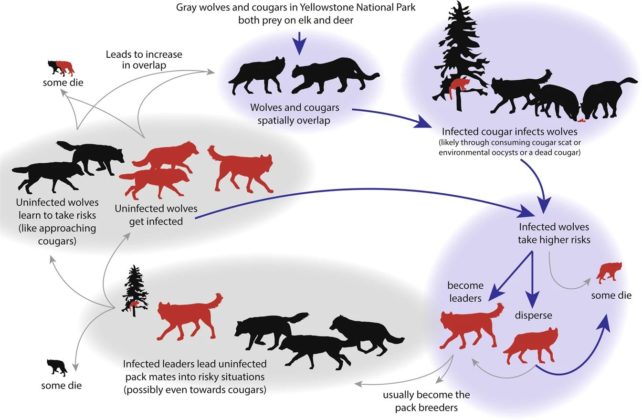 Diagram appearing the hypothesized wolf-cougar-T. gondii comments loop. (Meyer, Cassidy et al., Communications Biology, 2022)Information accumulated at the wolves and their habits for almost 27 years introduced a unprecedented alternative to check the results of the parasite on a wild, intermediate host.
Diagram appearing the hypothesized wolf-cougar-T. gondii comments loop. (Meyer, Cassidy et al., Communications Biology, 2022)Information accumulated at the wolves and their habits for almost 27 years introduced a unprecedented alternative to check the results of the parasite on a wild, intermediate host.
The researchers, led by means of biologists Connor Meyer and Kira Cassidy of the Yellowstone Wolf Challenge, additionally took a have a look at blood samples from wolves and cougars to gauge the speed of T. gondii an infection.
They discovered that wolves with a large number of territory overlap with cougars have been much more likely to be inflamed with T. gondii.
However there used to be a behavioral end result, too, with considerably higher risk-taking.
Inflamed wolves have been 11 instances much more likely to disperse from their pack, into new territory. Inflamed men had a 50 % chance of leaving their pack inside six months, when compared with a extra standard 21 months for the uninfected.
In a similar fashion, inflamed women folk had 25 % probability of leaving their pack inside 30 months, when compared with 48 months for individuals who were not inflamed.
Inflamed wolves have been additionally manner much more likely to develop into pack leaders. T. gondii might building up testosterone ranges, which might in flip result in heightened aggression and dominance, that are characteristics that may assist a wolf assert itself as a pack chief.
This has a few necessary penalties. Pack leaders are those who reproduce, and T. gondii transmission may also be congenital, handed from mom to offspring. However it might probably additionally impact the dynamics of all of the pack. frameborder=”0″ permit=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>”Because of the group-living construction of the grey wolf pack, the pack leaders have a disproportionate affect on their pack pals and on organization selections,” the researchers write of their paper.
“If the lead wolves are inflamed with T. gondii and display behavioral adjustments … this may occasionally create a dynamic wherein habits, precipitated by means of the parasite in a single wolf, influences the remainder of the wolves within the pack.”
If, as an example, the pack chief seeks out the smell of cougar pee as they boldly push into new territory, they may face better publicity to the parasite, thus a better charge of T. gondii an infection all over the wolf inhabitants. This generates a type of comments loop of higher overlap and an infection.
It is compelling proof that tiny, understudied brokers may have an enormous affect on ecosystem dynamics.
“This find out about demonstrates how community-level interactions can impact particular person habits and may just probably scale as much as group-level decision-making, inhabitants biology, and network ecology,” the researchers write.
“Incorporating the consequences of parasite infections into long term natural world analysis is essential to figuring out the affects of parasites on folks, teams, populations, and ecosystem processes.”
The analysis has been printed in Communications Biology.An previous model of this text used to be printed in November 2022.
One thing Odd Occurs to Wolves Inflamed by means of an Notorious Thoughts-Changing Parasite














