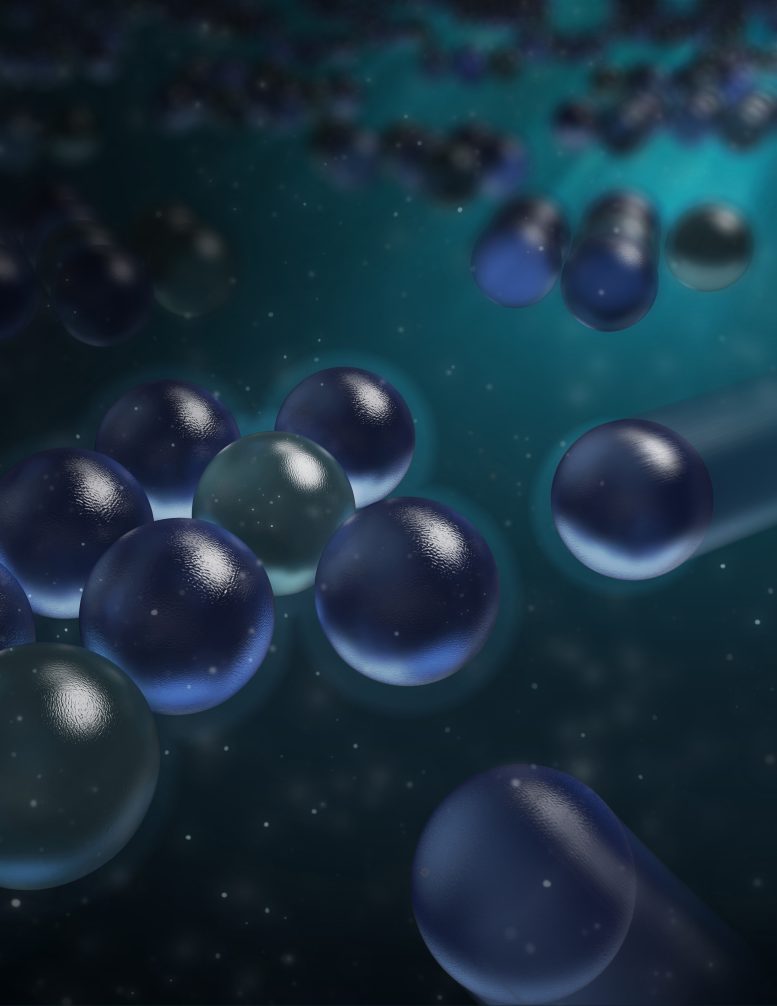
A brand new find out about has overturned a basic concept of physics by means of demonstrating that in a similar fashion charged debris can draw in every different in an answer, with the impact various between sure and adverse fees relying at the solvent. This discovery has important implications for quite a lot of clinical processes, together with self-assembly and crystallization. The analysis unearths the significance of solvent construction on the interface in figuring out interparticle interactions, difficult long-held ideals and indicating a necessity for a re-assessment of our working out of electromagnetic forces. Credit score: Zhang Kang“Opposites fees draw in; like fees repel” is a basic concept of fundamental physics. Then again, a brand new find out about from Oxford College, lately printed within the magazine Nature Nanotechnology, has demonstrated that in a similar fashion charged debris in answer can, in truth, draw in every different over lengthy distances.Simply as strangely, the workforce discovered that the impact is other for definitely and negatively charged debris, relying at the solvent.But even so overturning long-held ideals, those effects have instant implications for a spread of processes that contain interparticle and intermolecular interactions throughout quite a lot of length-scales, together with self-assembly, crystallization, and segment separation.The workforce of researchers, primarily based at Oxford’s Division of Chemistry, discovered that negatively charged debris draw in every different at massive separations while definitely charged debris repel, whilst the opposite used to be the case for solvents akin to alcohols.Those findings are unexpected as a result of they appear to contradict the central electromagnetic concept that the pressure between fees of the similar signal is repulsive in any respect separations.Experimental ObservationsNow, the usage of bright-field microscopy, the workforce tracked negatively charged silica microparticles suspended in water and located that the debris attracted every different to shape hexagonally organized clusters. Undoubtedly charged aminated silica debris, on the other hand, didn’t shape clusters in water.The usage of a idea of interparticle interactions that considers the construction of the solvent on the interface, the workforce established that for negatively charged debris in water, there may be a good looking pressure that outweighs electrostatic repulsion at massive separations, resulting in cluster formation. For definitely charged debris in water, this solvent-driven interplay is at all times repulsive, and no clusters shape.This impact used to be discovered to be pH dependent: the workforce used to be ready to regulate the formation (or now not) of clusters for negatively charged debris by means of various the pH. Regardless of the pH, the definitely charged debris didn’t shape clusters.Solvent-Particular Results and Additional DiscoveriesNaturally, the workforce questioned whether or not the impact on charged debris may well be switched, such that the definitely charged debris shape clusters and the negatives don’t. By way of converting the solvent to alcohols, akin to ethanol, which has other interface habits to water, that is precisely what they seen: definitely charged aminated silica debris shaped hexagonal clusters, while negatively charged silica didn’t.Consistent with the researchers, this find out about implies a basic re-calibration in working out that may affect the way in which we consider processes as other as the stableness of pharmaceutical and high-quality chemical merchandise or the pathological malfunction related to molecular aggregation in human illness. The brand new findings additionally supply proof for the power to probe homes of the interfacial electric doable because of the solvent, akin to its signal and magnitude, which have been prior to now concept immeasurable.Professor Madhavi Krishnan (Division of Chemistry, Oxford College), who led the find out about, says: “I’m truly very happy with my two graduate scholars, in addition to the undergraduates, who’ve all labored in combination to transport the needle in this basic discovery.”Sida Wang (Division of Chemistry, Oxford College), a first-author at the find out about, says: “I nonetheless in finding it interesting to look those debris draw in, even having noticed this one thousand instances.”Reference: “A charge-dependent long-ranged pressure drives adapted meeting of subject in answer” by means of Sida Wang, Rowan Walker-Gibbons, Bethany Watkins, Melissa Flynn and Madhavi Krishnan, 30 February 2024, Nature Nanotechnology.
A brand new find out about has overturned a basic concept of physics by means of demonstrating that in a similar fashion charged debris can draw in every different in an answer, with the impact various between sure and adverse fees relying at the solvent. This discovery has important implications for quite a lot of clinical processes, together with self-assembly and crystallization. The analysis unearths the significance of solvent construction on the interface in figuring out interparticle interactions, difficult long-held ideals and indicating a necessity for a re-assessment of our working out of electromagnetic forces. Credit score: Zhang Kang“Opposites fees draw in; like fees repel” is a basic concept of fundamental physics. Then again, a brand new find out about from Oxford College, lately printed within the magazine Nature Nanotechnology, has demonstrated that in a similar fashion charged debris in answer can, in truth, draw in every different over lengthy distances.Simply as strangely, the workforce discovered that the impact is other for definitely and negatively charged debris, relying at the solvent.But even so overturning long-held ideals, those effects have instant implications for a spread of processes that contain interparticle and intermolecular interactions throughout quite a lot of length-scales, together with self-assembly, crystallization, and segment separation.The workforce of researchers, primarily based at Oxford’s Division of Chemistry, discovered that negatively charged debris draw in every different at massive separations while definitely charged debris repel, whilst the opposite used to be the case for solvents akin to alcohols.Those findings are unexpected as a result of they appear to contradict the central electromagnetic concept that the pressure between fees of the similar signal is repulsive in any respect separations.Experimental ObservationsNow, the usage of bright-field microscopy, the workforce tracked negatively charged silica microparticles suspended in water and located that the debris attracted every different to shape hexagonally organized clusters. Undoubtedly charged aminated silica debris, on the other hand, didn’t shape clusters in water.The usage of a idea of interparticle interactions that considers the construction of the solvent on the interface, the workforce established that for negatively charged debris in water, there may be a good looking pressure that outweighs electrostatic repulsion at massive separations, resulting in cluster formation. For definitely charged debris in water, this solvent-driven interplay is at all times repulsive, and no clusters shape.This impact used to be discovered to be pH dependent: the workforce used to be ready to regulate the formation (or now not) of clusters for negatively charged debris by means of various the pH. Regardless of the pH, the definitely charged debris didn’t shape clusters.Solvent-Particular Results and Additional DiscoveriesNaturally, the workforce questioned whether or not the impact on charged debris may well be switched, such that the definitely charged debris shape clusters and the negatives don’t. By way of converting the solvent to alcohols, akin to ethanol, which has other interface habits to water, that is precisely what they seen: definitely charged aminated silica debris shaped hexagonal clusters, while negatively charged silica didn’t.Consistent with the researchers, this find out about implies a basic re-calibration in working out that may affect the way in which we consider processes as other as the stableness of pharmaceutical and high-quality chemical merchandise or the pathological malfunction related to molecular aggregation in human illness. The brand new findings additionally supply proof for the power to probe homes of the interfacial electric doable because of the solvent, akin to its signal and magnitude, which have been prior to now concept immeasurable.Professor Madhavi Krishnan (Division of Chemistry, Oxford College), who led the find out about, says: “I’m truly very happy with my two graduate scholars, in addition to the undergraduates, who’ve all labored in combination to transport the needle in this basic discovery.”Sida Wang (Division of Chemistry, Oxford College), a first-author at the find out about, says: “I nonetheless in finding it interesting to look those debris draw in, even having noticed this one thousand instances.”Reference: “A charge-dependent long-ranged pressure drives adapted meeting of subject in answer” by means of Sida Wang, Rowan Walker-Gibbons, Bethany Watkins, Melissa Flynn and Madhavi Krishnan, 30 February 2024, Nature Nanotechnology.
DOI: 10.1038/s41565-024-01621-5
Opposites Draw in, Likes Repel? Scientists Overturn Basic Theory of Physics