Buried dozens of meters below the equator of Mars is a big honeycomb development very similar to what is discovered close to Earth’s frigid poles.Each and every crevasse spans 70 meters (230 ft) — about part a soccer box — and is bordered by way of 30-meter-wide (98-feet-wide) slurries of ice and dust. It is most likely, scientists say, that this subject material is someplace between 2 billion and three.5 billion years outdated. The patterns had been noticed within the information despatched house by way of China’s now-incommunicado Zhurong rover which explored an expansive, bumpy area north of Mars’ equator named Utopia Planitia. Zhruong rolled just a bit over one kilometer (0.6 miles) towards Mars’ southern area in that three hundred and sixty five days, however even all the way through this sort of brief go back and forth, its radar had sensed a continuing development of 15 buried polygons — suggesting there could also be extra ready to be discovered, learn about lead creator Lei Zhang of the Chinese language Academy of Sciences instructed Area.com in an e-mail.On Earth, identical patterns are recognized to shape handiest in Greenland, Iceland and Antarctica when drastic temperature dips led to by way of seasonal adjustments contract and fracture the bottom. Ice and dust that once in a while fill those cracks stops them from ever therapeutic, inflicting the outside to ultimately cut up additional. A identical procedure on Mars, some 2 billion to three.5 billion years in the past, would have led to the newly detected crevasses, that are tens of meters higher than any discovered on our planet. “Those polygons are massive,” stated Zhang.Similar: China may use a foldable helicopter to gather samples on MarsThis discovery, in brief, supplies contemporary proof that the Crimson Planet as soon as hosted water and a pleasant local weather to lifestyles as we are aware of it.Puzzlingly, the development additionally suggests tropical areas on Mars had been chilly sufficient to reason cracks very similar to the ones noticed close to Earth’s icy pole. The thriller might be responded by way of an present (however unproven) idea that means Mars used to be as soon as much more tilted on its axis than it’s nowadays — as much as 40 levels or extra — roughly 5 million years in the past. “Such an especially tilted situation muddies the waters between considering of polar areas as chilly and low-latitudes as heat,” Zhang stated.William Rapin, a scientist on the Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie in Paris, who used to be now not affiliated with the brand new analysis, says the newfound buried polygon development is “a captivating to find” and would lend a hand perceive the interior workings of a important length on Mars which can have been hospitable towards lifestyles. Rapin used to be a part of a staff that just lately discovered in a similar fashion formed, centimeter-sized dust cracks at the Martian floor close to the Gale crater at this time being explored by way of NASA’s Interest rover.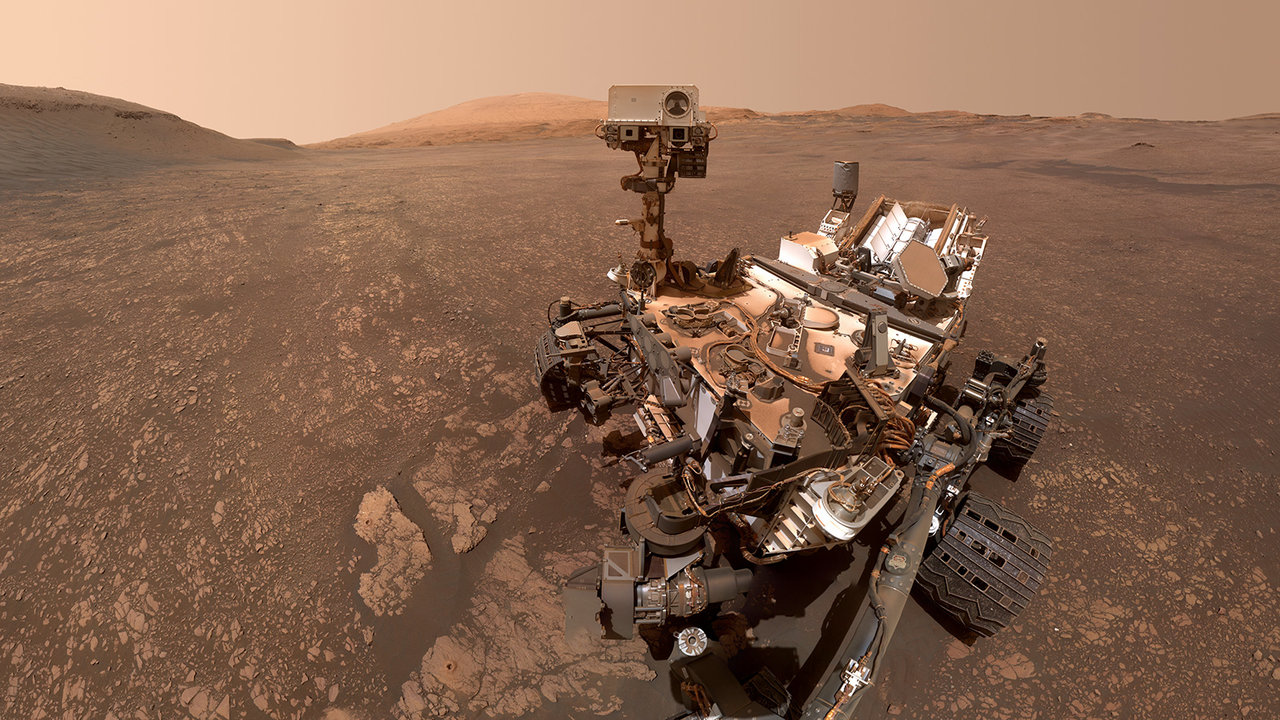 A picture of NASA’s Interest rover on Mars composed of 57 separate images the rover took on Would possibly 12, 2019. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS)Having access to spaces from a in a similar fashion historical length on Earth is hard as a result of our planet mechanically recycles its floor. However on Mars, “we have now all the ones strata in excellent situation,” Rapin stated. “So we will be able to examine an generation that used to be possibly favorable for the beginning of lifestyles itself.”Mars’ tilt or obliquity has shifted over the last 3.5 billion years. If it were not tilted in any respect, its equator will be the warmest because of receiving probably the most direct daylight, and temperature would dip towards the poles. However laptop fashions display the wobbly planet used to be excessively tipped a couple of million years in the past, which means that the place daylight landed modified all through the 12 months. For part of its orbit across the solar, about six months, Mars on this epoch skilled nights that “reached” so far as its equator, Rapin stated.Mars’ tilt has been recognized to alter greater than Earth’s does, having shifted by way of greater than ten levels over 100,000 years. In reality, that modify is what scientists consider led to such dramatic adjustments to its local weather, turning it from a once-blue oasis to the arid crimson land we at this time see. However the newly detected polygon development may lend a hand scientists slim down precisely when the ones drastic local weather adjustments came about, stated Zhang.The truth that the development used to be detected 35 meters (115 ft) underneath the outside “method the polygons shaped, evolved over a while, however then stopped abruptly,” he defined. Martian soil within the fresh previous will have to now not have skilled the similar temperature swings, inflicting it to layer on most sensible of the ones crevices. “The time that the polygons stopped may well be a time that the local weather modified — abruptly moving from a fairly chilly to a fairly great, temperate local weather.”The Zhurong rover went silent past due ultimate 12 months after it didn’t get up from its scheduled hibernation, and scientists presume it succumbed to Mars’ heavy mud storms. In the meantime, NASA’s Interest rover, which notched 4,000 days on Mars ultimate month, will succeed in a terrain subsequent 12 months pockmarked with fractures sufficiently big to be noticed from orbit. Rapin hypothesizes the ones might constitute the incidence of an historical, excessive drought and hopes to match them to the newfound polygons at Utopia Planitia.”They’re beautiful a ways,” stated Rapin. “It is more or less a dream that we succeed in them.”This analysis is described in a paper printed ultimate month within the magazine Nature Astronomy.
A picture of NASA’s Interest rover on Mars composed of 57 separate images the rover took on Would possibly 12, 2019. (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS)Having access to spaces from a in a similar fashion historical length on Earth is hard as a result of our planet mechanically recycles its floor. However on Mars, “we have now all the ones strata in excellent situation,” Rapin stated. “So we will be able to examine an generation that used to be possibly favorable for the beginning of lifestyles itself.”Mars’ tilt or obliquity has shifted over the last 3.5 billion years. If it were not tilted in any respect, its equator will be the warmest because of receiving probably the most direct daylight, and temperature would dip towards the poles. However laptop fashions display the wobbly planet used to be excessively tipped a couple of million years in the past, which means that the place daylight landed modified all through the 12 months. For part of its orbit across the solar, about six months, Mars on this epoch skilled nights that “reached” so far as its equator, Rapin stated.Mars’ tilt has been recognized to alter greater than Earth’s does, having shifted by way of greater than ten levels over 100,000 years. In reality, that modify is what scientists consider led to such dramatic adjustments to its local weather, turning it from a once-blue oasis to the arid crimson land we at this time see. However the newly detected polygon development may lend a hand scientists slim down precisely when the ones drastic local weather adjustments came about, stated Zhang.The truth that the development used to be detected 35 meters (115 ft) underneath the outside “method the polygons shaped, evolved over a while, however then stopped abruptly,” he defined. Martian soil within the fresh previous will have to now not have skilled the similar temperature swings, inflicting it to layer on most sensible of the ones crevices. “The time that the polygons stopped may well be a time that the local weather modified — abruptly moving from a fairly chilly to a fairly great, temperate local weather.”The Zhurong rover went silent past due ultimate 12 months after it didn’t get up from its scheduled hibernation, and scientists presume it succumbed to Mars’ heavy mud storms. In the meantime, NASA’s Interest rover, which notched 4,000 days on Mars ultimate month, will succeed in a terrain subsequent 12 months pockmarked with fractures sufficiently big to be noticed from orbit. Rapin hypothesizes the ones might constitute the incidence of an historical, excessive drought and hopes to match them to the newfound polygons at Utopia Planitia.”They’re beautiful a ways,” stated Rapin. “It is more or less a dream that we succeed in them.”This analysis is described in a paper printed ultimate month within the magazine Nature Astronomy.
Ordinary underground polygons on Mars trace at Crimson Planet’s rainy previous