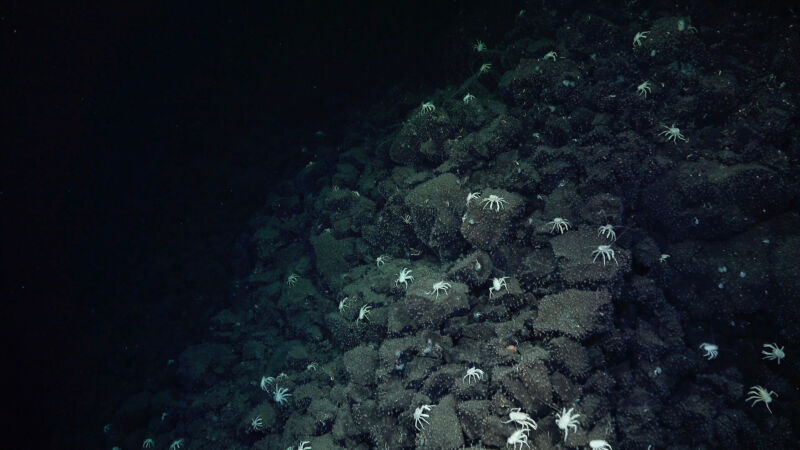
Amplify / “Main us like breadcrumbs…” A path of squat lobsters helped researchers find prior to now unknown hydrothermal vents. The hydrothermal vents create chemosynthetic ecosystems, so in spaces which can be most commonly barren of existence, the illusion of bigger animals may also be a hallmark of vents close by.
Impressive surroundings, from lush rainforests to towering mountain levels, dots the skin of our planet. However a few of Earth’s maximum iconic landmarks––ones that can harbor clues to the starting place of existence on Earth and most likely in different places––lay hidden on the backside of the sea. Scientists not too long ago discovered one such treasure in Ecuadorian waters: a submerged mini Yellowstone referred to as Sendero del Cangrejo.
This hazy alien realm simmers within the deep sea in a space referred to as the Western Galápagos Spreading Heart––an underwater mountain vary the place tectonic plates are slowly shifting clear of each and every different. Magma wells up from Earth’s mantle right here to create new oceanic crust in a procedure that created the Galápagos Islands and smaller underwater options, like hydrothermal vents. Those vents, which pump heated, mineral-rich water into the sea in billowing plumes, might be offering clues to the starting place of existence on Earth. Finding out Earth’s hydrothermal vents may just additionally be offering a gateway to discovering existence, or no less than its development blocks, on different worlds.
The newly came upon Sendero del Cangrejo accommodates a series of hydrothermal vents that spans just about two soccer fields. It hosts scorching springs and geyser chimneys that enhance an array of creatures, from large, spaghetti-like tube worms to alabaster Galatheid crabs.
The crabs, often referred to as squat lobsters, helped information researchers to Sendero del Cangrejo. Ecuadorian observers selected the website’s identify, which interprets to “Path of the Crabs,” of their honor.
“It did really feel just like the squat lobsters had been main us like breadcrumbs, like we had been Hansel and Gretel, to the true vent website,” mentioned Hayley Drennon, a senior analysis assistant at Columbia College’s Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, who participated within the expedition.
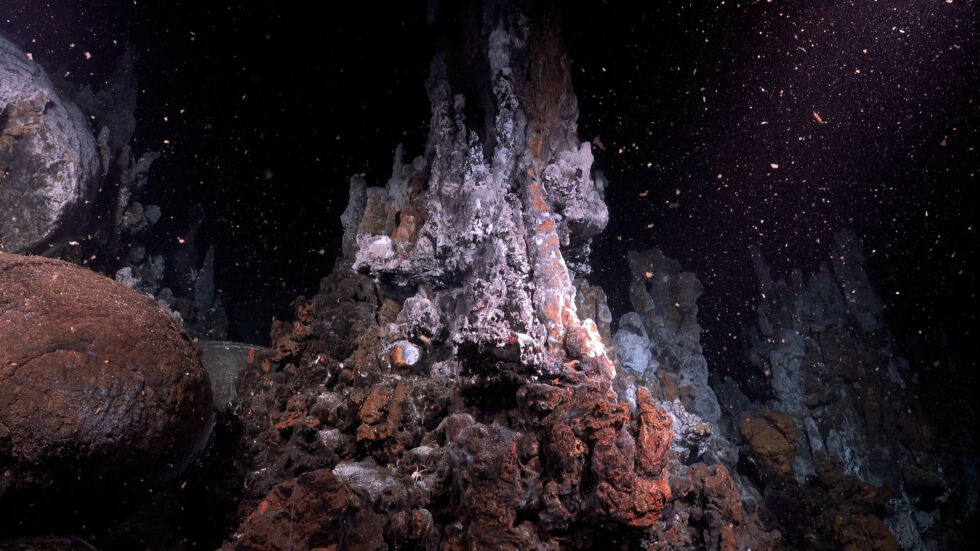 Amplify / The Iguanas Vent Box, the place the group did some sampling.
Amplify / The Iguanas Vent Box, the place the group did some sampling.
The joint American and Ecuadorian analysis group set sail aboard the Schmidt Ocean Institute’s Falkor (too) analysis vessel in mid-August on the lookout for new hydrothermal vents. They did some mapping and sampling on how one can their goal location, about 300 miles off the west coast of the Galápagos.
The group used a ‘Tow-Yo’ method to acquire and transmit real-time knowledge to the workforce aboard the send. “We reduced sensors connected to a protracted cord to the seafloor, after which towed the cord up and down like a yo-yo,” defined Roxanne Beinart, an affiliate professor on the College of Rhode Island and the expedition’s leader scientist. “This procedure allowed us to watch adjustments in temperature, water readability, and chemical composition to assist pinpoint doable hydrothermal vent places.”
Commercial
Once they reached a area that gave the impression promising, they deployed the remotely operated car SuBastian for a greater glance. Lower than 24 hours later, the group started seeing an increasing number of Galatheid crabs, which they adopted till they discovered the vents.
The crabs had been in particular helpful guides for the reason that vent fluids there are transparent, in contrast to “black people who smoke” that create easy-to-see plumes. SuBastian explored the world for roughly 43 hours immediately within the robotic’s longest dive up to now.
However the real discovery procedure spanned many years. Researchers have recognized for just about two decades that the world used to be most likely house to hydrothermal task because of chemical alerts measured in 2005. A couple of decade later, groups ventured out once more and picked up animal samples. Now, because of the Schmidt Ocean Institute’s contemporary expedition, scientists have essentially the most complete knowledge set ever for this location. It comprises chemical, geological, and organic knowledge, along side the primary high-temperature water samples.
“It’s now not unusual for a real discovery like this to take many years,” mentioned Jill McDermott, an affiliate professor at Lehigh College and the expedition’s co-chief scientist. “The sea is a large position, and the places are very far off, so it takes numerous time and logistics to get out to them.” The group will proceed their analysis onshore to assist us know the way hydrothermal vents affect our planet.
Genesis from hell?
Sendero del Cangrejo might evaluate to a small-scale Yellowstone in many ways, but it surely’s no vacationer vacation spot. It’s pitch-black since daylight can’t achieve the deep ocean ground. The crushing weight of a mile of water presses down from overhead. And the vents are scorching and poisonous. A few of them clocked in at 290º C (550º F)—just about scorching sufficient to soften lead.
Ahead of scientists came upon hydrothermal vents in 1977, they assumed such excessive prerequisites would preclude the opportunity of existence. But that trailblazing group noticed a couple of species thriving, together with white clams that guided them to the vents the similar means the Galatheid crabs led the trendy researchers to Sendero del Cangrejo.
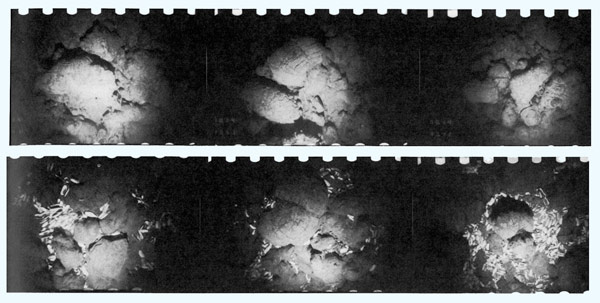 A sequence of seafloor pictures displays the unexpected look of are living white clams that led scientists to search out hydrothermal vents for the primary time.
A sequence of seafloor pictures displays the unexpected look of are living white clams that led scientists to search out hydrothermal vents for the primary time.
Ahead of the 1977 in finding, nobody knew existence may just live on in this kind of adverse position. Now, scientists know there are microbes referred to as thermophiles that may most effective are living in excessive temperatures (as much as about 120º C, or 250º F).
Micro organism that encompass hydrothermal vents don’t consume different organisms or create calories from daylight like vegetation do. As a substitute, they produce calories the usage of chemical substances like methane or hydrogen sulfide that emanate from the vents. This procedure, referred to as chemosynthesis, used to be first known during the characterization of organisms came upon at those vents. Chemosynthetic micro organism are the spine of hydrothermal vent ecosystems, serving as a vitamin supply for upper organisms.
Commercial
Some researchers recommend existence on Earth could have originated close to hydrothermal vents because of their distinctive chemical and energy-rich prerequisites. Whilst the proposal stays unproven, the invention of chemosynthesis opened our eyes to new puts that would host existence.
The opportunity of chemosynthetic creatures diminishes the importance of so-called liveable zones round stars, which describe the orbital distances between which floor water can stay liquid on a planet or moon. The liveable zone in our personal Sun Gadget extends from about Venus’ orbit out just about to Mars’.
NASA’s Europa Clipper challenge is ready to release past due subsequent yr to decide whether or not there are puts underneath the skin of Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa, that would enhance existence. It’s so much chillier available in the market, well past our Sun Gadget’s liveable zone, however scientists suppose Europa is internally heated. It reviews robust tidal forces from Jupiter’s gravity, which might create hydrothermal task at the moon’s ocean ground.
A number of different moons in our Sun Gadget additionally host subsurface oceans and revel in the similar tidal heating that would doubtlessly create liveable prerequisites. By means of exploring Earth’s hydrothermal vents, scientists may just be informed extra about what to search for in identical environments in different places in our Sun Gadget.
“The Ocean’s Multivitamin”
Whilst hydrothermal vents are reasonably new to science, they’re by no means new to our planet. “Vents had been lively since Earth’s oceans first shaped,” McDermott mentioned. “They’ve been found in our oceans for so long as we’ve had them, so about 3 billion years.”
All over that point, they’ve most likely reworked our planet’s chemistry and geology through biking chemical substances and minerals from Earth’s crust all the way through the sea.
“All residing issues on Earth want minerals and parts that they get from the crust,” mentioned Peter Girguis, a professor at Harvard College, who participated within the expedition. “It’s no exaggeration to mention that each one existence on earth is inextricably tied to the rocks upon which we are living and the geological processes happening deep throughout the planet…it’s like the sea’s multivitamin.”
However the complete extent of the have an effect on hydrothermal vents have in the world stays unknown. Within the just about 50 years since hydrothermal vents had been first came upon, scientists have exposed masses extra unfold all over the world. But nobody is aware of what number of stay unidentified; there are possibly hundreds extra vents hidden within the deep. Detailed research, like the ones the expedition scientists are proceeding onshore, may just assist us know the way hydrothermal task influences the sea.
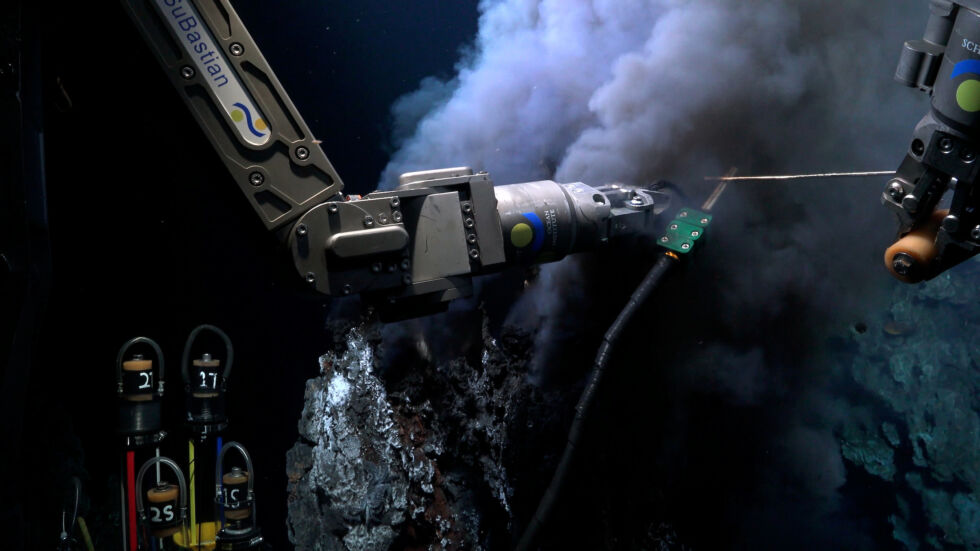 Amplify / ROV SuBastian takes water and chemical samples from a black smoker hydrothermal vent within the Iguanas Vent Box, Galapagos Islands.
Amplify / ROV SuBastian takes water and chemical samples from a black smoker hydrothermal vent within the Iguanas Vent Box, Galapagos Islands.
The group’s instant observations be offering a just right start line for his or her persevered clinical sleuthing.
“I in reality anticipated to search out denser animal populations in some puts,” Beinart mentioned.
McDermott thinks which may be related to the composition of the vent fluids. “A number of of the vents had been transparent—now not very particle-rich,” she mentioned. “They’re most likely decrease in minerals, however we’re now not positive why.” Now, the group will measure other steel ranges in water samples from the vent fluids to determine why they’re low in minerals and whether or not that has influenced the animals the vents host.
Researchers are finding out extra about hydrothermal vents each day, however many mysteries stay, such because the eventual affect ocean acidification may have on vents. As they search solutions, they’re positive to search out extra questions and open up new avenues of clinical exploration.
Ashley writes about area as a contractor for NASA’s Goddard House Flight Heart through day and freelances as an environmental creator. She holds a grasp’s stage in area research from the College of North Dakota and is completing a grasp’s in science writing thru The Johns Hopkins College. She writes maximum of her articles with certainly one of her children on her lap.











