Lucy and her fellow australopithecines can have created and used equipment greater than 3 million years in the past, a brand new find out about of hand muscle groups suggests. The discovering supplies additional proof that instrument use began lengthy prior to the Homo genus emerged.”Whilst we will be able to’t definitively say that those early people crafted stone equipment, our findings display that their arms had been regularly utilized in ways in which carefully align with the movements vital for human instrument manipulation,” find out about co-author Fotios Alexandros Karakostis, a paleoanthropologist on the College of Tübingen in Germany, informed Are living Science in an e mail.In a find out about printed within the November factor of the Magazine of Human Evolution, researchers tested muscle attachment websites at the hand bones of 3 australopithecine species and in comparison them with ape and human arms to take a look at to know when our ancestors received the dexterity that trendy people have. Since australopithecines constitute the chronological mid-point within the evolution of people from historical apes, the researchers suspected that australopithecine hand bones might also have characteristics of each apes and people.The researchers keen on hand entheses, which might be puts the place tendons connect muscle groups to bones. When muscle groups and joints are used regularly, those attachment websites adapt, leading to a trend of bony adjustments that counsel particular recurring actions.”By means of finding out those muscle attachment websites, we will be able to reconstruct how muscle groups and ligaments had been actively engaged right through lifestyles, giving us a clearer image of early hominin conduct,” Karakostis stated.Comparable: Our mixed-up human circle of relatives: 8 human family members that went extinct (and 1 that did not)Muscle attachment websites at the arms of 3 australopithecine species published that they had been all most probably ready to control items. However the relatively contemporary hominin Australopithecus sediba (1.95 million to at least one.78 million years in the past) had a extra humanlike hand than did the extra historical A. africanus (3.7 million to three.4 million years in the past) and A. afarensis (3.7 million to three million years in the past), which each had a mosaic of humanlike and apelike characteristics.Get the sector’s most attractive discoveries delivered immediately on your inbox.Despite the fact that apes can seize and manipulate items, their dexterity in those duties is proscribed by way of their hand anatomy. Homo sapiens, in the meantime, have two key anatomical options which might be very important to the facility to exactly seize, grip and pinch items, the researchers discovered.The primary dorsal interosseus muscle is positioned within the palm between the thumb and index finger and we could us exactly pinch issues. “This distinctive capability supplied early hominins with the dexterity had to manipulate items — together with equipment — successfully, paving the best way for each technological and cultural development,” find out about first writer Jana Kunze, a paleoanthropologist on the College of Tübingen, stated.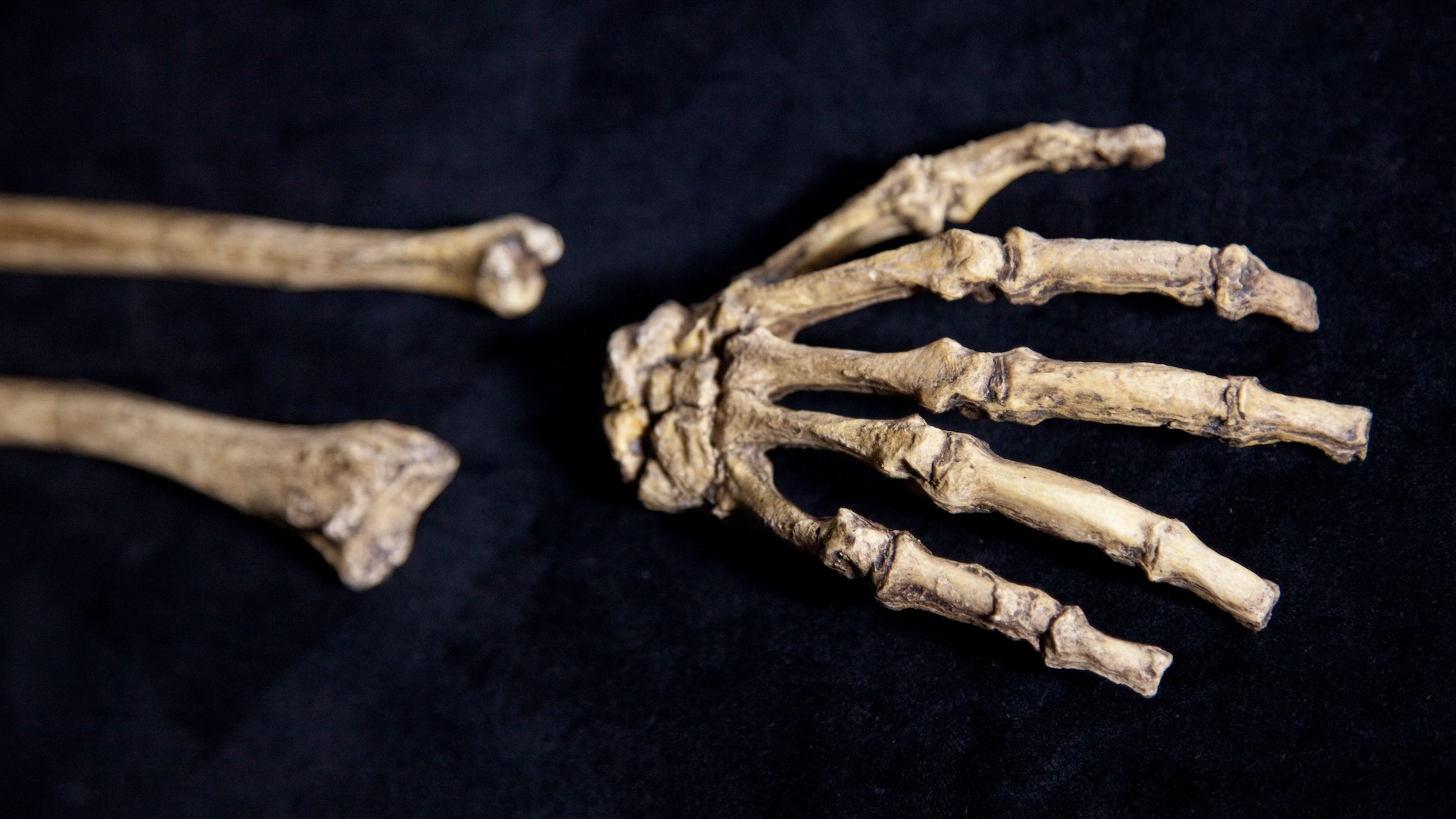 The hand bones of Australopithecus sediba. A brand new find out about presentations that A. sediba had hand muscle groups extra very similar to people than to apes. (Symbol credit score: The Herbal Historical past Museum by way of Alamy Inventory Photograph)The pinky finger additionally performs a an important function in humanlike greedy, the researchers famous. Early hominins like A. afarensis and A. sediba almost certainly trusted pinky muscle groups for very important day-to-day duties similar to dealing with equipment and getting ready meals.”Extra extensively talking, the co-evolution of the thumb and pinky had been decisive for hominin biocultural evolution, surroundings the degree for the complex humanlike dexterity we see in people these days,” Kunze stated.The query of the way dexterous australopithecines’ arms had been is without delay tied to the query of which species first made and used equipment. When Homo habilis used to be found out within the Sixties, scientists named it “handyman” as it used to be discovered with very previous stone equipment relationship again 2.3 million years. For a few years, researchers assumed australopithecines didn’t have the psychological or bodily capability to make equipment. However the 2015 discovery of three.3 million-year-old equipment at a website known as Lomekwi in Kenya raised the arguable chance that A. afarensis made them.”Our find out about signifies that Australopithecus afarensis — the species Lucy belonged to — regularly carried out humanlike greedy patterns, the usage of their arms in ways in which counsel common, professional manipulation of items inside the hand,” Karakostis stated. Alternatively, “those findings do not without delay display that A. afarensis or A. sediba made or used stone equipment particularly.”Tracy Kivell, director of Human Origins on the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology who used to be no longer concerned within the find out about, informed Are living Science in an e mail that this muscle attachment analysis is novel and fascinating, appearing that every species interacted with its atmosphere in several techniques, together with their manipulative skills.”It’s most probably that every of those australopiths had been the usage of equipment and mountaineering,” Kivell stated, and the muscle attachment websites “supply thrilling details about how those explicit australopith folks had been the usage of their arms all through lifestyles.”
The hand bones of Australopithecus sediba. A brand new find out about presentations that A. sediba had hand muscle groups extra very similar to people than to apes. (Symbol credit score: The Herbal Historical past Museum by way of Alamy Inventory Photograph)The pinky finger additionally performs a an important function in humanlike greedy, the researchers famous. Early hominins like A. afarensis and A. sediba almost certainly trusted pinky muscle groups for very important day-to-day duties similar to dealing with equipment and getting ready meals.”Extra extensively talking, the co-evolution of the thumb and pinky had been decisive for hominin biocultural evolution, surroundings the degree for the complex humanlike dexterity we see in people these days,” Kunze stated.The query of the way dexterous australopithecines’ arms had been is without delay tied to the query of which species first made and used equipment. When Homo habilis used to be found out within the Sixties, scientists named it “handyman” as it used to be discovered with very previous stone equipment relationship again 2.3 million years. For a few years, researchers assumed australopithecines didn’t have the psychological or bodily capability to make equipment. However the 2015 discovery of three.3 million-year-old equipment at a website known as Lomekwi in Kenya raised the arguable chance that A. afarensis made them.”Our find out about signifies that Australopithecus afarensis — the species Lucy belonged to — regularly carried out humanlike greedy patterns, the usage of their arms in ways in which counsel common, professional manipulation of items inside the hand,” Karakostis stated. Alternatively, “those findings do not without delay display that A. afarensis or A. sediba made or used stone equipment particularly.”Tracy Kivell, director of Human Origins on the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology who used to be no longer concerned within the find out about, informed Are living Science in an e mail that this muscle attachment analysis is novel and fascinating, appearing that every species interacted with its atmosphere in several techniques, together with their manipulative skills.”It’s most probably that every of those australopiths had been the usage of equipment and mountaineering,” Kivell stated, and the muscle attachment websites “supply thrilling details about how those explicit australopith folks had been the usage of their arms all through lifestyles.”












