How do you satiate the starvation of a supermassive black hollow? With light-years-long rivers of cosmic mud, astronomers say.Scientists have discovered proof of remarkably lengthy mud streams spiraling in towards the supermassive black hollow residing on the center of our neighboring galaxy, Andromeda. It will seem that those massive streams quietly, however often, feed the cosmic abyss — and it is most likely this has been occurring for eons. The newfound streams illustrate how black holes billions of occasions heavier than our solar stay exceptionally quiet whilst they gorge on close by mud, fuel and ill-fated stars. The findings owe themselves to scientists in Germany, Spain and Chile who analyzed archival photographs from NASA’s now-retired Spitzer House Telescope.Supermassive black holes have up to now been noticed feeding frenzies, gobbling such huge chunks of sparkling subject that their darkish silhouettes shine brighter than complete galaxies chock-full of stars. Then again, the diets of alternative black holes, just like the very quiet ones lurking within the hearts of Andromeda and our personal Milky Means, were unclear.Comparable: Shocking symbol of Andromeda galaxy takes most sensible astronomy pictures prize of 2023 (gallery)Those silent beasts are fed via streams of fuel spiraling into them slowly and frequently, with sufficient subtlety that rings of sparkling subject material round them hardly differ in brightness, in keeping with a find out about revealed closing 12 months within the Astronomical Magazine. This cosmic etiquette can also be likened to water swirling down a drain, astronomers stated on Thursday (Might 9) in a NASA observation.At about 2.5 million light-years from Earth, the Andromeda galaxy is the closest main galaxy to the Milky Means and some of the few galaxies visual to the unaided eye on darkish, moonless nights. Not like the unique spiral fingers curved across the middle of our personal galaxy, Andromeda’s core is turned around via more than one rings of mud.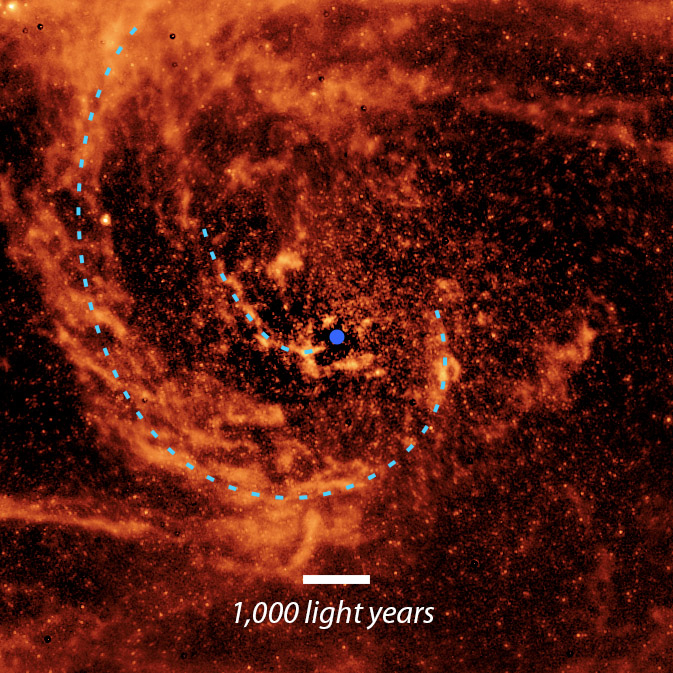 An annotated, close-up view of the mud close to the middle of the Andromeda galaxy. Blue dotted strains spotlight the trail of 2 mud streams flowing towards the supermassive black hollow on the galaxy’s middle (indicated via a pink dot). (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech)To reach at their conclusions, the astronomers first simulated how subject material round Andromeda’s black hollow behaves over the years. That simulation confirmed a tiny disk of scorching fuel would possibly shape on the subject of the black hollow, which might feed it prior to getting replenished via many different streams of fuel and dirt within the surrounding neighborhood. The ones streams, the researchers discovered, will have to be inside a selected dimension and pace vary to help secure feeding, with out which the black hollow would belch and its brightness range. Certain sufficient, when the researchers in comparison their findings to information from the Spitzer telescope, they discovered the telescope had already recorded spirals of mud throughout the required constraints.Breaking house information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!”It is a nice instance of scientists reexamining archival information to expose extra about galaxy dynamics via evaluating it to the newest pc simulations,” find out about co-author Almudena Prieto, an astrophysicist on the Institute of Astrophysics of the Canary Islands and the College Observatory Munich, stated within the observation. “We’ve got 20-year-old information telling us issues we didn’t acknowledge in it once we first gathered it.”The findings contradict some effects from closing 12 months regarding a special team of astronomers who urged all cosmic voids gulp close by subject the similar manner regardless of their urge for food. The noticed glow of subject being gobbled via 100 different supermassive black holes used to be “incompatible with an ordered go with the flow of subject.” Such contradictions permit astronomers to re-evaluate what we learn about black hollow habits. NASA retired the Spitzer telescope in January 2020 after its 16-year tenure of amassing infrared information about comets and asteroids in our sun machine, exoplanets past our sun machine, and getting even deeper, quite a lot of wallet of our universe clouded via interstellar fuel and dirt. The distance company necessarily “changed” Spitzer with the James Webb House Telescope, which introduced in 2021 and likewise sees the universe in infrared. In Might of closing 12 months, then again, the U.S. House Drive proposed a bold plan to resurrect Spitzer by the use of a robot venture to provider the telescope and go back it on-line, harkening again to the Hubble House Telescope servicing missions. For context, Spitzer is now over 180 million miles (289 million kilometers) from Earth. Hubble used to be proper in our planet’s orbit.
An annotated, close-up view of the mud close to the middle of the Andromeda galaxy. Blue dotted strains spotlight the trail of 2 mud streams flowing towards the supermassive black hollow on the galaxy’s middle (indicated via a pink dot). (Symbol credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech)To reach at their conclusions, the astronomers first simulated how subject material round Andromeda’s black hollow behaves over the years. That simulation confirmed a tiny disk of scorching fuel would possibly shape on the subject of the black hollow, which might feed it prior to getting replenished via many different streams of fuel and dirt within the surrounding neighborhood. The ones streams, the researchers discovered, will have to be inside a selected dimension and pace vary to help secure feeding, with out which the black hollow would belch and its brightness range. Certain sufficient, when the researchers in comparison their findings to information from the Spitzer telescope, they discovered the telescope had already recorded spirals of mud throughout the required constraints.Breaking house information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!”It is a nice instance of scientists reexamining archival information to expose extra about galaxy dynamics via evaluating it to the newest pc simulations,” find out about co-author Almudena Prieto, an astrophysicist on the Institute of Astrophysics of the Canary Islands and the College Observatory Munich, stated within the observation. “We’ve got 20-year-old information telling us issues we didn’t acknowledge in it once we first gathered it.”The findings contradict some effects from closing 12 months regarding a special team of astronomers who urged all cosmic voids gulp close by subject the similar manner regardless of their urge for food. The noticed glow of subject being gobbled via 100 different supermassive black holes used to be “incompatible with an ordered go with the flow of subject.” Such contradictions permit astronomers to re-evaluate what we learn about black hollow habits. NASA retired the Spitzer telescope in January 2020 after its 16-year tenure of amassing infrared information about comets and asteroids in our sun machine, exoplanets past our sun machine, and getting even deeper, quite a lot of wallet of our universe clouded via interstellar fuel and dirt. The distance company necessarily “changed” Spitzer with the James Webb House Telescope, which introduced in 2021 and likewise sees the universe in infrared. In Might of closing 12 months, then again, the U.S. House Drive proposed a bold plan to resurrect Spitzer by the use of a robot venture to provider the telescope and go back it on-line, harkening again to the Hubble House Telescope servicing missions. For context, Spitzer is now over 180 million miles (289 million kilometers) from Earth. Hubble used to be proper in our planet’s orbit.
Our neighboring galaxy’s supermassive black hollow would most likely be a well mannered dinner visitor