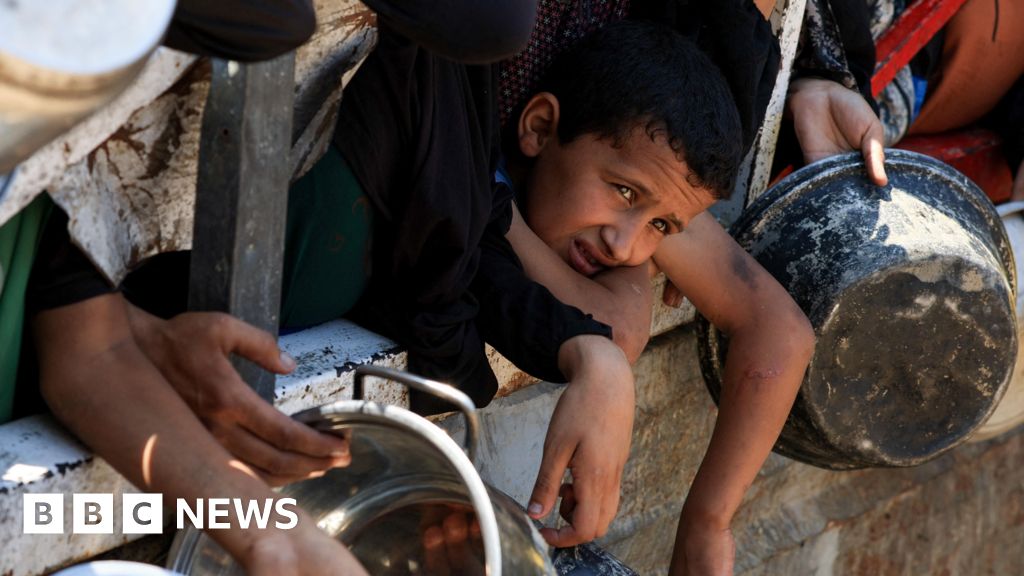
Neatly, take a look at that. The Perseverance rover has clambered out of the crater that’s been its cradle for almost 4 years at the Purple Planet. Perseverance landed on Mars in February 2021. The rover is charged with on the lookout for biosignatures—proof that the inhospitable international was once now not most effective as soon as able to supporting lifestyles, however in reality did. To temporarily sum what the rover has been as much as: Percy has been toiling at the Martian floor for the previous 3.5 years. In its tenure, the rover has drilled into rocks, taken photographs of the Martian floor and the Mars helicopter Ingenuity, and compiled a selection of rock samples that can confidently— one day—be delivered to Earth for learn about. The rover landed in Jezero Crater, which as soon as held a big lake. The crater was once shaped through an affect match some 3.9 billion years in the past. At the crater’s western edge was once a river delta, which accommodates compelling rocks that researchers are keen to check on Earth—sooner or later.
In a consultation held the day past at the yearly assembly of the American Geophysical Union, Perseverance mission scientists mentioned Perseverance’s new atmosphere, and what’s in retailer for the rover because it continues its trek around the rusty terrain. Briony Horgan, a planetary scientist at Purdue College and co-investigator at the Perseverance challenge, hopped at the telephone with Gizmodo to talk about what’s subsequent. “At the crater rim itself is terrain that was once uplifted through the affect,” Horgan stated. “What’s truly thrilling about this is that we’re now above where the place there was once status water. We will be able to in reality see the rocks that had been there sooner than the affect—truly historical stuff.”
The secret for Perseverance is: bizarre rocks. The rover group has been imaging and sampling bits of the Martian terrain that experience extraordinary appearances or chemical compositions, such because the “leopard spot” rocks published in July. Those rocks may just be offering hints at historical lifestyles, but additionally the evolution of Mars itself. Since historical Mars is theorized to had been Earth-like, those rocks can make clear how our international ended up verdant and rainy and Mars ended up so—smartly—Martian. “One of the most causes we’re eager about the crater rim is that affect craters generate warmth from this large affect,” Horgan stated. “It drives hydrothermal methods during the crust, and the ones are truly liveable environments.”
The Perseverance samples shall be game-changing, permitting scientists to interrogate Mars’ historical previous in some way this is very tough, if now not inconceivable, to do remotely with a rover from over 100 million miles away. As Perseverance friends into Mars superlatively historical previous, scientists can glean details about its historical attainable to host microbial lifestyles and the way in which the planet become the arid, rocky, windswept international we all know as of late.
“Those are one-of-a-kind samples that can educate us about virtually each facet of the early sun device and the way planets evolve,” Horgan stated, “and so they’ll stay doing that for many years to come back.” It’s a disgrace that we’ll need to look forward to NASA to search out the investment and the fitting plan to carry the samples house—it’s exhausting to carry ones’ breath for greater than a minute, a lot much less years—however the wait will undoubtedly be price it. Till then, there are many insights to be gleaned remotely, as Perseverance starts its paintings with one of the most sun device’s maximum historical rocks.