Join The Gentleman Report’s Marvel Principle science e-newsletter. Discover the universe with information on interesting discoveries, medical developments and extra.
The Gentleman Report
—
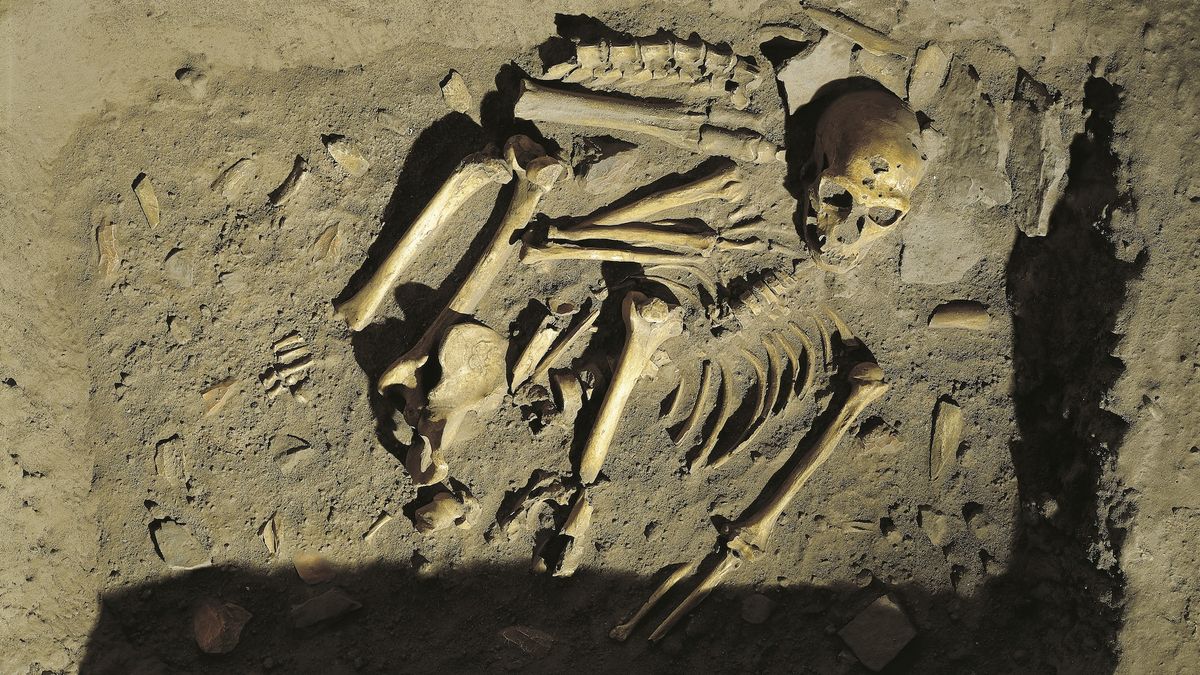
After spending 1,000 days at the Martian floor, NASA’s Perseverance rover has exposed new information about the historical past of an historical lake and river delta at the crimson planet.
The brand new insights, detectable because of the rover’s detailed on-the-ground sleuthing, are serving to scientists piece in combination the puzzle of Mars’ mysterious previous, and so they in the long run may decide whether or not existence ever existed there.
Perseverance and its helicopter better half, Ingenuity, landed in Jezero Crater on February 18, 2021, to seek for indicators of historical microbial existence.
As a part of the hunt, the robot explorer simply finished its investigation of a river delta that after fed right into a lake that crammed Jezero Crater billions of years in the past. Alongside the way in which, Perseverance has additionally accrued 23 rock samples from other places all through the crater and delta.
Each and every pattern, in regards to the dimension of study room chalk and encased in steel tubes, is also returned to Earth one day by means of NASA and the Eu House Company’s joint Mars Pattern Go back marketing campaign. Learning the samples on Earth would permit for a extra detailed research the use of lab apparatus too unwieldy to ship to Mars aboard the rover.
Scientists shared one of the insights they’ve gleaned from Perseverance’s trek throughout Mars on Tuesday on the American Geophysical Union fall assembly in San Francisco.
The rover collects samples by means of the use of an abrasion software on its arm to scrape away at Martian rock surfaces after which analyzes the rock’s composition the use of its Planetary Software for X-ray Lithochemistry, referred to as PIXL.
A few of Perseverance’s contemporary rock samples come with silica, a fine-grained mineral that aids within the preservation of historical fossils and natural molecules on Earth. Natural molecules can shape right through geological and organic processes.
“On Earth, this fine-grained silica is what you regularly in finding in a location that used to be as soon as sandy,” mentioned Morgan Cable, deputy most important investigator of PIXL at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California, in a commentary. “It’s the type of setting the place, on Earth, the stays of historical existence might be preserved and located later.”
JPL-Caltech/ASU/MSSS/NASA
The Perseverance rover took a 360-degree mosaic comprising 993 photographs and a couple of.38 billion pixels from a location dubbed “Airey Hill” in November.
One of the most rocks additionally incorporated iron related to phosphate, a herbal supply of the component phosphorus that acts as an element of DNA and mobile membranes.
Carbonate used to be additionally detected within the samples. Those minerals point out previous water-rich environments, appearing like time tablets for the environmental stipulations on Mars from when the rocks to begin with shaped.
“We picked Jezero Crater as a touchdown website as a result of orbital imagery confirmed a delta — transparent proof that an enormous lake as soon as crammed the crater. A lake is a probably liveable setting, and delta rocks are a perfect setting for entombing indicators of historical existence as fossils within the geologic report,” mentioned Ken Farley, Perseverance venture scientist and professor of geochemistry on the California Institute of Generation, in a commentary. “After thorough exploration, we’ve pieced in combination the crater’s geologic historical past, charting its lake and river segment from starting to finish.”
Scientists consider that Jezero Crater shaped when an asteroid slammed into Mars 4 billion years in the past.
Perseverance started its venture by means of learning and sampling the crater flooring quickly after touchdown. The rover’s detective paintings helped scientists decide that the crater flooring is made from volcanic rock that shaped both because of magma that bubbled as much as the outside or volcanic task at the Martian floor.
As Perseverance rolled alongside, the rover got here throughout examples of sandstone and mudstone, suggesting {that a} river flowed into the crater hundreds of thousands of years after it shaped. A most sensible layer of mudstones wealthy with salt is all that continues to be to indicate {that a} shallow lake crammed the crater, achieving 22 miles (35 kilometers) vast and 100 toes (30 meters) deep, sooner than some climatic shift led to the lake to evaporate.
Perseverance additionally discovered proof of boulders that originated from in other places on Mars and had been deposited throughout the river delta and within the crater by means of fast-flowing rivers.
“We had been ready to look a huge define of those chapters in Jezero’s historical past in orbital photographs, however it required getting up shut with Perseverance to actually perceive the timeline intimately,” mentioned Libby Ives, a postdoctoral fellow at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in a commentary.
JPL-Caltech/NASA
This representation depicts water breaking during the rim of Jezero Crater billions of years in the past. The rover is now exploring the realm.
Perseverance’s suite of tools has the facility to locate microscopic fossil constructions and the chemical strains left at the back of by means of microbial existence, however the rover hasn’t detected both one. Then again, the geological proof that the rover has accrued up to now paints an attractive image.
“We now have splendid stipulations for locating indicators of historical existence the place we discover carbonates and phosphates, which level to a watery, liveable setting, in addition to silica, which is superb at preservation,” Cable mentioned.
And the venture isn’t over but. Subsequent, the rover will learn about a space close to the crater’s front the place a river flooded around the crater flooring, leaving at the back of deposits of carbonate that resemble a bath ring.