Noise-resistant section imaging with depth correlation. Credit score: College of Physics, College of Warsaw
Researchers on the College of Warsaw’s College of Physics with colleagues from Stanford College and Oklahoma State College have offered a quantum-inspired phase-imaging approach in keeping with mild depth correlation measurements this is tough to section noise.
The brand new imaging approach can function even with extraordinarily dim illumination and will turn out helpful in rising programs similar to in infrared and X-ray interferometric imaging and quantum and matter-wave interferometry. The result of the analysis had been revealed in Science Advances.
Regardless of if you are taking pictures of a cat along with your smartphone or symbol mobile cultures with a complicated microscope, you do that by way of measuring the depth (brightness) of sunshine pixel by way of pixel. Mild is characterised now not best by way of its depth but in addition by way of its section. Apparently, clear gadgets can grow to be visual in case you are in a position to measure the section extend of sunshine that they introduce.
Segment distinction microscopy, for which Frits Zernike gained a Nobel Prize in 1953, led to a revolution in biomedical imaging because of the potential of acquiring high-resolution pictures of more than a few clear and optically skinny samples. The analysis box that emerged from Zernike’s discovery contains trendy imaging ways similar to virtual holography and quantitative section imaging.
“It permits label-free and quantitative characterization of residing specimens, similar to mobile cultures, and will to find programs in neurobiology or most cancers analysis” explains Dr. Radek Lapkiewicz, head of the Quantum Imaging Laboratory on the College of Warsaw’s College of Physics.
On the other hand, there may be nonetheless room for growth. “For instance, interferometry, an ordinary size approach for exact thickness measurements at any level of the tested object, best works when the device is solid, now not topic to any shocks or disturbances. It is rather difficult to hold out this kind of check, as an example, in a shifting automotive or on a shaking desk,” explains Jerzy Szuniewcz, a doctoral pupil on the College of Warsaw’s College of Physics.
Researchers from the College of Physics on the College of Warsaw with colleagues from Stanford College and Oklahoma State College made up our minds to take on this drawback and expand a brand new approach of section imaging this is resistant to section instability.
Again to the old fashioned
How did the researchers get a hold of the speculation for the brand new methodology? Already within the Nineteen Sixties Leonard Mandel and his workforce demonstrated that even if interference isn’t detectable in depth, correlations can expose its presence. “Impressed by way of the vintage experiments of Mandel, we would have liked to research how depth correlation measurements can be utilized for section imaging,” explains Lapkiewicz.
In a correlation size they checked out pairs of pixels and noticed whether or not they become brighter or darker on the identical time.
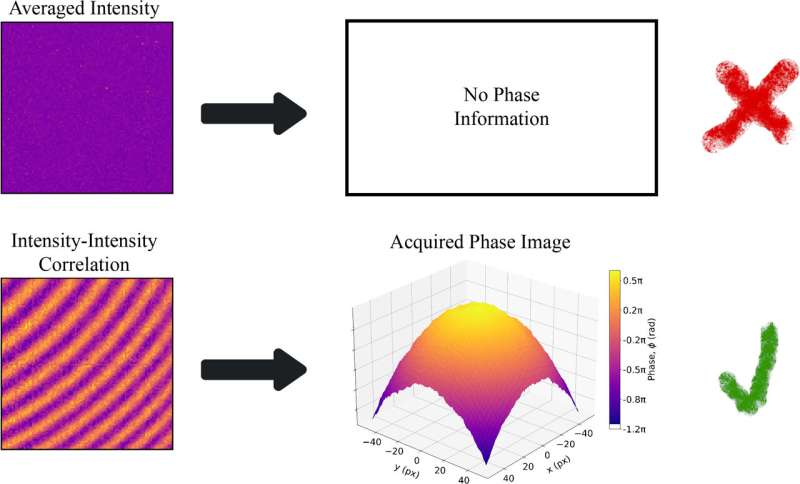
“We’ve proven that such measurements comprise additional info that can’t be bought the use of a unmarried picture, i.e., depth size. The use of this reality, we demonstrated that during section microscopy in keeping with interference, observations are conceivable even if usual interferograms reasonable out dropping the entire section data and there aren’t any fringes recorded within the depth.
“With an ordinary manner, one would suppose that there’s no helpful data in such a picture. On the other hand, it seems that the tips is hidden within the correlations and will also be recovered by way of examining more than one unbiased pictures of an object permitting us to procure very best interferograms, even if the odd interference is undetectable because of the noise” provides Lapkiewicz.
“In our experiment, the sunshine which passes via a section object (our goal, which we wish to examine) is superposed with a reference mild. A random section extend is offered between the thing and reference mild beams—this section extend simulates a disturbance obstructing the usual section imaging strategies. As a result, no interference is noticed when the depth is measured, this is, no details about the section object will also be bought from depth measurements.
“On the other hand, the spatially dependent depth–depth correlation presentations a perimeter trend that comprises your complete details about the section object. This depth–depth correlation is unaffected by way of any temporal section noise various slower then the rate of the detector (~10 nanoseconds within the carried out experiment) and will also be measured by way of accruing information over an arbitrarily lengthy time frame—which is a sport changer—longer size approach extra photons, which interprets to better accuracy,” explains Jerzy Szuniewicz, the primary writer of the paintings.
Put merely, if we have been to file a unmarried movie body, that unmarried body would give us no helpful details about what the thing beneath find out about seems like. “Due to this fact, first we recorded an entire sequence of such frames the use of a digital camera after which multiplied the size values at every pair of issues from each body. We averaged those correlations, and recorded a complete symbol of our object,” explains Szuniewicz.
“There are lots of conceivable tactics to get well the section profile of an noticed object from a chain of pictures. On the other hand, we proved that our approach in keeping with intensity-intensity correlation and a so-called off-axis holography methodology supplies an optimum reconstruction precision” says Stanisław Kurdziałek, the second one writer of the paper.
A vivid thought for darkish environments
A section imaging manner in keeping with depth correlation will also be extensively utilized in very noisy environments. The brand new approach works with each classical (laser and thermal) and quantum mild. It may also be applied within the photon counting regime, as an example the use of unmarried photon avalanche diodes. “We will use it in instances the place there may be little mild to be had or after we can not use excessive mild depth in order to not harm the thing, as an example a gentle organic pattern or a murals,” explains Szuniewicz.
“Our methodology will develop potentialities in section measurements, together with rising programs similar to in infrared and X-ray imaging and quantum and matter-wave interferometry,” concludes Lapkiewicz.
Additional info:
Jerzy Szuniewicz et al, Noise-resistant section imaging with depth correlation, Science Advances (2023). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adh5396
Equipped by way of
College of Warsaw
Quotation:
Pictures hidden in noise published by way of a quantum-inspired phase-imaging approach (2023, December 27)
retrieved 28 December 2023
from
This report is topic to copyright. Except any honest dealing for the aim of personal find out about or analysis, no
phase could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is equipped for info functions best.



![Local weather startup develops era that would disrupt the concrete trade: ‘No person on the earth has [done this]’ Local weather startup develops era that would disrupt the concrete trade: ‘No person on the earth has [done this]’](https://www.thecooldown.com/wp-content/themes/tcd/assets/images/divider-icon-earth.svg)





