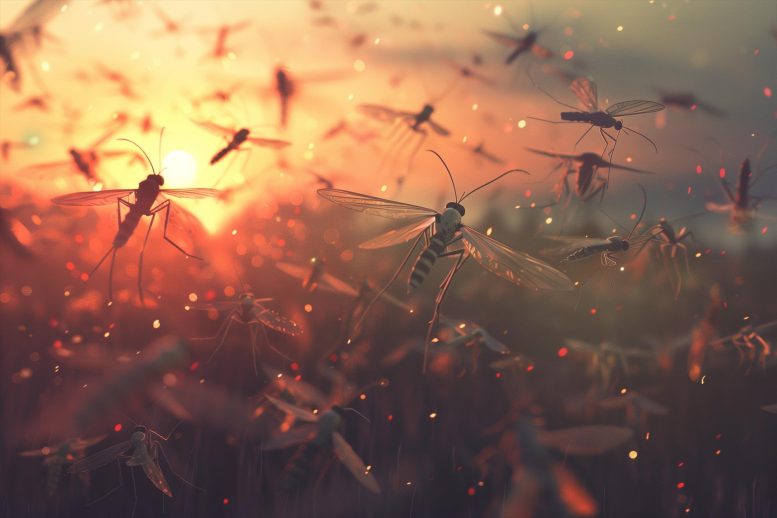
 Researchers at Johns Hopkins College came upon that an enzyme from fruit fly testes, prior to now regarded as interested in thyroid hormone law, performs a the most important position in controlling spermatogenesis. This discovering gives a brand new method to pest keep an eye on, probably affecting the fertility of disease-carrying and crop-damaging bugs. Credit score: SciTechDaily.comA Johns Hopkins learn about published that an enzyme in fruit fly testes may just obstruct insect replica via managing bromotyrosine accumulation, presenting a singular means for managing pests that threaten agriculture and unfold illnesses.A unique technique to curb nagging bugs has been flying beneath our radar—an enzyme from fruit fly testes.The compound may just keep an eye on insects that elevate illness and hurt vegetation via stunting their talent to procreate, in line with new analysis via Johns Hopkins College.“We’ve a toe within the door to keep an eye on fruit fly populations with this enzyme,” stated Steven Rokita, a professor of chemistry at Johns Hopkins who led the analysis. “It will be offering a great way to keep an eye on the fertility of a wide variety of organic and agricultural pests, beginning with mosquito populations.”The findings had been printed in Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.Unexpected Ubiquity and Serve as of the EnzymeRokita’s workforce stumbled upon the invention whilst finding out how iodide works within the thyroid gland. The crew prior to now demonstrated the ubiquity of the enzyme iodotyrosine deiodinase, which looked as if it would play an surprising position in key physiological processes of sure micro organism, invertebrates, and lots of different organisms.The brand new insights display suppressing it in fruit flies results in an overload of bromotyrosine, a herbal variation of the typical amino acid tyrosine. An excessive amount of of that compound hinders the insect’s sperm-making talent.Implications for Spermatogenesis in Fruit FliesScientists prior to now idea the enzyme used to be restricted to organisms that generate thyroxine, one of the crucial thyroid hormones produced via all vertebrates, together with mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. The enzyme’s process is to stay the frame’s iodine ranges at wholesome thresholds to provide thyroid hormones, which control metabolism, enlargement, and different purposes.“To our wonder, this enzyme is in an enormous collection of animals, some micro organism, fruit flies, sea anemones—a wide variety of organisms that don’t want iodide,” Rokita stated. “What’s it doing there if those organisms don’t want it?”Through eliminating and dissecting the testes of fruit flies, the crew tracked how the enzyme regulates bromotyrosine ranges. After they grew to become off the particular gene chargeable for the enzyme, they noticed bromotyrosine building up within the fruit fly testes.Doable Pest Keep watch over Packages“It seems that if the enzyme is missing, bromotyrosine accumulates in male fruit flies, and that overload significantly inhibits spermatogenesis,” Rokita stated. “All flies have a identical gene, this means that they may react to bromotyrosine similarly.”Doable pest keep an eye on methods may just come with the use of same old sugar-based mosquito traps combined with bromotyrosine or different components that prevent the enzyme from running, Rokita stated.Analysis Enlargement and Protection ConsiderationsThe scientists are checking out their findings on mosquitoes with the Johns Hopkins Malaria Analysis Institute.Enzymes are proteins that lend a hand accelerate quite a lot of organic processes that maintain our our bodies. Despite the fact that the enzyme in query is sort of a mammalian enzyme of identical serve as, people don’t specific it of their testes, and bromotyrosine is not going to have an effect on human fertility, Rokita stated.Unexplored Organic Processes and Their SignificanceThe findings display the worth of exploring organic processes scientists continuously forget about, Rokita stated. In particular, the findings display many residing issues depend at the strategy of halogenation, the place bromine or identical components are added to molecules just like the amino acid tyrosine to keep an eye on key physically purposes.This response is commonplace to many organisms, however its serve as had most effective been obviously outlined within the thyroid, Rokita stated.“That is opening our eyes to the concept halogenation of tyrosine may well be commonplace and essential both as it’s adverse or as it’s some roughly regulatory reaction that we had neglected all this time,” he stated.Reference: “Misregulation of bromotyrosine compromises fertility in male Drosophila” via Qi Su, Bing Xu, Xin Chen and Steven E. Rokita, 15 Would possibly 2024, Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.
Researchers at Johns Hopkins College came upon that an enzyme from fruit fly testes, prior to now regarded as interested in thyroid hormone law, performs a the most important position in controlling spermatogenesis. This discovering gives a brand new method to pest keep an eye on, probably affecting the fertility of disease-carrying and crop-damaging bugs. Credit score: SciTechDaily.comA Johns Hopkins learn about published that an enzyme in fruit fly testes may just obstruct insect replica via managing bromotyrosine accumulation, presenting a singular means for managing pests that threaten agriculture and unfold illnesses.A unique technique to curb nagging bugs has been flying beneath our radar—an enzyme from fruit fly testes.The compound may just keep an eye on insects that elevate illness and hurt vegetation via stunting their talent to procreate, in line with new analysis via Johns Hopkins College.“We’ve a toe within the door to keep an eye on fruit fly populations with this enzyme,” stated Steven Rokita, a professor of chemistry at Johns Hopkins who led the analysis. “It will be offering a great way to keep an eye on the fertility of a wide variety of organic and agricultural pests, beginning with mosquito populations.”The findings had been printed in Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.Unexpected Ubiquity and Serve as of the EnzymeRokita’s workforce stumbled upon the invention whilst finding out how iodide works within the thyroid gland. The crew prior to now demonstrated the ubiquity of the enzyme iodotyrosine deiodinase, which looked as if it would play an surprising position in key physiological processes of sure micro organism, invertebrates, and lots of different organisms.The brand new insights display suppressing it in fruit flies results in an overload of bromotyrosine, a herbal variation of the typical amino acid tyrosine. An excessive amount of of that compound hinders the insect’s sperm-making talent.Implications for Spermatogenesis in Fruit FliesScientists prior to now idea the enzyme used to be restricted to organisms that generate thyroxine, one of the crucial thyroid hormones produced via all vertebrates, together with mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. The enzyme’s process is to stay the frame’s iodine ranges at wholesome thresholds to provide thyroid hormones, which control metabolism, enlargement, and different purposes.“To our wonder, this enzyme is in an enormous collection of animals, some micro organism, fruit flies, sea anemones—a wide variety of organisms that don’t want iodide,” Rokita stated. “What’s it doing there if those organisms don’t want it?”Through eliminating and dissecting the testes of fruit flies, the crew tracked how the enzyme regulates bromotyrosine ranges. After they grew to become off the particular gene chargeable for the enzyme, they noticed bromotyrosine building up within the fruit fly testes.Doable Pest Keep watch over Packages“It seems that if the enzyme is missing, bromotyrosine accumulates in male fruit flies, and that overload significantly inhibits spermatogenesis,” Rokita stated. “All flies have a identical gene, this means that they may react to bromotyrosine similarly.”Doable pest keep an eye on methods may just come with the use of same old sugar-based mosquito traps combined with bromotyrosine or different components that prevent the enzyme from running, Rokita stated.Analysis Enlargement and Protection ConsiderationsThe scientists are checking out their findings on mosquitoes with the Johns Hopkins Malaria Analysis Institute.Enzymes are proteins that lend a hand accelerate quite a lot of organic processes that maintain our our bodies. Despite the fact that the enzyme in query is sort of a mammalian enzyme of identical serve as, people don’t specific it of their testes, and bromotyrosine is not going to have an effect on human fertility, Rokita stated.Unexplored Organic Processes and Their SignificanceThe findings display the worth of exploring organic processes scientists continuously forget about, Rokita stated. In particular, the findings display many residing issues depend at the strategy of halogenation, the place bromine or identical components are added to molecules just like the amino acid tyrosine to keep an eye on key physically purposes.This response is commonplace to many organisms, however its serve as had most effective been obviously outlined within the thyroid, Rokita stated.“That is opening our eyes to the concept halogenation of tyrosine may well be commonplace and essential both as it’s adverse or as it’s some roughly regulatory reaction that we had neglected all this time,” he stated.Reference: “Misregulation of bromotyrosine compromises fertility in male Drosophila” via Qi Su, Bing Xu, Xin Chen and Steven E. Rokita, 15 Would possibly 2024, Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2322501121Other authors are Qi Su, Bing Xu, and Xin Chen, all of Johns Hopkins.The analysis used to be supported via the Nationwide Institutes of Well being R01GM130937, R21AI119540, R01HD102474, and R35GM1270775, and the Howard Hughes Clinical Institute.
Progressive New Pest Keep watch over Software Found out via Johns Hopkins












:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/KFheadshot-9fe00fcb29c24a589a05cb7dea9ca150.jpeg)

