Earthquakes are one of the vital maximum devastating catastrophes our planet can unharness, but we’re nonetheless all-too-often taken through marvel when one moves.New analysis has printed main points of the lead-up to a tremor: a gradual and secure duration of displacements at a well-defined pressure level in Earth’s crust is a required cause for big seismic occasions.
“Our findings problem and refine standard fashions of rupture dynamics,” says physicist Jay Fineberg of the Hebrew College of Jerusalem.
“We display that gradual, aseismic processes are a prerequisite for seismic rupture, pushed through localized pressure and geometric constraints. This has profound implications for working out when and the way earthquakes start.” frameborder=”0″ permit=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>For a tremor to happen, weaknesses within the crust wish to construct right into a crack that may unexpectedly give manner. Many earlier research have proven that the technology of this crack is preceded through a chain of gradual actions that do not shimmy and shake the encircling rocks. Then again, the main points of those processes have trusted generalizations, usally in a two-dimensional house, which won’t expose transitions within the three-D global.
A group led through physicists Jay Fineberg and Shahar Gvirtzman of the Hebrew College of Jerusalem sought to know the function this gradual, aseismic pressure performs within the final unlock of earthquake job, the use of experimentation and theoretical modeling to discover how the method evolves.
One form of function this is vital for an earthquake to happen is a rupture which gives a point of interest for the elastic power presented through exterior loading. With out cracks, there’s no manner for pressure to magnify, which in flip signifies that surprising releases of power won’t happen.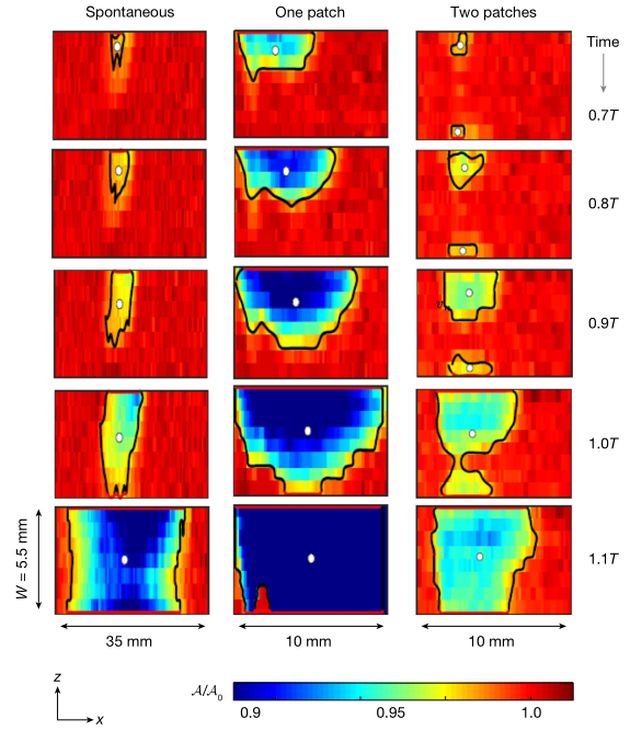 The evolution over the years of two-dimensional frictional nucleation patches within the group’s experiment. (Gvirtzman et al., Nature, 2025)The researchers studied cracks in a single, two, and 3 dimensions, in addition to the mechanics of small actions within the crust referred to as creep. Their findings confirmed that small, slow-moving, two-dimensional patches of frictional movement are the primary steps in opposition to a fracture. After a duration of gradual, secure creep at pressure issues, those patches progressively extend and escalate to the purpose of seismic rupture.
The evolution over the years of two-dimensional frictional nucleation patches within the group’s experiment. (Gvirtzman et al., Nature, 2025)The researchers studied cracks in a single, two, and 3 dimensions, in addition to the mechanics of small actions within the crust referred to as creep. Their findings confirmed that small, slow-moving, two-dimensional patches of frictional movement are the primary steps in opposition to a fracture. After a duration of gradual, secure creep at pressure issues, those patches progressively extend and escalate to the purpose of seismic rupture.
This extra element added to our working out of the evolution of an earthquake has vital implications. It is helping us higher perceive pressure and friction, basically; but it surely additionally supplies key data that might assist us are expecting seismic job and occasions one day.
“Excluding its relevance to fracture and subject matter energy, this new photograph of rupture nucleation dynamics is at once related to earthquake nucleation dynamics; gradual, aseismic rupture will have to all the time precede speedy seismic rupture,” the researchers write.
“The speculation would possibly supply a brand new framework for working out how and when earthquakes nucleate.”The analysis has been printed in Nature.
Quake Triggers A ways Much less Earth-Shattering Than We Idea, Learn about Unearths












