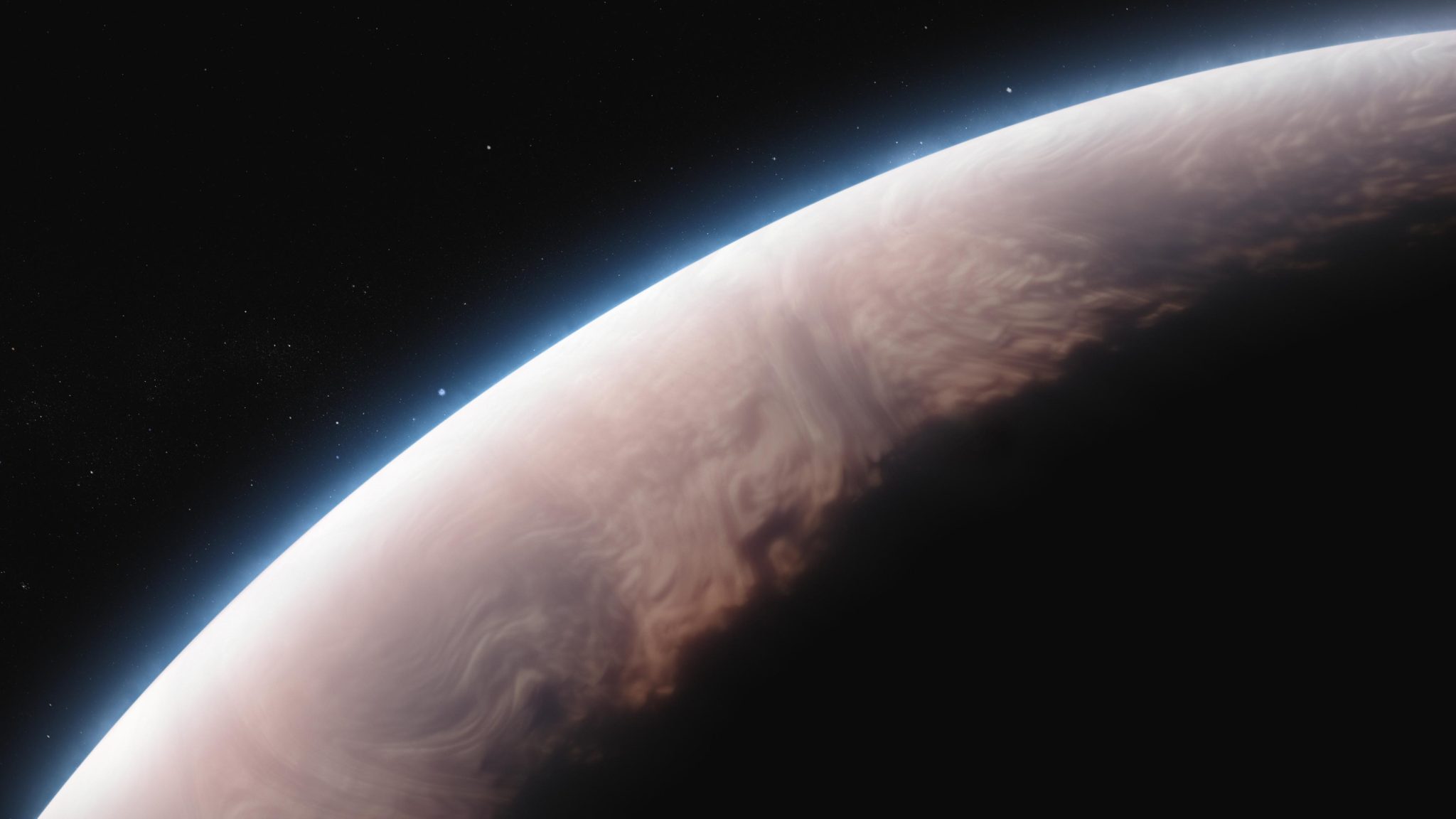
This artist’s idea displays what the exoplanet WASP-17 b may just appear to be. WASP-17 b, often known as Ditsö̀, is a scorching gasoline large that orbits its superstar at a distance of simply 0.051 AU (about 4.75 million miles, or one-eighth the gap between Mercury and the Solar), finishing one complete circuit in about 3.7 Earth-days. The machine lies inside the Milky Manner, about 1,300 light-years from Earth, within the constellation Scorpius. With a quantity greater than seven instances that of Jupiter and a mass lower than one-half of Jupiter, WASP-17 b is a particularly puffy planet. Its brief orbital duration, huge dimension, and thick, prolonged environment make it perfect for statement the usage of transmission spectroscopy, which comes to measuring the consequences of the planet’s environment at the starlight filtering thru it. Credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, Ralf Crawford (STScI)Flakes of silica “snow” fill the skies of puffy, searing-hot exoplanet WASP-17 b.Catching a glimpse of probably the most commonplace and acquainted minerals on Earth hardly ever deserves a headline. Quartz is located in seashore sands, development stones, geodes, and gem retail outlets all over the world. It’s melted to supply glass, subtle for silicon microchips, and utilized in watches to stay time.So what’s so particular about the newest discovery from NASA’s James Webb House Telescope? Believe quartz crystals that seem fairly actually out of skinny air. A mist of glittering grains so small that 10,000 may just match side-by-side throughout a human hair. Swarms of pointy, glassy nanoparticles racing in the course of the sweltering environment of a puffy gasoline large exoplanet at hundreds of miles in line with hour.Webb’s distinctive skill to measure the extraordinarily refined results of the ones crystals on starlight – and from a distance of greater than seven million billion miles, no much less – is offering important details about the composition of exoplanet atmospheres and new insights into their climate.
This artist’s idea displays what the exoplanet WASP-17 b may just appear to be. WASP-17 b, often known as Ditsö̀, is a scorching gasoline large that orbits its superstar at a distance of simply 0.051 AU (about 4.75 million miles, or one-eighth the gap between Mercury and the Solar), finishing one complete circuit in about 3.7 Earth-days. The machine lies inside the Milky Manner, about 1,300 light-years from Earth, within the constellation Scorpius. With a quantity greater than seven instances that of Jupiter and a mass lower than one-half of Jupiter, WASP-17 b is a particularly puffy planet. Its brief orbital duration, huge dimension, and thick, prolonged environment make it perfect for statement the usage of transmission spectroscopy, which comes to measuring the consequences of the planet’s environment at the starlight filtering thru it. Credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, Ralf Crawford (STScI)Flakes of silica “snow” fill the skies of puffy, searing-hot exoplanet WASP-17 b.Catching a glimpse of probably the most commonplace and acquainted minerals on Earth hardly ever deserves a headline. Quartz is located in seashore sands, development stones, geodes, and gem retail outlets all over the world. It’s melted to supply glass, subtle for silicon microchips, and utilized in watches to stay time.So what’s so particular about the newest discovery from NASA’s James Webb House Telescope? Believe quartz crystals that seem fairly actually out of skinny air. A mist of glittering grains so small that 10,000 may just match side-by-side throughout a human hair. Swarms of pointy, glassy nanoparticles racing in the course of the sweltering environment of a puffy gasoline large exoplanet at hundreds of miles in line with hour.Webb’s distinctive skill to measure the extraordinarily refined results of the ones crystals on starlight – and from a distance of greater than seven million billion miles, no much less – is offering important details about the composition of exoplanet atmospheres and new insights into their climate. A transmission spectrum of the new gasoline large exoplanet WASP-17 b captured by way of MIRI (Webb’s Mid-Infrared Device) on March 12-13, 2023, finds the primary proof for quartz (crystalline silica, SiO2) within the clouds of an exoplanet.
A transmission spectrum of the new gasoline large exoplanet WASP-17 b captured by way of MIRI (Webb’s Mid-Infrared Device) on March 12-13, 2023, finds the primary proof for quartz (crystalline silica, SiO2) within the clouds of an exoplanet.
The spectrum was once made by way of measuring the exchange in brightness of 28 wavelength-bands of mid-infrared gentle because the planet transited its superstar. Webb noticed the WASP-17 machine the usage of MIRI’s low-resolution spectrograph for almost 10 hours, accumulating greater than 1,275 measurements prior to, throughout, and after the transit.
For each and every wavelength, the volume of sunshine blocked by way of the planet’s environment (white circles) was once calculated by way of subtracting the volume that made it in the course of the environment from the volume at the start emitted by way of the superstar.
The cast red line is a best-fit fashion to the Webb (MIRI), Hubble, and Spitzer knowledge. (The Hubble and Spitzer knowledge quilt wavelengths from 0.34 to 4.5 microns and aren’t proven at the graph.) The spectrum displays a transparent characteristic round 8.6 microns, which astronomers assume is led to by way of silica debris soaking up one of the most starlight passing in the course of the environment.
The dashed yellow line displays what that a part of the transmission spectrum would appear to be if the clouds in WASP-17 b’s environment didn’t include SiO2.
This marks the primary time that SiO2 has been recognized in an exoplanet, and the primary time any explicit cloud species has been recognized in a transiting exoplanet.
Credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA, Ralf Crawford (STScI), David Grant (College of Bristol), Hannah R. Wakeford (College of Bristol), Nikole Lewis (Cornell College)Webb House Telescope Detects Tiny Quartz Crystals in Clouds of Scorching Fuel GiantResearchers the usage of NASA’s James Webb House Telescope have detected proof for quartz nanocrystals within the high-altitude clouds of WASP-17 b, a scorching Jupiter exoplanet 1,300 light-years from Earth. The detection, which was once uniquely conceivable with MIRI (Webb’s Mid-Infrared Device), marks the primary time that silica (SiO2) debris had been noticed in an exoplanet environment.“We have been delighted!” stated David Grant, a researcher on the College of Bristol in the United Kingdom and primary writer on a paper that was once printed as of late (October 16) within the Astrophysical Magazine Letters. “We knew from Hubble observations that there should be aerosols – tiny debris making up clouds or haze – in WASP-17 b’s environment, however we didn’t be expecting them to be manufactured from quartz.”Silicates (minerals wealthy in silicon and oxygen) make up the majority of Earth and the Moon in addition to different rocky gadgets in our sun machine, and are extraordinarily commonplace around the galaxy. However the silicate grains prior to now detected within the atmospheres of exoplanets and brown dwarfs seem to be manufactured from magnesium-rich silicates like olivine and pyroxene, now not quartz by myself – which is natural SiO2.The outcome from this workforce, which additionally contains researchers from NASA’s Ames Analysis Heart and NASA’s Goddard House Flight Heart, places a brand new spin on our figuring out of ways exoplanet clouds shape and evolve. “We absolutely anticipated to look magnesium silicates,” stated co-author Hannah Wakeford, additionally from the College of Bristol. “However what we’re seeing as a substitute are most probably the development blocks of the ones, the tiny ‘seed’ debris had to shape the bigger silicate grains we come across in cooler exoplanets and brown dwarfs.”Detecting Delicate VariationsWith a quantity greater than seven instances that of Jupiter and a mass lower than one-half of Jupiter, WASP-17 b is among the biggest and puffiest recognized exoplanets. This, together with its brief orbital duration of simply 3.7 Earth-days, makes the planet perfect for transmission spectroscopy: one way that comes to measuring the filtering and scattering results of a planet’s environment on starlight.Webb noticed the WASP-17 machine for almost 10 hours, accumulating greater than 1,275 brightness measurements of 5- to 12-micron mid-infrared gentle because the planet crossed its superstar. Via subtracting the brightness of person wavelengths of sunshine that reached the telescope when the planet was once in entrance of the superstar from the ones of the superstar by itself, the workforce was once in a position to calculate the volume of each and every wavelength blocked by way of the planet’s environment.What emerged was once an sudden “bump” at 8.6 microns, a characteristic that will now not be anticipated if the clouds have been manufactured from magnesium silicates or different conceivable high-temperature aerosols like aluminum oxide, however which makes best sense if they’re manufactured from quartz.Crystals, Clouds, and WindsWhile those crystals are most certainly equivalent in form to the sharp hexagonal prisms present in geodes and gem retail outlets on Earth, each and every one is most effective about 10 nanometers throughout – one-millionth of 1 centimeter.“Hubble knowledge in truth performed a key position in constraining the scale of those debris,” defined co-author Nikole Lewis of Cornell College, who leads the Webb Assured Time Remark (GTO) program designed to assist construct a 3-dimensional view of a scorching Jupiter environment. “We all know there may be silica from Webb’s MIRI knowledge by myself, however we wanted the visual and near-infrared observations from Hubble for context, to determine how huge the crystals are.”Not like mineral debris present in clouds on Earth, the quartz crystals detected within the clouds of WASP-17 b aren’t swept up from a rocky floor. As an alternative, they originate within the environment itself. “WASP-17 b is terribly scorching – round 2,700 levels Fahrenheit (1,500 levels Celsius) – and the power the place the quartz crystals shape excessive within the environment is most effective about one-thousandth of what we revel in on Earth’s floor,” defined Grant. “In those stipulations, forged crystals can shape without delay from gasoline, with out going thru a liquid segment first.”Figuring out what the clouds are manufactured from is a very powerful for figuring out the planet as an entire. Scorching Jupiters like WASP-17 b are made essentially of hydrogen and helium, with small quantities of different gases like water vapor (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2). “If we most effective believe the oxygen this is in those gases, and forget to incorporate the entire oxygen locked up in minerals like quartz (SiO2), we can considerably underestimate the full abundance,” defined Wakeford. “Those stunning silica crystals let us know in regards to the stock of various fabrics and the way all of them come in combination to form the surroundings of this planet.”Precisely how a lot quartz there may be, and the way pervasive the clouds are, is tricky to decide. “The clouds are most probably provide alongside the day/night time transition (the terminator), which is the area that our observations probe,” stated Grant. For the reason that the planet is tidally locked with a extremely popular day aspect and cooler night time aspect, it’s most probably that the clouds flow into across the planet, however vaporize once they achieve the warmer day aspect. “The winds might be transferring those tiny glassy debris round at hundreds of miles in line with hour.”WASP-17 b is certainly one of 3 planets centered by way of the JWST Telescope Scientist Crew’s Deep Reconnaissance of Exoplanet Atmospheres the usage of Multi-instrument Spectroscopy (DREAMS) investigations, that are designed to assemble a complete set of observations of 1 consultant from each and every key elegance of exoplanets: a scorching Jupiter, a heat Neptune, and a temperate rocky planet. The MIRI observations of scorching Jupiter WASP-17 b have been made as a part of GTO program 1353.Reference: “JWST-TST DREAMS: Quartz Clouds within the Surroundings of WASP-17b” by way of David Grant, Nikole Okay. Lewis, Hannah R. Wakeford, Natasha E. Batalha, Ana Glidden, Jayesh Goyal, Elijah Mullens, Ryan J. MacDonald, Erin M. Might, Sara Seager, Kevin B. Stevenson, Jeff A. Valenti, Channon Visscher, Lili Alderson, Natalie H. Allen, Caleb I. Cañas, Knicole Colón, Mark Clampin, Néstor Espinoza, Amélie Gressier, Jingcheng Huang, Zifan Lin, Douglas Lengthy, Dana R. Louie, Maria Peña-Guerrero, Sukrit Ranjan, Kristin S. Sotzen, Daniel Valentine, Jay Anderson, William O. Balmer, Andrea Bellini, Kielan Okay. W. Hoch, Jens Kammerer, Mattia Libralato, C. Matt Mountain, Marshall D. Perrin, Laurent Pueyo, Emily Rickman, Isabel Rebollido, Sangmo Tony Sohn, Roeland P. van der Marel and Laura L. Watkins, 16 October 2023, The Astrophysical Magazine Letters.
DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/acfc3bThe James Webb House Telescope is the arena’s premier area science observatory. Webb is fixing mysteries in our sun machine, having a look past to far away worlds round different stars, and probing the mysterious constructions and origins of our universe and our position in it. Webb is a global program led by way of NASA with its companions, ESA (Ecu House Company) and the Canadian House Company.
Quartz Showers: Silica Snow Envelops the Fiery Surroundings of Scorching Jupiter Exoplanet