The usage of viruses that infect micro organism to discover proteins sprouted by means of a infamous parasite, scientists have honed in on conceivable vaccine objectives for schistosomiasis, a overlooked tropical illness that lately impacts an estimated 600 million other people international, inflicting 280,000 deaths according to 12 months.
The Brazil-based crew harnessed a technique referred to as phage show, which used to be first described within the Eighties, to probe Schistosoma parasites that motive the illness, quicker and extra comprehensively than earlier, slow analysis efforts may just muster.
“You steadily pay attention the argument {that a} schistosomiasis vaccine is not possible,” says Sergio Verjovski-Almeida, a molecular biologist on the Butantan Institute in São Paulo, Brazil, and senior creator of the learn about.
However each and every pathogen has tell-tale markings that an individual’s immune gadget can discover ways to acknowledge, if primed with a vaccine. The trick is discovering which protein to focus on, to ignite a robust immune reaction.
Screening disease-causing pathogens for possible vaccine objectives is a expensive and time-consuming workout that in most cases simplest finds a small fraction of a pathogen’s unique proteins, expressed on its outer floor.
There may be additionally little monetary incentive for pharmaceutical firms to put money into vaccine construction for tropical sicknesses affecting the arena’s poorest other people if they may be able to’t recoup their prices – therefore why those sicknesses were overlooked for goodbye.
Schistosomiasis, sometimes called snail fever or water stomach, is led to by means of parasitic worms that infect snails in addition to people. It spreads in spaces with deficient hygiene and sanitation the place water has been infected with the bug’s eggs, which hatch to shape larvae that penetrate other people’s pores and skin.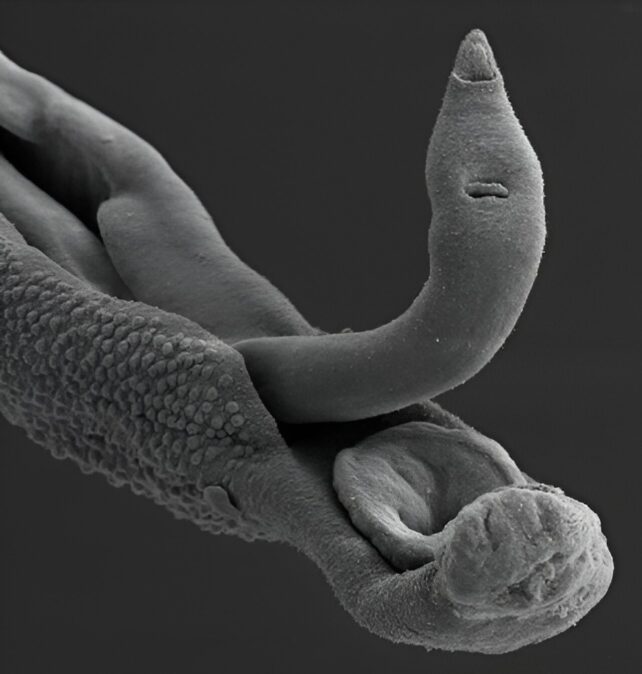 A feminine Schistosoma mansoni within a male bug. (Butantan Institute)As soon as in an individual’s bloodstream, the larvae turn out to be into grownup worms that resort within the veins of the intestines, inflicting illness two to 6 weeks after the preliminary an infection.
A feminine Schistosoma mansoni within a male bug. (Butantan Institute)As soon as in an individual’s bloodstream, the larvae turn out to be into grownup worms that resort within the veins of the intestines, inflicting illness two to 6 weeks after the preliminary an infection.
To reveal the beastly parasites, the Brazilian crew became to phage show, a method that has come to the fore lately, used to profile pathogens inflicting Chagas illness, Leptospirosis or even COVID-19.
“Phage show had by no means been deployed for this objective in analysis on parasitic sicknesses, which typically comes to preselection of a couple of objectives for checking out of candidate vaccines,” explains Butantan Institute molecular biologist Murilo Sena Amaral.
The process comes to the use of bacteriophages to check protein-protein interactions. On this case, the researchers assembled a military of bacteriophages engineered to hold snippets of DNA encoding all 11,641 recognized proteins of Schistosoma mansoni worms from each and every degree in their existence cycle.
The bacteriophages showing those Schistosoma proteins have been then incubated with blood plasma samples from 10 rhesus macaques inflamed with S. mansoni, certainly one of a number of Schistosoma bug species that motive other types of the illness.
If a bacteriophage met its fit in antibodies produced by means of the rhesus monkeys in keeping with their an infection, the ones phages may well be separated out and analyzed.
In overall, the researchers detected 99.6 % of the 119,747 DNA sequences encoding Schistosoma proteins within the monkey’s plasma – and located some have been in particular considerable, suggesting they’re key proteins riding the immune reaction to Schistosoma infections.
“Our discoveries have published a substantial amount of the immune reaction and spread out promising potentialities for the improvement of an efficient vaccine,” Verjovski-Almeida says.
For example, the researchers discovered that extracellular parasite proteins have been extra outstanding within the early levels of an infection, while intracellular proteins turned into extra pronounced in a while.
Take into account, then again, that this protein id is solely the primary milestone in a protracted procedure to expand a running vaccine. The proteins of pastime, or strips in their genetic codes, wish to be packaged up with an adjuvant, an factor used to spice up immune responses to vaccines, and examined to peer if it really works in components.
A pilot vaccination assay in mice checking out a number of probably the most promising protein applicants, pooled in combination however no longer packaged like a standard vaccine, did reach lowering the selection of worms the immunized animals carried.
So the early effects are encouraging, however the monitor report of schistosomiasis vaccines tells of the stark fact of vaccine construction.
So far, maximum protein-based vaccines for schistosomiasis have failed in scientific trials to elicit a robust immune reaction or give protection to in opposition to the illness.
Just one vaccine candidate has reached the overall section of scientific trial checking out, the place knowledge confirmed it used to be secure however no longer efficient. Hopes are pinned on every other vaccine no longer a ways in the back of in section II checking out, even though it will face the similar destiny.
The great factor is, after this learn about, researchers have quite a bit extra applicants to discover if one fails.The learn about has been revealed in npj Vaccines.
Radical Vaccine Technique May Lend a hand Quash Parasite Afflicting Hundreds of thousands