Abstract: Researchers have advanced tiny, wi-fi gadgets able to wrapping round person neurons, doubtlessly helping within the remedy of neurological problems like a couple of sclerosis.Those gadgets, constructed from a comfortable polymer, roll up snugly round mobile constructions when uncovered to gentle, permitting exact dimension and modulation of mobile job. As they’re battery-free and actuated noninvasively via gentle, 1000’s of them may well be deployed within the frame concurrently.This groundbreaking way may just repair neuron serve as via performing as artificial myelin for broken axons. Long term packages would possibly come with integrating circuits for neuron tracking and coverings. The analysis issues towards a singular path in developing minimally invasive neural interfaces.Key Details:Those cell-wearable gadgets are activated via gentle, making them battery-free.The gadgets wrap round neuronal constructions, providing artificial myelin advantages.Doable packages come with neuron recovery and noninvasive neural modulation.Supply: MITWearable gadgets like smartwatches and health trackers engage with portions of our our bodies to measure and be informed from interior processes, comparable to our center fee or sleep levels.Now, MIT researchers have advanced wearable gadgets that might be able to carry out identical purposes for person cells throughout the frame.Those battery-free, subcellular-sized gadgets, manufactured from a comfortable polymer, are designed to softly wrap round other portions of neurons, comparable to axons and dendrites, with out destructive the cells, upon wi-fi actuation with gentle. 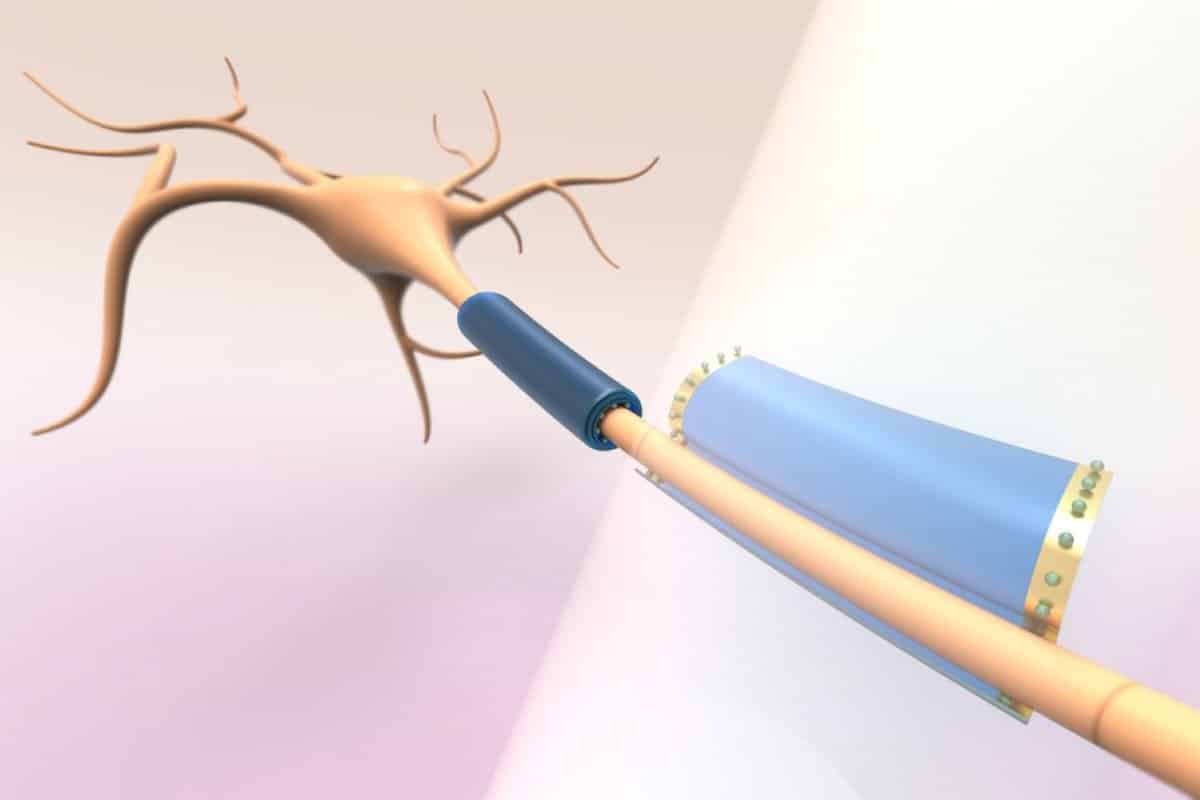 This symbol presentations the researchers’ subcellular-sized gadgets, which can be designed to softly wrap round other portions of neurons, comparable to axons and dendrites, with out destructive the cells. The gadgets may well be used to measure or modulate a neuron’s electric job. Credit score: Pablo Penso and Marta AiraghiBy snugly wrapping neuronal processes, they may well be used to measure or modulate a neuron’s electric and metabolic job at a subcellular degree.As a result of those gadgets are wi-fi and free-floating, the researchers envision that 1000’s of tiny gadgets may just at some point be injected after which actuated noninvasively the usage of gentle.Researchers would exactly keep watch over how the wearables gently wrap round cells, via manipulating the dose of sunshine shined from out of doors the frame, which might penetrate the tissue and actuate the gadgets.By way of enfolding axons that transmit electric impulses between neurons and to different portions of the frame, those wearables may just assist repair some neuronal degradation that happens in sicknesses like a couple of sclerosis. In the end, the gadgets may well be built-in with different fabrics to create tiny circuits that would measure and modulate person cells.“The idea that and platform era we introduce right here is sort of a founding stone that brings about immense probabilities for long run analysis,” says Deblina Sarkar, the AT&T Profession Construction Assistant Professor within the MIT Media Lab and Middle for Neurobiological Engineering, head of the Nano-Cybernetic Biotrek Lab, and the senior creator of a paper in this methodology.Sarkar is joined at the paper via lead creator Marta J. I. Airaghi Leccardi, a former MIT postdoc who’s now a Novartis Innovation Fellow; Benoît X. E. Desbiolles, an MIT postdoc; Anna Y. Haddad ’23, who used to be an MIT undergraduate researcher all the way through the paintings; and MIT graduate scholars Baju C. Pleasure and Chen Tune.The analysis seems nowadays in Nature Communications Chemistry.Snugly wrapping cellsBrain cells have advanced shapes, which makes it exceedingly tricky to create a bioelectronic implant that may tightly comply with neurons or neuronal processes. For example, axons are narrow, tail-like constructions that connect to the mobile frame of neurons, and their period and curvature range broadly.On the identical time, axons and different mobile elements are fragile, so any tool that interfaces with them will have to be comfortable sufficient to make just right touch with out harming them.To triumph over those demanding situations, the MIT researchers advanced thin-film gadgets from a comfortable polymer referred to as azobenzene, that don’t injury cells they enfold.Because of a subject material transformation, skinny sheets of azobenzene will roll when uncovered to gentle, enabling them to wrap round cells. Researchers can exactly keep watch over the path and diameter of the rolling via various the depth and polarization of the sunshine, in addition to the form of the gadgets.The skinny movies can shape tiny microtubes with diameters which might be not up to a micrometer. This permits them to softly, however snugly, wrap round extremely curved axons and dendrites.“It’s conceivable to very finely keep watch over the diameter of the rolling. You’ll be able to prevent if whilst you succeed in a selected size you need via tuning the sunshine power accordingly,” Sarkar explains.The researchers experimented with a number of fabrication tactics to discover a procedure that used to be scalable and wouldn’t require using a semiconductor blank room.Making microscopic wearablesThey start via depositing a drop of azobenzene onto a sacrificial layer composed of a water-soluble subject material. Then the researchers press a stamp onto the drop of polymer to mildew 1000’s of tiny gadgets on most sensible of the sacrificial layer. The stamping methodology allows them to create advanced constructions, from rectangles to flower shapes.A baking step guarantees all solvents are evaporated after which they use etching to scrape away any subject material that continues to be between person gadgets. In the end, they dissolve the sacrificial layer in water, leaving 1000’s of microscopic gadgets freely floating within the liquid.As soon as they have got an answer with free-floating gadgets, they wirelessly actuated the gadgets with gentle to urge the gadgets to roll. They discovered that free-floating constructions can take care of their shapes for days after illumination stops.The researchers carried out a chain of experiments to make sure all the manner is biocompatible.After perfecting using gentle to keep watch over rolling, they examined the gadgets on rat neurons and located they may tightly wrap round even extremely curved axons and dendrites with out inflicting injury.“To have intimate interfaces with those cells, the gadgets will have to be comfortable and ready to evolve to those advanced constructions. That’s the problem we solved on this paintings. We had been the primary to turn that azobenzene may just even wrap round dwelling cells,” she says.A few of the greatest demanding situations they confronted used to be growing a scalable fabrication procedure which may be carried out out of doors a blank room. In addition they iterated at the very best thickness for the gadgets, since making them too thick reasons cracking once they roll.As a result of azobenzene is an insulator, one direct utility is the usage of the gadgets as artificial myelin for axons which have been broken. Myelin is an insulating layer that wraps axons and permits electric impulses to trip successfully between neurons.In non-myelinating sicknesses like a couple of sclerosis, neurons lose some insulating myelin sheets. There is not any organic method of regenerating them. By way of performing as artificial myelin, the wearables would possibly assist repair neuronal serve as in MS sufferers.The researchers additionally demonstrated how the gadgets may also be mixed with optoelectrical fabrics that may stimulate cells.Additionally, atomically skinny fabrics may also be patterned on most sensible of the gadgets, which will nonetheless roll to shape microtubes with out breaking. This opens up alternatives for integrating sensors and circuits within the gadgets.As well as, as a result of they make this sort of tight reference to cells, one may just use little or no power to stimulate subcellular areas. This might allow a researcher or clinician to modulate electric job of neurons for treating mind sicknesses.“It’s thrilling to show this symbiosis of a man-made tool with a mobile at an unheard of answer. Now we have proven that this era is conceivable,” Sarkar says.Along with exploring those packages, the researchers need to check out functionalizing the tool surfaces with molecules that might allow them to focus on particular mobile varieties or subcellular areas.“This paintings is a thrilling step towards new symbiotic neural interfaces performing on the degree of the person axons and synapses.“When built-in with nanoscale 1- and 2D conductive nanomaterials, those light-responsive azobenzene sheets may just grow to be a flexible platform to sense and ship various kinds of indicators (i.e., electric, optical, thermal, and many others.) to neurons and different kinds of cells in a minimally or noninvasive approach.“Despite the fact that initial, the cytocompatibility information reported on this paintings could also be very promising for long run use in vivo,” says Flavia Vitale, affiliate professor of neurology, bioengineering, and bodily medication and rehabilitation on the College of Pennsylvania, who used to be no longer concerned with this paintings.Investment: The analysis used to be supported via the Swiss Nationwide Science Basis and the U.S. Nationwide Institutes of Well being Mind Initiative.About this neurotech analysis newsAuthor: Adam Zewe
This symbol presentations the researchers’ subcellular-sized gadgets, which can be designed to softly wrap round other portions of neurons, comparable to axons and dendrites, with out destructive the cells. The gadgets may well be used to measure or modulate a neuron’s electric job. Credit score: Pablo Penso and Marta AiraghiBy snugly wrapping neuronal processes, they may well be used to measure or modulate a neuron’s electric and metabolic job at a subcellular degree.As a result of those gadgets are wi-fi and free-floating, the researchers envision that 1000’s of tiny gadgets may just at some point be injected after which actuated noninvasively the usage of gentle.Researchers would exactly keep watch over how the wearables gently wrap round cells, via manipulating the dose of sunshine shined from out of doors the frame, which might penetrate the tissue and actuate the gadgets.By way of enfolding axons that transmit electric impulses between neurons and to different portions of the frame, those wearables may just assist repair some neuronal degradation that happens in sicknesses like a couple of sclerosis. In the end, the gadgets may well be built-in with different fabrics to create tiny circuits that would measure and modulate person cells.“The idea that and platform era we introduce right here is sort of a founding stone that brings about immense probabilities for long run analysis,” says Deblina Sarkar, the AT&T Profession Construction Assistant Professor within the MIT Media Lab and Middle for Neurobiological Engineering, head of the Nano-Cybernetic Biotrek Lab, and the senior creator of a paper in this methodology.Sarkar is joined at the paper via lead creator Marta J. I. Airaghi Leccardi, a former MIT postdoc who’s now a Novartis Innovation Fellow; Benoît X. E. Desbiolles, an MIT postdoc; Anna Y. Haddad ’23, who used to be an MIT undergraduate researcher all the way through the paintings; and MIT graduate scholars Baju C. Pleasure and Chen Tune.The analysis seems nowadays in Nature Communications Chemistry.Snugly wrapping cellsBrain cells have advanced shapes, which makes it exceedingly tricky to create a bioelectronic implant that may tightly comply with neurons or neuronal processes. For example, axons are narrow, tail-like constructions that connect to the mobile frame of neurons, and their period and curvature range broadly.On the identical time, axons and different mobile elements are fragile, so any tool that interfaces with them will have to be comfortable sufficient to make just right touch with out harming them.To triumph over those demanding situations, the MIT researchers advanced thin-film gadgets from a comfortable polymer referred to as azobenzene, that don’t injury cells they enfold.Because of a subject material transformation, skinny sheets of azobenzene will roll when uncovered to gentle, enabling them to wrap round cells. Researchers can exactly keep watch over the path and diameter of the rolling via various the depth and polarization of the sunshine, in addition to the form of the gadgets.The skinny movies can shape tiny microtubes with diameters which might be not up to a micrometer. This permits them to softly, however snugly, wrap round extremely curved axons and dendrites.“It’s conceivable to very finely keep watch over the diameter of the rolling. You’ll be able to prevent if whilst you succeed in a selected size you need via tuning the sunshine power accordingly,” Sarkar explains.The researchers experimented with a number of fabrication tactics to discover a procedure that used to be scalable and wouldn’t require using a semiconductor blank room.Making microscopic wearablesThey start via depositing a drop of azobenzene onto a sacrificial layer composed of a water-soluble subject material. Then the researchers press a stamp onto the drop of polymer to mildew 1000’s of tiny gadgets on most sensible of the sacrificial layer. The stamping methodology allows them to create advanced constructions, from rectangles to flower shapes.A baking step guarantees all solvents are evaporated after which they use etching to scrape away any subject material that continues to be between person gadgets. In the end, they dissolve the sacrificial layer in water, leaving 1000’s of microscopic gadgets freely floating within the liquid.As soon as they have got an answer with free-floating gadgets, they wirelessly actuated the gadgets with gentle to urge the gadgets to roll. They discovered that free-floating constructions can take care of their shapes for days after illumination stops.The researchers carried out a chain of experiments to make sure all the manner is biocompatible.After perfecting using gentle to keep watch over rolling, they examined the gadgets on rat neurons and located they may tightly wrap round even extremely curved axons and dendrites with out inflicting injury.“To have intimate interfaces with those cells, the gadgets will have to be comfortable and ready to evolve to those advanced constructions. That’s the problem we solved on this paintings. We had been the primary to turn that azobenzene may just even wrap round dwelling cells,” she says.A few of the greatest demanding situations they confronted used to be growing a scalable fabrication procedure which may be carried out out of doors a blank room. In addition they iterated at the very best thickness for the gadgets, since making them too thick reasons cracking once they roll.As a result of azobenzene is an insulator, one direct utility is the usage of the gadgets as artificial myelin for axons which have been broken. Myelin is an insulating layer that wraps axons and permits electric impulses to trip successfully between neurons.In non-myelinating sicknesses like a couple of sclerosis, neurons lose some insulating myelin sheets. There is not any organic method of regenerating them. By way of performing as artificial myelin, the wearables would possibly assist repair neuronal serve as in MS sufferers.The researchers additionally demonstrated how the gadgets may also be mixed with optoelectrical fabrics that may stimulate cells.Additionally, atomically skinny fabrics may also be patterned on most sensible of the gadgets, which will nonetheless roll to shape microtubes with out breaking. This opens up alternatives for integrating sensors and circuits within the gadgets.As well as, as a result of they make this sort of tight reference to cells, one may just use little or no power to stimulate subcellular areas. This might allow a researcher or clinician to modulate electric job of neurons for treating mind sicknesses.“It’s thrilling to show this symbiosis of a man-made tool with a mobile at an unheard of answer. Now we have proven that this era is conceivable,” Sarkar says.Along with exploring those packages, the researchers need to check out functionalizing the tool surfaces with molecules that might allow them to focus on particular mobile varieties or subcellular areas.“This paintings is a thrilling step towards new symbiotic neural interfaces performing on the degree of the person axons and synapses.“When built-in with nanoscale 1- and 2D conductive nanomaterials, those light-responsive azobenzene sheets may just grow to be a flexible platform to sense and ship various kinds of indicators (i.e., electric, optical, thermal, and many others.) to neurons and different kinds of cells in a minimally or noninvasive approach.“Despite the fact that initial, the cytocompatibility information reported on this paintings could also be very promising for long run use in vivo,” says Flavia Vitale, affiliate professor of neurology, bioengineering, and bodily medication and rehabilitation on the College of Pennsylvania, who used to be no longer concerned with this paintings.Investment: The analysis used to be supported via the Swiss Nationwide Science Basis and the U.S. Nationwide Institutes of Well being Mind Initiative.About this neurotech analysis newsAuthor: Adam Zewe
Supply: MIT
Touch: Adam Zewe – MIT
Symbol: The picture is credited to Pablo Penso and Marta AiraghiOriginal Analysis: Open get right of entry to.
“Mild-induced rolling of azobenzene polymer skinny movies for wrapping subcellular neuronal constructions” via Deblina Sarkar et al. Nature Communications ChemistryAbstractLight-induced rolling of azobenzene polymer skinny movies for wrapping subcellular neuronal structuresNeurons are very important cells composing our worried gadget and orchestrating our frame, ideas, and feelings. Not too long ago, analysis efforts had been occupied with learning no longer handiest their collective construction and purposes but additionally the single-cell houses as a person advanced gadget.Nanoscale era has the prospective to resolve mysteries in neuroscience and supply fortify to the neuron via measuring and influencing a number of facets of the mobile.As wearable gadgets engage with other portions of our frame, lets envision one thousand instances smaller interface to evolve on and round subcellular areas of the neurons for unheard of touch, probing, and keep watch over.Alternatively, a big problem is to expand an interface that may morph to the extraordinary curvatures of subcellular constructions.Right here, we cope with this problem with the advance of a platform that conforms even to small neuronal processes.To succeed in this, we produced a wi-fi platform manufactured from an azobenzene polymer that undergoes on-demand light-induced folding with sub-micrometer radius of curvature.We display that those platforms may also be fabricated with an adjustable shape issue, micro-injected onto neuronal cultures, and will delicately wrap quite a lot of morphologies of neuronal processes in vitro, towards acquiring seamless biointerfaces with an larger coupling with the mobile membrane. Our in vitro testings didn’t display any adversarial results of the platforms involved with the neurons.Moreover, for long run capability, nanoparticles or optoelectronic fabrics may well be combined with the azobenzene polymer, and 2D fabrics at the platform floor may well be safely folded to the top curvatures with out mechanical failure, as consistent with our calculations.In the end, this era may just lay the root for long run integration of wirelessly actuated fabrics inside of or on its platform for neuromodulation, recording, and neuroprotection on the subcellular degree.
Researchers Create Cellular-Degree Wearable Units to Repair Neuron Serve as – Neuroscience Information














