![]()
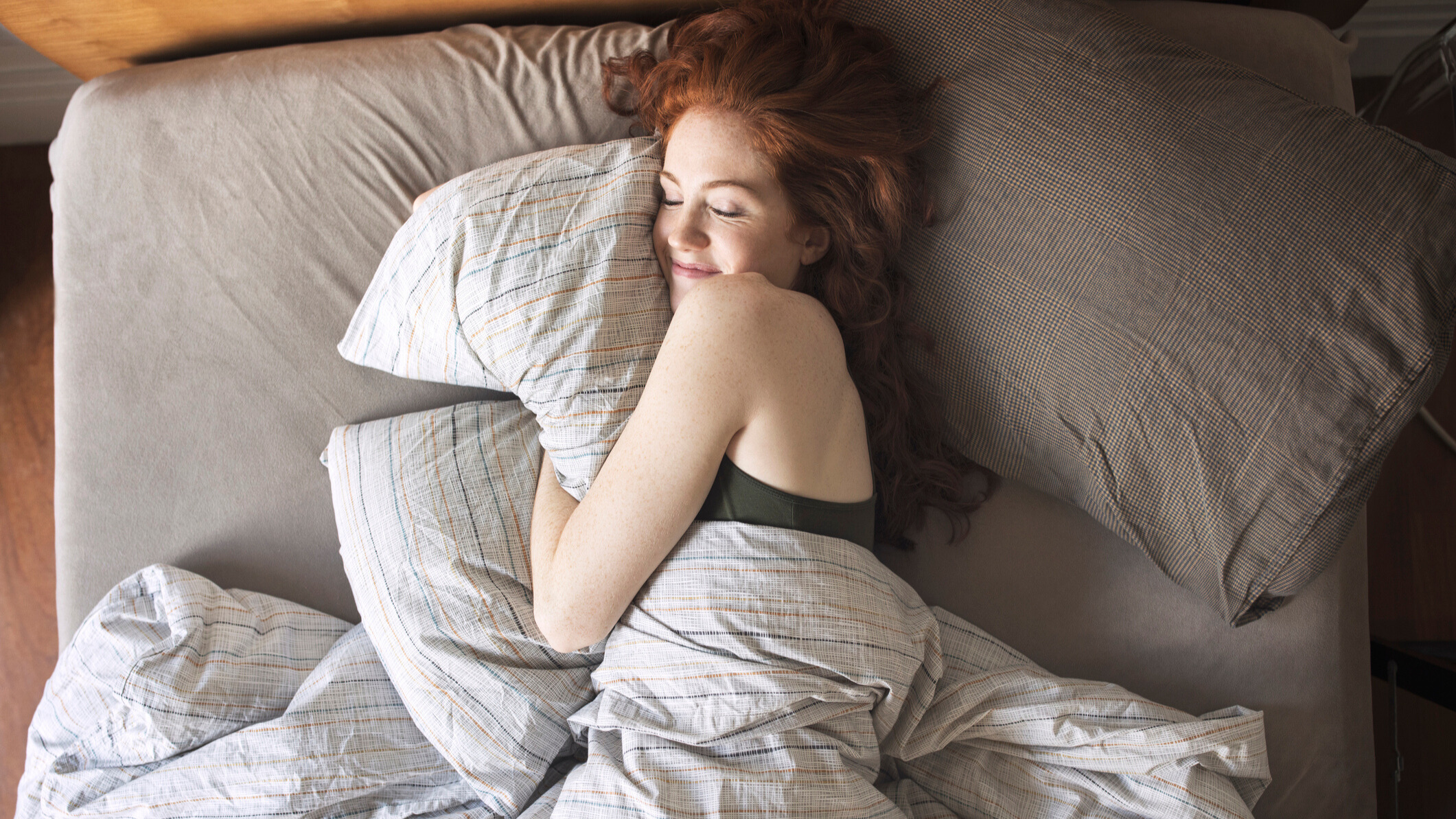
![]() A find out about involving 9 and 10-year-olds found out that youngsters who eat caffeinated soda beverages day-to-day are two times as more likely to start sipping alcohol inside the subsequent 365 days when compared to those that eat those beverages much less incessantly. Moreover, those youngsters looked to be extra impulsive and had poorer running reminiscence. The paper used to be revealed in Substance Use & Misuse.Caffeinated soda beverages are carbonated drinks that comprise caffeine, a stimulant that may building up alertness and effort ranges. Those drinks come with common choices like Mountain Dew, Jolt, Coke, Pepsi, Dr. Pepper, and Barq’s root beer, amongst others. But even so caffeine, those sodas continuously comprise prime ranges of sugar or synthetic sweeteners, together with quite a few flavors and components, making them a favourite international for a fast power spice up or a refreshing drink.On the other hand, research have advised that the intake of caffeinated soda beverages could also be connected to substance misuse. Incessantly consuming those sodas, particularly in huge quantities, has been related to an higher probability of experimenting with different elements that supply identical stimulating results. Whilst maximum research have fascinated with youth, the hyperlink between caffeinated soda intake and substance use in preadolescent youngsters has been much less explored.Find out about writer Mina Kwon of Seoul Nationwide College and her colleagues sought after to discover the hyperlinks between the consumption of caffeinated soda drinks and substance use chance elements in preadolescent youngsters. They hypothesized that day-to-day caffeinated soda consumption would expect alcohol sipping a 12 months later. Alcohol sipping in youngsters refers back to the apply of permitting youngsters to style or eat small quantities of alcoholic drinks. Alcohol sipping happens in circle of relatives or more than a few social settings the place it’s continuously observed as innocuous. On the other hand, it may possibly building up the danger of creating alcohol-related issues later in lifestyles.The researchers analyzed knowledge from the Adolescent Mind Cognitive Building find out about (ABCD find out about), an intensive, long-term undertaking geared toward working out how mind construction impacts cognitive, social, and emotional functioning in youth. They fascinated with knowledge from 11,878 youngsters elderly 9-10, recruited from 21 other U.S. places by the use of their faculties. For his or her research, they used knowledge from 2,092 youngsters who supplied complete knowledge on their caffeinated soda intake and met different standards.Individuals reported their weekly consumption of caffeinated sodas and underwent tests for running reminiscence, impulsivity, and praise processing thru more than a few exams. Youngsters accustomed to alcohol additionally stuffed out a questionnaire about their stories with alcohol sipping. The researchers selected to concentrate on running reminiscence, impulsivity, and praise processing as a result of disruptions in those spaces are thought to be chance elements for creating substance use problems.Effects confirmed that youngsters from households with a historical past of drug use and decrease ranges of schooling have been much more likely to eat caffeinated sodas. Those drinks have been additionally extra common amongst boys, Black youngsters, the ones with upper frame mass indexes, low parental tracking, decrease circle of relatives earning, inadequate sleep, and extra externalizing behaviors. Externalizing behaviors, which come with competitive and delinquent movements, are continuously an indication of a person’s fight to keep an eye on feelings or impulses.Youngsters who ate up huge quantities of caffeinated beverages have been extra impulsive and had decrease ratings on running reminiscence exams. Praise processing, then again, didn’t display a vital correlation with caffeinated soda intake. Significantly, the consumption of those drinks used to be a predictor of alcohol sipping 365 days later, with day-to-day shoppers being two times as more likely to get started sipping alcohol when compared to those that drank much less or none in any respect.“Our effects published the possible dangers of caffeinated soda intake in youngsters by way of investigating the associations between caffeinated soda intake and chance elements for SUDs [substance use disorders] and inspecting the facility of caffeinated soda intake to expect long term alcohol sipping, the usage of the massive ABCD dataset,” the find out about authors concluded.“The existing effects strongly recommend that caffeinated soda consuming in youngsters may be related to altered neurobehavioral serve as and will expect alcohol sipping after 365 days. Our find out about additional suggests a robust want to increase evidence-based suggestions for caffeinated soda intake in minors, as there is not any consensus on a secure dose of caffeinated soda in youngsters, and a few youngsters are at upper chance of inauspicious occasions from common caffeinated soda consumption.”The find out about sheds mild at the hyperlinks between caffeinated soda consumption and elements related to substance use chance later in lifestyles. On the other hand, it must be famous that the design of the find out about does now not permit any cause-and-effect conclusions to be drawn from the consequences.The paper, “Caffeinated Soda Consumption in Youngsters Is Related to Neurobehavioral Possibility Elements for Substance Misuse,” used to be authored by way of Mina Kwon, Hyeonjin Kim, Jaeyeong Yang, Yoseph Lee, Jihyun Okay. Hur, Tae-Ho Lee, James M. Bjork, and Woo-Younger Ahn.
A find out about involving 9 and 10-year-olds found out that youngsters who eat caffeinated soda beverages day-to-day are two times as more likely to start sipping alcohol inside the subsequent 365 days when compared to those that eat those beverages much less incessantly. Moreover, those youngsters looked to be extra impulsive and had poorer running reminiscence. The paper used to be revealed in Substance Use & Misuse.Caffeinated soda beverages are carbonated drinks that comprise caffeine, a stimulant that may building up alertness and effort ranges. Those drinks come with common choices like Mountain Dew, Jolt, Coke, Pepsi, Dr. Pepper, and Barq’s root beer, amongst others. But even so caffeine, those sodas continuously comprise prime ranges of sugar or synthetic sweeteners, together with quite a few flavors and components, making them a favourite international for a fast power spice up or a refreshing drink.On the other hand, research have advised that the intake of caffeinated soda beverages could also be connected to substance misuse. Incessantly consuming those sodas, particularly in huge quantities, has been related to an higher probability of experimenting with different elements that supply identical stimulating results. Whilst maximum research have fascinated with youth, the hyperlink between caffeinated soda intake and substance use in preadolescent youngsters has been much less explored.Find out about writer Mina Kwon of Seoul Nationwide College and her colleagues sought after to discover the hyperlinks between the consumption of caffeinated soda drinks and substance use chance elements in preadolescent youngsters. They hypothesized that day-to-day caffeinated soda consumption would expect alcohol sipping a 12 months later. Alcohol sipping in youngsters refers back to the apply of permitting youngsters to style or eat small quantities of alcoholic drinks. Alcohol sipping happens in circle of relatives or more than a few social settings the place it’s continuously observed as innocuous. On the other hand, it may possibly building up the danger of creating alcohol-related issues later in lifestyles.The researchers analyzed knowledge from the Adolescent Mind Cognitive Building find out about (ABCD find out about), an intensive, long-term undertaking geared toward working out how mind construction impacts cognitive, social, and emotional functioning in youth. They fascinated with knowledge from 11,878 youngsters elderly 9-10, recruited from 21 other U.S. places by the use of their faculties. For his or her research, they used knowledge from 2,092 youngsters who supplied complete knowledge on their caffeinated soda intake and met different standards.Individuals reported their weekly consumption of caffeinated sodas and underwent tests for running reminiscence, impulsivity, and praise processing thru more than a few exams. Youngsters accustomed to alcohol additionally stuffed out a questionnaire about their stories with alcohol sipping. The researchers selected to concentrate on running reminiscence, impulsivity, and praise processing as a result of disruptions in those spaces are thought to be chance elements for creating substance use problems.Effects confirmed that youngsters from households with a historical past of drug use and decrease ranges of schooling have been much more likely to eat caffeinated sodas. Those drinks have been additionally extra common amongst boys, Black youngsters, the ones with upper frame mass indexes, low parental tracking, decrease circle of relatives earning, inadequate sleep, and extra externalizing behaviors. Externalizing behaviors, which come with competitive and delinquent movements, are continuously an indication of a person’s fight to keep an eye on feelings or impulses.Youngsters who ate up huge quantities of caffeinated beverages have been extra impulsive and had decrease ratings on running reminiscence exams. Praise processing, then again, didn’t display a vital correlation with caffeinated soda intake. Significantly, the consumption of those drinks used to be a predictor of alcohol sipping 365 days later, with day-to-day shoppers being two times as more likely to get started sipping alcohol when compared to those that drank much less or none in any respect.“Our effects published the possible dangers of caffeinated soda intake in youngsters by way of investigating the associations between caffeinated soda intake and chance elements for SUDs [substance use disorders] and inspecting the facility of caffeinated soda intake to expect long term alcohol sipping, the usage of the massive ABCD dataset,” the find out about authors concluded.“The existing effects strongly recommend that caffeinated soda consuming in youngsters may be related to altered neurobehavioral serve as and will expect alcohol sipping after 365 days. Our find out about additional suggests a robust want to increase evidence-based suggestions for caffeinated soda intake in minors, as there is not any consensus on a secure dose of caffeinated soda in youngsters, and a few youngsters are at upper chance of inauspicious occasions from common caffeinated soda consumption.”The find out about sheds mild at the hyperlinks between caffeinated soda consumption and elements related to substance use chance later in lifestyles. On the other hand, it must be famous that the design of the find out about does now not permit any cause-and-effect conclusions to be drawn from the consequences.The paper, “Caffeinated Soda Consumption in Youngsters Is Related to Neurobehavioral Possibility Elements for Substance Misuse,” used to be authored by way of Mina Kwon, Hyeonjin Kim, Jaeyeong Yang, Yoseph Lee, Jihyun Okay. Hur, Tae-Ho Lee, James M. Bjork, and Woo-Younger Ahn.
Researchers discover hyperlink between caffeinated soda intake and alcohol sipping in youngsters