The East Antarctic Ice Sheet, a limiteless expanse spanning over 10 million sq. kilometers, has lengthy hid a panorama thousands and thousands of years outdated. Because of satellite tv for pc generation and groundbreaking geophysical analysis, scientists have pierced during the icy veil to discover a relic from an generation when Antarctica teemed with river networks and luxurious crops. This discovery no longer simplest provides a glimpse into Earth’s prehistoric previous but in addition supplies vital insights into how the continent might reply to fashionable local weather demanding situations.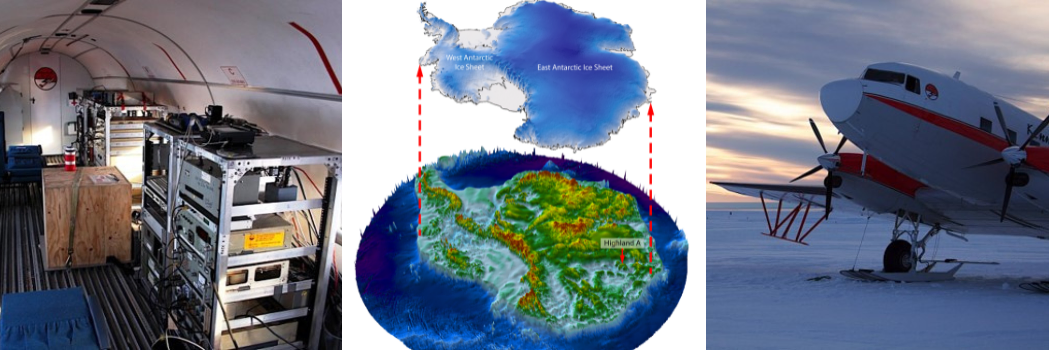 The analysis crew have mapped out hidden mountain levels, canyon techniques and lakes underneath the ice in Antarctica. (CREDIT: Durham College) A Hidden Panorama RevealedResearchers, led through Stewart Jamieson of Durham College, used complicated satellite tv for pc imaging to discover an historical terrain buried underneath just about two kilometers of ice. This fossilized panorama, kind of the scale of Wales, used to be printed during the leading edge use of RADARSAT, a Canadian satellite tv for pc constellation able to detecting delicate permutations within the ice floor that trace on the contours under.Jamieson describes the method as “like uncovering a time pill.” The terrain’s survival below such immense ice suggests its outstanding antiquity. Carved through rivers earlier than the ice sheet grew, this panorama most likely dates again over 34 million years. It supplies a snapshot of an Antarctica that after thrived as a part of the supercontinent Gondwana, the place dinosaurs roamed a verdant expanse earlier than the continent succumbed to glaciation round 20 million years in the past.
The analysis crew have mapped out hidden mountain levels, canyon techniques and lakes underneath the ice in Antarctica. (CREDIT: Durham College) A Hidden Panorama RevealedResearchers, led through Stewart Jamieson of Durham College, used complicated satellite tv for pc imaging to discover an historical terrain buried underneath just about two kilometers of ice. This fossilized panorama, kind of the scale of Wales, used to be printed during the leading edge use of RADARSAT, a Canadian satellite tv for pc constellation able to detecting delicate permutations within the ice floor that trace on the contours under.Jamieson describes the method as “like uncovering a time pill.” The terrain’s survival below such immense ice suggests its outstanding antiquity. Carved through rivers earlier than the ice sheet grew, this panorama most likely dates again over 34 million years. It supplies a snapshot of an Antarctica that after thrived as a part of the supercontinent Gondwana, the place dinosaurs roamed a verdant expanse earlier than the continent succumbed to glaciation round 20 million years in the past. The Canadian satellite tv for pc constellation RADARSAT-2, which is able to discern delicate irregularities within the ice floor that betray the contours under, has confirmed instrumental on this enterprise. (CREDIT: Inventive Commons) “We’ve had an established passion in, successfully, the form of the land underneath the ice sheet,” Jamieson stated. “The implication is this should be an overly outdated panorama carved through rivers earlier than the ice sheet itself grew.”From Gondwana to GlaciationThe East Antarctic Ice Sheet (EAIS) started forming right through the Eocene-Oligocene transition round 34 million years in the past, as international temperatures plummeted and CO2 ranges dropped under a vital threshold. Top-altitude areas such because the Gamburtsev Subglacial Mountains and Transantarctic Mountains changed into nuclei for the rising ice lots. Over thousands and thousands of years, those glaciers expanded, in the end coalescing into the huge ice sheet that persists nowadays.The EAIS has passed through important fluctuations right through its historical past. All the way through the Miocene, roughly 17 to fourteen million years in the past, the ice sheet expanded and retreated in line with climatic shifts. Proof from marine sediments suggests classes of retreat right through hotter periods, such because the mid-Pliocene heat length and the interglacial classes of the Pleistocene. Those fluctuations left lasting imprints at the subglacial panorama, shaping options that are actually detectable via trendy geophysical surveys.Satellite tv for pc Generation and Geophysical SurveysThe RADARSAT constellation has been instrumental in uncovering those hidden options. Through examining adjustments in ice floor slope, researchers can infer the large-scale subglacial topography.
The Canadian satellite tv for pc constellation RADARSAT-2, which is able to discern delicate irregularities within the ice floor that betray the contours under, has confirmed instrumental on this enterprise. (CREDIT: Inventive Commons) “We’ve had an established passion in, successfully, the form of the land underneath the ice sheet,” Jamieson stated. “The implication is this should be an overly outdated panorama carved through rivers earlier than the ice sheet itself grew.”From Gondwana to GlaciationThe East Antarctic Ice Sheet (EAIS) started forming right through the Eocene-Oligocene transition round 34 million years in the past, as international temperatures plummeted and CO2 ranges dropped under a vital threshold. Top-altitude areas such because the Gamburtsev Subglacial Mountains and Transantarctic Mountains changed into nuclei for the rising ice lots. Over thousands and thousands of years, those glaciers expanded, in the end coalescing into the huge ice sheet that persists nowadays.The EAIS has passed through important fluctuations right through its historical past. All the way through the Miocene, roughly 17 to fourteen million years in the past, the ice sheet expanded and retreated in line with climatic shifts. Proof from marine sediments suggests classes of retreat right through hotter periods, such because the mid-Pliocene heat length and the interglacial classes of the Pleistocene. Those fluctuations left lasting imprints at the subglacial panorama, shaping options that are actually detectable via trendy geophysical surveys.Satellite tv for pc Generation and Geophysical SurveysThe RADARSAT constellation has been instrumental in uncovering those hidden options. Through examining adjustments in ice floor slope, researchers can infer the large-scale subglacial topography.  Inferred evolution of the traditional panorama. a Unique fluvial land floor; b Gondwana break-up turns on pre-existing tectonic constructions, inflicting drainage re-organisation. (CREDIT: Nature Communications) Jamieson’s crew complemented this knowledge with radio-echo sounding (RES) surveys carried out as a part of the World Collaborative Exploration of the Cryosphere via Airborne Profiling (ICECAP) challenge.The usage of RES, researchers quantified the panorama traits and recognized historical topographic options inconsistent with present ice glide patterns. The findings counsel a panorama formed through fluvial erosion lengthy earlier than the ice sheet’s formation.The crew additionally implemented flexural modeling to guage whether or not highland blocks underneath the ice had been as soon as a part of a unmarried land floor, therefore incised and uplifted through selective erosion. Those analyses divulge a extra detailed image of the way the EAIS advanced and the position of historical river networks in shaping its underlying terrain.Implications for Local weather ScienceUnderstanding the historical past of the EAIS has profound implications for predicting its long run conduct in a warming international. The ice sheet’s sensitivity to climatic and oceanic adjustments makes it a vital indicator of the way emerging temperatures would possibly reshape the polar areas.
Inferred evolution of the traditional panorama. a Unique fluvial land floor; b Gondwana break-up turns on pre-existing tectonic constructions, inflicting drainage re-organisation. (CREDIT: Nature Communications) Jamieson’s crew complemented this knowledge with radio-echo sounding (RES) surveys carried out as a part of the World Collaborative Exploration of the Cryosphere via Airborne Profiling (ICECAP) challenge.The usage of RES, researchers quantified the panorama traits and recognized historical topographic options inconsistent with present ice glide patterns. The findings counsel a panorama formed through fluvial erosion lengthy earlier than the ice sheet’s formation.The crew additionally implemented flexural modeling to guage whether or not highland blocks underneath the ice had been as soon as a part of a unmarried land floor, therefore incised and uplifted through selective erosion. Those analyses divulge a extra detailed image of the way the EAIS advanced and the position of historical river networks in shaping its underlying terrain.Implications for Local weather ScienceUnderstanding the historical past of the EAIS has profound implications for predicting its long run conduct in a warming international. The ice sheet’s sensitivity to climatic and oceanic adjustments makes it a vital indicator of the way emerging temperatures would possibly reshape the polar areas. Floor elevation of the Antarctic Ice Sheet from the Reference Elevation Type of Antarctica68. The black line marks the present-day grounding line74; faded spaces are floating ice cabinets. (CREDIT: Nature Communications) Jamieson’s analysis, revealed within the magazine Nature Communications, underscores the significance of learning subglacial landscapes to reconstruct the ice sheet’s previous dynamics. “Working out how this large sheet would possibly reply to human-driven local weather exchange is a urgent worry,” he emphasised. The EAIS, specifically in low-lying marine-based sectors just like the Aurora and Wilkes Subglacial Basins, is at risk of retreat right through heat periods. Such adjustments may just give a contribution considerably to international sea-level upward thrust.The crew’s findings spotlight the desire for endured tracking of the EAIS and its reaction to present warming tendencies. Through linking historical panorama options to previous local weather prerequisites, researchers can refine fashions predicting the ice sheet’s long run conduct. This information is essential for informing international methods to mitigate the consequences of local weather exchange.Bridging Eras: Courses from the PastThe discovery of Antarctica’s historical river networks is a testomony to the ability of recent generation to remove darkness from Earth’s far-off previous. Through piecing in combination clues from subglacial topography and geological data, scientists are bridging thousands and thousands of years to attach prehistoric landscapes with nowadays’s local weather dynamics.
Floor elevation of the Antarctic Ice Sheet from the Reference Elevation Type of Antarctica68. The black line marks the present-day grounding line74; faded spaces are floating ice cabinets. (CREDIT: Nature Communications) Jamieson’s analysis, revealed within the magazine Nature Communications, underscores the significance of learning subglacial landscapes to reconstruct the ice sheet’s previous dynamics. “Working out how this large sheet would possibly reply to human-driven local weather exchange is a urgent worry,” he emphasised. The EAIS, specifically in low-lying marine-based sectors just like the Aurora and Wilkes Subglacial Basins, is at risk of retreat right through heat periods. Such adjustments may just give a contribution considerably to international sea-level upward thrust.The crew’s findings spotlight the desire for endured tracking of the EAIS and its reaction to present warming tendencies. Through linking historical panorama options to previous local weather prerequisites, researchers can refine fashions predicting the ice sheet’s long run conduct. This information is essential for informing international methods to mitigate the consequences of local weather exchange.Bridging Eras: Courses from the PastThe discovery of Antarctica’s historical river networks is a testomony to the ability of recent generation to remove darkness from Earth’s far-off previous. Through piecing in combination clues from subglacial topography and geological data, scientists are bridging thousands and thousands of years to attach prehistoric landscapes with nowadays’s local weather dynamics. Traits of the subglacial highlands and troughs of ‘Highland A’. (CREDIT: Nature Communications) The insights won from this analysis prolong past educational interest. They underscore the interconnectedness of Earth’s previous, gift, and long run. The geological imprints of historical Antarctica be offering precious courses for figuring out present environmental adjustments and forecasting the worldwide have an effect on of human-driven local weather exchange.As humanity grapples with the demanding situations of a warming international, the data embedded in Antarctica’s icy depths will play a a very powerful position in guiding efforts to maintain the planet’s subtle ecosystems. This discovery is a poignant reminder of Earth’s dynamism and the transformative processes that experience formed it over millennia. Through learning the buried landscapes of Antarctica, researchers are setting up a clearer image of our planet’s climatic long run and the pathways had to adapt to a impulsively converting setting.
Traits of the subglacial highlands and troughs of ‘Highland A’. (CREDIT: Nature Communications) The insights won from this analysis prolong past educational interest. They underscore the interconnectedness of Earth’s previous, gift, and long run. The geological imprints of historical Antarctica be offering precious courses for figuring out present environmental adjustments and forecasting the worldwide have an effect on of human-driven local weather exchange.As humanity grapples with the demanding situations of a warming international, the data embedded in Antarctica’s icy depths will play a a very powerful position in guiding efforts to maintain the planet’s subtle ecosystems. This discovery is a poignant reminder of Earth’s dynamism and the transformative processes that experience formed it over millennia. Through learning the buried landscapes of Antarctica, researchers are setting up a clearer image of our planet’s climatic long run and the pathways had to adapt to a impulsively converting setting.
Researchers discover prehistoric panorama buried underneath Antarctica













:focal(0x0:2400x1600)/static.texastribune.org/media/files/33969d744520660b68279346baf0bfbd/0416%20Solarcycle%20EH%20TT%2027.jpg)
