 Researchers at UNSW Sydney have found out novel mechanisms of intercourse chromosome dosage reimbursement in platypus and rooster, difficult earlier assumptions and offering new insights into genetic law throughout species.A brand new find out about finds that platypuses and chickens steadiness protein ranges between sexes via a novel dosage reimbursement mechanism, other from people, difficult long-standing genetic assumptions and embellishing our figuring out of genetic evolution and law.Researchers at UNSW Sydney have exposed elementary variations in organic processes between men and women via inspecting the original and numerous intercourse chromosome methods of the platypus and the rooster.The findings, revealed in Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences (PNAS), are a wonder within the box of genetics. The discoveries will assist construct a greater figuring out of ways intercourse chromosomes developed, how our our bodies serve as—they usually may result in new discoveries in biology.“Mammals, similar to people, have women folk with two X chromosomes and men with one X chromosome and one Y chromosome, which creates an imbalance between the sexes,” says lead writer Dr Nicholas Lister from UNSW’s Faculty of Biotechnology and Biomolecular Sciences. “This imbalance is corrected via a procedure referred to as intercourse chromosome dosage reimbursement.”Scientists have lengthy identified that animals have answers to steadiness intercourse chromosome variations and succeed in ‘commonplace’ serve as.Dr Lister says: “In feminine mammals, similar to people and mice, XX women folk and XY men have other numbers of the X chromosome. To steadiness this distinction, probably the most X chromosomes in women folk is in most cases silenced. Silencing one X chromosome in women folk equalizes the gene merchandise at the intercourse chromosomes. This prevents women folk from generating double the collection of proteins from the X in comparison to men.”Balancing the scalesEvery mobile in our our bodies makes use of proteins to accomplish explicit purposes.“They’re translated from mRNA, which elevate the directions for cells to make proteins,” the find out about’s analysis lead, Affiliate Professor Paul Waters, additionally from UNSW’s Faculty of Biotechnology and Biomolecular Sciences, says. “Being male or feminine impacts mRNA ranges of X chromosome genes, which we’d then be expecting to impact protein manufacturing.”
Researchers at UNSW Sydney have found out novel mechanisms of intercourse chromosome dosage reimbursement in platypus and rooster, difficult earlier assumptions and offering new insights into genetic law throughout species.A brand new find out about finds that platypuses and chickens steadiness protein ranges between sexes via a novel dosage reimbursement mechanism, other from people, difficult long-standing genetic assumptions and embellishing our figuring out of genetic evolution and law.Researchers at UNSW Sydney have exposed elementary variations in organic processes between men and women via inspecting the original and numerous intercourse chromosome methods of the platypus and the rooster.The findings, revealed in Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences (PNAS), are a wonder within the box of genetics. The discoveries will assist construct a greater figuring out of ways intercourse chromosomes developed, how our our bodies serve as—they usually may result in new discoveries in biology.“Mammals, similar to people, have women folk with two X chromosomes and men with one X chromosome and one Y chromosome, which creates an imbalance between the sexes,” says lead writer Dr Nicholas Lister from UNSW’s Faculty of Biotechnology and Biomolecular Sciences. “This imbalance is corrected via a procedure referred to as intercourse chromosome dosage reimbursement.”Scientists have lengthy identified that animals have answers to steadiness intercourse chromosome variations and succeed in ‘commonplace’ serve as.Dr Lister says: “In feminine mammals, similar to people and mice, XX women folk and XY men have other numbers of the X chromosome. To steadiness this distinction, probably the most X chromosomes in women folk is in most cases silenced. Silencing one X chromosome in women folk equalizes the gene merchandise at the intercourse chromosomes. This prevents women folk from generating double the collection of proteins from the X in comparison to men.”Balancing the scalesEvery mobile in our our bodies makes use of proteins to accomplish explicit purposes.“They’re translated from mRNA, which elevate the directions for cells to make proteins,” the find out about’s analysis lead, Affiliate Professor Paul Waters, additionally from UNSW’s Faculty of Biotechnology and Biomolecular Sciences, says. “Being male or feminine impacts mRNA ranges of X chromosome genes, which we’d then be expecting to impact protein manufacturing.”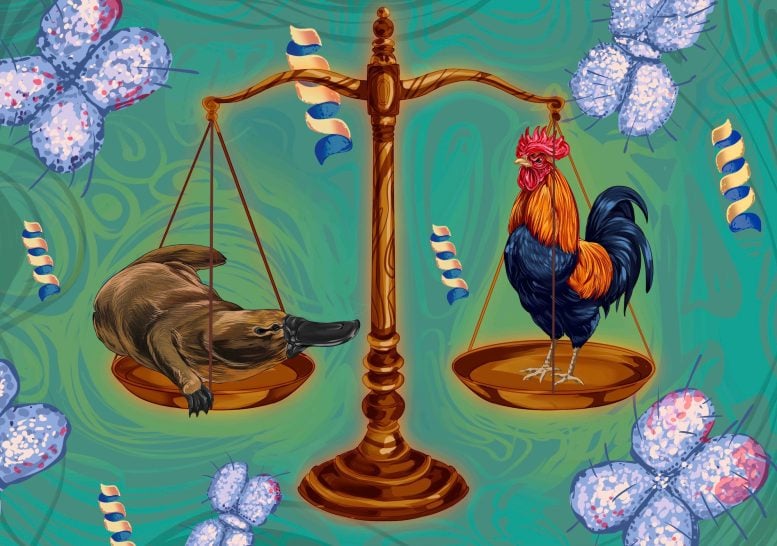 The platypus and rooster have hugely other intercourse chromosome methods to people—which may give us treasured insights into our personal our bodies paintings. Credit score: Shafagh Waters and Lisa MelisaBut A/Prof. Waters says this find out about demonstrates—for the primary time—{that a} steadiness of proteins happens between the sexes, even if mRNA ranges aren’t balanced.“The findings counsel that dosage reimbursement is a the most important procedure in species with differentiated intercourse chromosomes to be sure that protein ranges are balanced,” he says. “Those effects are vital as they counsel that dosage reimbursement of intercourse chromosomes is very important in spite of everything—and throughout all vertebrate species, now not simply placental and marsupial mammals.”Why the platypus and the rooster?The find out about centered at the platypus and the rooster—two species with hugely other intercourse chromosome methods that provide treasured insights into the evolution and mechanisms of dosage reimbursement.“Platypus are monotreme mammals, with fascinating intercourse chromosome methods,” Dr Lister says. “They’ve 5 pairs of X chromosomes in women folk and 5 Xs and 5 Ys in men. Birds—similar to chickens—have a ZW device, the place men have two copies of a Z chromosome and women folk have a Z and a W chromosome.”A/Prof. Waters says the scientists had already seen near-perfect intercourse chromosome dosage reimbursement of RNA between men and women in placental and marsupial mammals.“Then again, in birds and monotremes, there’s an imbalance of mRNA between the sexes,” he says. “That is one thing we concept was once unattainable. For the primary time, we display that this imbalance is corrected on the protein degree. Which means platypus and rooster have a unique mechanism of dosage reimbursement this is other from how we people do it.”Are our genes truly in keep watch over?Co-author Professor Jenny Graves, from the Division of Atmosphere and Genetics at Los angeles Trobe College, had demonstrated that genes at the inactive human X chromosome aren’t copied into RNA again in 1986.Silencing on the degree of RNA then changed into the paradigm for all epigenetic silencing.“Because the genes had been silenced via their failure to make RNA, the keep watch over of dosage reimbursement was once assumed to be on the degree of RNA best—now not on the degree of constructing proteins,” Prof. Graves says.“However mRNA ranges for genes on intercourse chromosomes weren’t balanced within the platypus or the rooster,” she says. “So, scientists puzzled the belief that dosage reimbursement is very important for lifestyles.”A/Prof. Waters says that measuring protein ranges has been a miles trickier undertaking than measuring mRNA ranges, because of technological demanding situations.“And now that the era is extra delicate, we will see that the dosage reimbursement of intercourse chromosomes between men and women is seen on the protein degree within the platypus and the rooster,” A/Prof. Waters says. “The men and women of those species make an identical quantities of proteins, regardless of the discrepancies in mRNA amounts.”How will this data be carried out?The authors emphasize the complexity of genetic law and the significance of taking into account more than one ranges of keep watch over in gene expression.Co-author Dr Shafagh Waters from UNSW’s Faculty of Biomedical Sciences says the find out about paves the way in which for a deeper figuring out of genetic law.“Learning distinctive species just like the platypus supplies us with new insights into the mobile and molecular mechanisms that might keep an eye on quite a lot of facets of human body structure, or be implicated in illness states,” she says. “So, whilst those processes would possibly indirectly practice to human dosage reimbursement, they remove darkness from how our our bodies set up gene expression and protein manufacturing. Our findings have the possible to advance wisdom in evolutionary biology and result in cutting edge remedies in clinical genetics. Figuring out those mechanisms throughout other species can assist determine new goals for illnesses the place protein disorder is essential.”Dr Lister says long run analysis will read about the mechanisms that give a contribution to dosage reimbursement.“This paintings will assist us uncover different dosage reimbursement methods in nature,” he says. “We will be able to learn how those developed and the way they paintings in different species.”A/Prof. Waters says, “Figuring out those processes in different species can give a boost to our grab of gene law at a elementary degree.”Reference: “Incomplete transcriptional dosage reimbursement of rooster and platypus intercourse chromosomes is balanced via post-transcriptional reimbursement” via Nicholas C. Lister, Ashley M. Milton, Hardip R. Patel, Shafagh A. Waters, Benjamin J. Hanrahan, Kim L. McIntyre, Alexandra M. Livernois, William B. Horspool, Lee Kian Wee, Alessa R. Ringel, Stefan Mundlos, Michael I. Robson, Linda Shearwin-Whyatt, Frank Grützner, Jennifer A. Marshall Graves, Aurora Ruiz-Herrera and Paul D. Waters, 29 July 2024, Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.
The platypus and rooster have hugely other intercourse chromosome methods to people—which may give us treasured insights into our personal our bodies paintings. Credit score: Shafagh Waters and Lisa MelisaBut A/Prof. Waters says this find out about demonstrates—for the primary time—{that a} steadiness of proteins happens between the sexes, even if mRNA ranges aren’t balanced.“The findings counsel that dosage reimbursement is a the most important procedure in species with differentiated intercourse chromosomes to be sure that protein ranges are balanced,” he says. “Those effects are vital as they counsel that dosage reimbursement of intercourse chromosomes is very important in spite of everything—and throughout all vertebrate species, now not simply placental and marsupial mammals.”Why the platypus and the rooster?The find out about centered at the platypus and the rooster—two species with hugely other intercourse chromosome methods that provide treasured insights into the evolution and mechanisms of dosage reimbursement.“Platypus are monotreme mammals, with fascinating intercourse chromosome methods,” Dr Lister says. “They’ve 5 pairs of X chromosomes in women folk and 5 Xs and 5 Ys in men. Birds—similar to chickens—have a ZW device, the place men have two copies of a Z chromosome and women folk have a Z and a W chromosome.”A/Prof. Waters says the scientists had already seen near-perfect intercourse chromosome dosage reimbursement of RNA between men and women in placental and marsupial mammals.“Then again, in birds and monotremes, there’s an imbalance of mRNA between the sexes,” he says. “That is one thing we concept was once unattainable. For the primary time, we display that this imbalance is corrected on the protein degree. Which means platypus and rooster have a unique mechanism of dosage reimbursement this is other from how we people do it.”Are our genes truly in keep watch over?Co-author Professor Jenny Graves, from the Division of Atmosphere and Genetics at Los angeles Trobe College, had demonstrated that genes at the inactive human X chromosome aren’t copied into RNA again in 1986.Silencing on the degree of RNA then changed into the paradigm for all epigenetic silencing.“Because the genes had been silenced via their failure to make RNA, the keep watch over of dosage reimbursement was once assumed to be on the degree of RNA best—now not on the degree of constructing proteins,” Prof. Graves says.“However mRNA ranges for genes on intercourse chromosomes weren’t balanced within the platypus or the rooster,” she says. “So, scientists puzzled the belief that dosage reimbursement is very important for lifestyles.”A/Prof. Waters says that measuring protein ranges has been a miles trickier undertaking than measuring mRNA ranges, because of technological demanding situations.“And now that the era is extra delicate, we will see that the dosage reimbursement of intercourse chromosomes between men and women is seen on the protein degree within the platypus and the rooster,” A/Prof. Waters says. “The men and women of those species make an identical quantities of proteins, regardless of the discrepancies in mRNA amounts.”How will this data be carried out?The authors emphasize the complexity of genetic law and the significance of taking into account more than one ranges of keep watch over in gene expression.Co-author Dr Shafagh Waters from UNSW’s Faculty of Biomedical Sciences says the find out about paves the way in which for a deeper figuring out of genetic law.“Learning distinctive species just like the platypus supplies us with new insights into the mobile and molecular mechanisms that might keep an eye on quite a lot of facets of human body structure, or be implicated in illness states,” she says. “So, whilst those processes would possibly indirectly practice to human dosage reimbursement, they remove darkness from how our our bodies set up gene expression and protein manufacturing. Our findings have the possible to advance wisdom in evolutionary biology and result in cutting edge remedies in clinical genetics. Figuring out those mechanisms throughout other species can assist determine new goals for illnesses the place protein disorder is essential.”Dr Lister says long run analysis will read about the mechanisms that give a contribution to dosage reimbursement.“This paintings will assist us uncover different dosage reimbursement methods in nature,” he says. “We will be able to learn how those developed and the way they paintings in different species.”A/Prof. Waters says, “Figuring out those processes in different species can give a boost to our grab of gene law at a elementary degree.”Reference: “Incomplete transcriptional dosage reimbursement of rooster and platypus intercourse chromosomes is balanced via post-transcriptional reimbursement” via Nicholas C. Lister, Ashley M. Milton, Hardip R. Patel, Shafagh A. Waters, Benjamin J. Hanrahan, Kim L. McIntyre, Alexandra M. Livernois, William B. Horspool, Lee Kian Wee, Alessa R. Ringel, Stefan Mundlos, Michael I. Robson, Linda Shearwin-Whyatt, Frank Grützner, Jennifer A. Marshall Graves, Aurora Ruiz-Herrera and Paul D. Waters, 29 July 2024, Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences.
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2322360121
Researchers Have Exposed Basic Variations in Organic Processes Between Men and Ladies