Abstract: Researchers have effectively reactivated reminiscence circuits in mice, inflicting them to hunt refuge even if no refuge used to be provide. Via stimulating neurons related to spatial reminiscence, the crew activated a prior reminiscence of shelter-seeking habits.This learn about sheds gentle on how reminiscence circuits paintings within the mind and may just lend a hand increase methods to gradual reminiscence loss in neurodegenerative illnesses. The findings be offering promising insights into reactivating or engineering reminiscence circuits to maintain mind serve as in circumstances of reminiscence decline.Key Info:Reactivating neurons led to mice to hunt refuge the place none existed.The reminiscence circuit concerned spatial reminiscence related to previous stories.This analysis may just result in remedies for reminiscence loss in neurodegenerative illnesses.Supply: Johns Hopkins UniversityUsing an advanced brain-imaging gadget, neuroscientists at Johns Hopkins Medication say they have got effectively reactivated a particular reminiscence circuit in mice, inflicting them to hunt out refuge when no refuge is if truth be told provide.The researchers say the learn about, printed Sept. 27 in Nature Neuroscience, advances working out of ways recollections are structured within the mammalian mind.The findings may just at some point level to new tactics of slowing down or combating the reminiscence loss that accompanies Alzheimer’s and different neurodegenerative illnesses.Particularly, the crew discovered that stimulating neurons in two spaces of mouse brains — the nucleus accumbens, sometimes called the mind’s “excitement middle” answerable for relaying dopamine-dependent behaviors, and the dorsal periaqueductal grey (dPAG), answerable for defensive habits — reactivated a “spatial reminiscence” and led to the mice to hunt refuge. 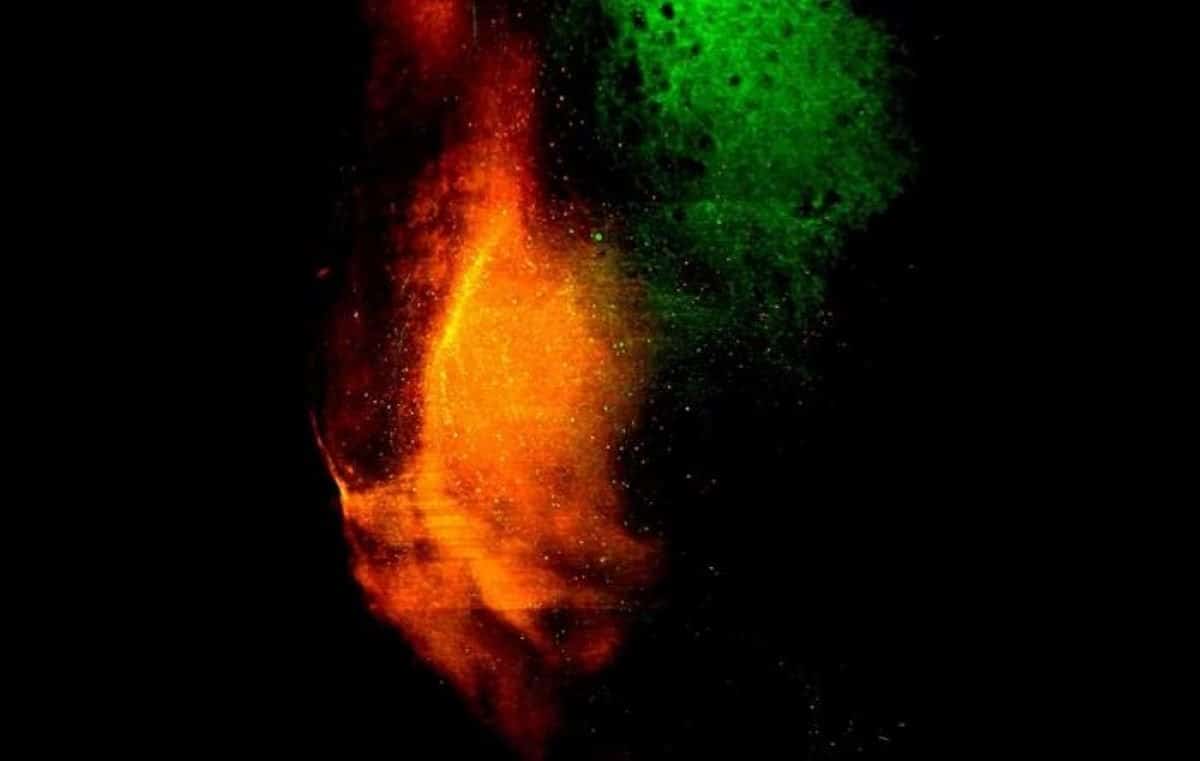 A mild-sheet microscope three-D symbol presentations the convergence of dopaminergic transmitter inputs from the ventral tegmental space (inexperienced), a midbrain construction related to praise and motivation, and glutamatergic inputs from the ventral hippocampus (purple), a space deep throughout the mind that is helping with navigation, onto the nucleus accumbens. Credit score: Kanghoon Jung“After we artificially reactivate the ones reminiscence circuits within the mind, it triggers the mouse to do the similar factor it did naturally, even with out the worry stimuli that lead them to search refuge to start with,” says senior creator Hyungbae Kwon, Ph.D., affiliate professor of neuroscience on the Johns Hopkins College College of Medication.The scientists say they aimed to map out which spaces of the mind are answerable for navigating one’s environment, a high-level cognitive serve as amongst mammals, together with people.Thus, those experiments, which examined whether or not such cognitive mind purposes may also be replayed randomly, can have programs in working out how different mammals behave, understand and sense their atmosphere.Within the new experiments, the researchers first allowed laboratory mice to discover their environment in a field with a refuge within the nook. The crew positioned a sequence of visible cues, together with triangles, circles and stripes in numerous colours, to lend a hand the mice find the refuge in line with within sight landmarks. The mice acclimated to the world for seven mins, getting into and exiting the refuge.Then, the researchers added a visible or auditory looming sign to spur them to hunt refuge – additionally forming a spatial reminiscence relative to their location and the visible cues.To selectively tag refuge reminiscence neurons, the researchers used a light-activated gene-expression switching gadget known as Cal-light, which Kwon advanced in 2017.As soon as the scientists recognized those neurons within the nucleus accumbens, they switched on expression of the genes related to them, reactivating the shelter-seeking reminiscence in mice whilst additionally activating neurons within the dPAG.In flip, the mice sought out the world of the field the place the refuge had as soon as been, when neither the unique danger nor the refuge had been provide.To get up to now, the researchers first selectively activated neurons within the nucleus accumbens after which, one by one, within the dPAG, to peer whether or not switching on neurons in only one space of the mind would motive this habits.“Strangely, we discovered that the mice didn’t hunt down refuge once we activated neurons within the nucleus accumbens on my own,” Kwon says.“While switching on neurons within the dPAG led to the mice to react randomly, however didn’t information them in particular to the world the place they sought refuge ahead of.” “The Cal-light gadget allowed us to selectively tag a particular serve as within the mind, serving to us to map out reminiscence on a cell point,” says Kwon. Ultimately, Kwon says this analysis may provide a basis for reactivating or engineering reminiscence circuits in other folks with Alzheimer’s. “If we perceive the macro-level construction of reminiscence, then we could possibly increase simpler methods to stop or decelerate neurodegenerative illnesses the use of this technique,” he says.The researchers say they hope to grasp brain-wide reminiscence construction through selectively tagging and reactivating neurons with other purposes in numerous spaces of the mind that result in different explicit behaviors.“Working out how all of those reminiscence circuits paintings in combination will lend a hand us perceive mind serve as higher,” he says.Different researchers concerned within the learn about are Kanghoon Jung, Sarah Krüssel, Sooyeon Yoo, Benjamin Burke, Nicholas Schappaugh, Youngjin Choi and Seth Blackshaw of Johns Hopkins; Myungmo An of the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience; and Zirong Gu and Rui M. Costa of the Zuckerman Thoughts Mind Habits Institute at Columbia College and the Allen Institute.Investment: Investment for this paintings used to be equipped through the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience, a Nationwide Alliance for Analysis on Schizophrenia and Melancholy Younger Investigator Grant and Nationwide Institutes of Well being Grants R01MH107460, 5U19NS104649, K99 NS119788, DK108230 and DP1MH119428.About this reminiscence and neuroscience analysis newsAuthor: Alexandria Carolan
A mild-sheet microscope three-D symbol presentations the convergence of dopaminergic transmitter inputs from the ventral tegmental space (inexperienced), a midbrain construction related to praise and motivation, and glutamatergic inputs from the ventral hippocampus (purple), a space deep throughout the mind that is helping with navigation, onto the nucleus accumbens. Credit score: Kanghoon Jung“After we artificially reactivate the ones reminiscence circuits within the mind, it triggers the mouse to do the similar factor it did naturally, even with out the worry stimuli that lead them to search refuge to start with,” says senior creator Hyungbae Kwon, Ph.D., affiliate professor of neuroscience on the Johns Hopkins College College of Medication.The scientists say they aimed to map out which spaces of the mind are answerable for navigating one’s environment, a high-level cognitive serve as amongst mammals, together with people.Thus, those experiments, which examined whether or not such cognitive mind purposes may also be replayed randomly, can have programs in working out how different mammals behave, understand and sense their atmosphere.Within the new experiments, the researchers first allowed laboratory mice to discover their environment in a field with a refuge within the nook. The crew positioned a sequence of visible cues, together with triangles, circles and stripes in numerous colours, to lend a hand the mice find the refuge in line with within sight landmarks. The mice acclimated to the world for seven mins, getting into and exiting the refuge.Then, the researchers added a visible or auditory looming sign to spur them to hunt refuge – additionally forming a spatial reminiscence relative to their location and the visible cues.To selectively tag refuge reminiscence neurons, the researchers used a light-activated gene-expression switching gadget known as Cal-light, which Kwon advanced in 2017.As soon as the scientists recognized those neurons within the nucleus accumbens, they switched on expression of the genes related to them, reactivating the shelter-seeking reminiscence in mice whilst additionally activating neurons within the dPAG.In flip, the mice sought out the world of the field the place the refuge had as soon as been, when neither the unique danger nor the refuge had been provide.To get up to now, the researchers first selectively activated neurons within the nucleus accumbens after which, one by one, within the dPAG, to peer whether or not switching on neurons in only one space of the mind would motive this habits.“Strangely, we discovered that the mice didn’t hunt down refuge once we activated neurons within the nucleus accumbens on my own,” Kwon says.“While switching on neurons within the dPAG led to the mice to react randomly, however didn’t information them in particular to the world the place they sought refuge ahead of.” “The Cal-light gadget allowed us to selectively tag a particular serve as within the mind, serving to us to map out reminiscence on a cell point,” says Kwon. Ultimately, Kwon says this analysis may provide a basis for reactivating or engineering reminiscence circuits in other folks with Alzheimer’s. “If we perceive the macro-level construction of reminiscence, then we could possibly increase simpler methods to stop or decelerate neurodegenerative illnesses the use of this technique,” he says.The researchers say they hope to grasp brain-wide reminiscence construction through selectively tagging and reactivating neurons with other purposes in numerous spaces of the mind that result in different explicit behaviors.“Working out how all of those reminiscence circuits paintings in combination will lend a hand us perceive mind serve as higher,” he says.Different researchers concerned within the learn about are Kanghoon Jung, Sarah Krüssel, Sooyeon Yoo, Benjamin Burke, Nicholas Schappaugh, Youngjin Choi and Seth Blackshaw of Johns Hopkins; Myungmo An of the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience; and Zirong Gu and Rui M. Costa of the Zuckerman Thoughts Mind Habits Institute at Columbia College and the Allen Institute.Investment: Investment for this paintings used to be equipped through the Max Planck Florida Institute for Neuroscience, a Nationwide Alliance for Analysis on Schizophrenia and Melancholy Younger Investigator Grant and Nationwide Institutes of Well being Grants R01MH107460, 5U19NS104649, K99 NS119788, DK108230 and DP1MH119428.About this reminiscence and neuroscience analysis newsAuthor: Alexandria Carolan
Supply: Johns Hopkins College
Touch: Alexandria Carolan – Johns Hopkins College
Symbol: The picture is credited to Kanghoon JungOriginal Analysis: Open get admission to.
“Dopamine-mediated formation of a reminiscence module within the nucleus accumbens for goal-directed navigation” through Kanghoon Jung et al. Nature NeuroscienceAbstractDopamine-mediated formation of a reminiscence module within the nucleus accumbens for goal-directed navigationSpatial recollections information navigation successfully towards desired locations. Alternatively, the neuronal and circuit mechanisms underlying the encoding of target places and its translation into goal-directed navigation stay unclear.Right here we show that mice all of a sudden shape a spatial reminiscence of a refuge throughout refuge stories, guiding break out habits towards the target location—a refuge—when underneath danger.Dopaminergic neurons within the ventral tegmental space and their projection to the nucleus accumbens (NAc) encode protection indicators related to the refuge.Optogenetically triggered phasic dopamine indicators are enough to create a spot reminiscence that directs break out navigation.Converging dopaminergic and hippocampal glutamatergic inputs to the NAc mediate the formation of a goal-related reminiscence inside of a subpopulation of NAc neurons throughout refuge stories.Synthetic co-activation of this goal-related NAc ensemble with neurons within the dorsal periaqueductal grey used to be enough to cause memory-guided, slightly than random, break out habits.Those findings supply causal proof of cognitive circuit modules linking reminiscence with goal-directed motion.
Researchers Reactivate Reminiscence Circuits in Mice to Cause Refuge-In search of – Neuroscience Information