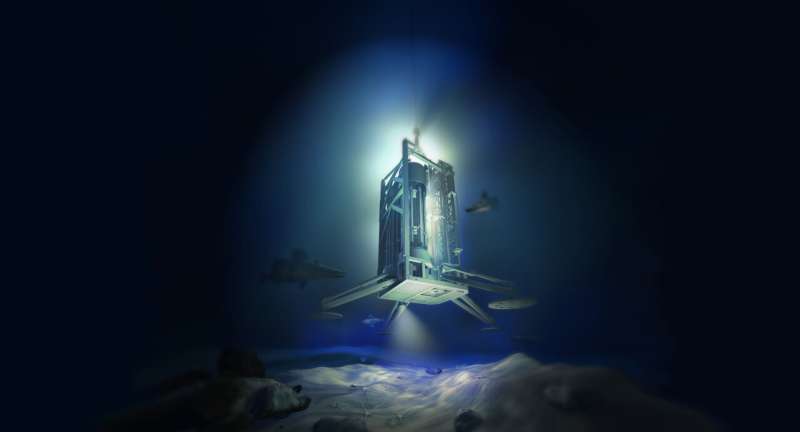
Rendered graphic of the MARUM-MeBo70 touchdown at the seabed of the Amundsen Sea. Credit score: MARUM – Heart for Marine Environmental Sciences, College of Bremen / Martin Künsting
Lately, world warming has left its mark at the Antarctic ice sheets. The “everlasting” ice in Antarctica is melting quicker than up to now assumed, specifically in West Antarctica greater than East Antarctica. The basis for this is able to lie in its formation, as a world analysis crew led through the Alfred Wegener Institute has now came upon.
Sediment samples from drill cores blended with complicated local weather and ice-sheet modeling display that everlasting glaciation of Antarctica started round 34 million years in the past—however didn’t surround all the continent as up to now assumed, however somewhat used to be confined to the jap area of the continent (East Antarctica). It used to be no longer till a minimum of 7 million years later that ice used to be in a position to advance against the West Antarctic coast.
The result of the brand new learn about display how considerably otherwise East and West Antarctica react to exterior forcing, because the researchers describe within the magazine Science.
Round 34 million years in the past, our planet underwent probably the most basic local weather shifts that also influences world local weather stipulations these days: the transition from a greenhouse international (without a or little or no accumulation of continental ice) to an icehouse international (with huge completely glaciated spaces). All through this time, the Antarctic ice sheet constructed up. How, when, and above all, the place weren’t but recognized because of a loss of dependable knowledge and samples from key areas, particularly from West Antarctica, that documented the adjustments previously.
Researchers from the Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Analysis (AWI) have now been in a position to near this data hole, along with colleagues from the British Antarctic Survey, Heidelberg College, Northumbria College (UK), and the MARUM—Heart for Marine Environmental Sciences on the College of Bremen, along with collaborators from the Universities in Aachen, Leipzig, Hamburg, Bremen, and Kiel, in addition to the College of Tasmania (Australia), Imperial School London (UK), Université de Fribourg (Switzerland), Universidad de Granada (Spain), Leicester College (UK), Texas A&M College (U.S.), Senckenberg am Meer, and the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Herbal Assets in Hanover, Germany.
In keeping with a drill core that the researchers retrieved the usage of the MARUM-MeBo70 seafloor drill rig in a location offshore the Pine Island and Thwaites glaciers at the Amundsen Beach of West Antarctica, they have been in a position to determine the historical past of the break of day of the icy Antarctic continent for the primary time. Strangely, no indicators of the presence of ice will also be discovered on this area right through the primary primary segment of Antarctic glaciation.
“Because of this a large-scale, everlasting first glaciation will have to have begun someplace in East Antarctica,” says Dr. Johann Klages, geologist on the AWI who led the analysis crew. It is because West Antarctica remained ice-free right through this primary glacial most. At the moment, it used to be nonetheless in large part lined through dense broadleaf forests and a cool-temperate local weather that avoided ice from forming in West Antarctica.
East and West Antarctica react very otherwise to exterior stipulations
In an effort to higher perceive the place the primary everlasting ice shaped in Antarctica, the AWI paleoclimate modelers blended the newly to be had knowledge along with current knowledge on air and water temperatures and the prevalence of ice.
“The simulation has supported the result of the geologists’ distinctive core,” says Prof Dr. Gerrit Lohmann, paleoclimate modeler on the AWI. “This utterly adjustments what we all know in regards to the first Antarctic glaciation.”
In keeping with the learn about, the fundamental climatic stipulations for the formation of everlasting ice simplest prevailed within the coastal areas of the East Antarctic Northern Victoria Land. Right here, wet air plenty reached the strongly emerging Transantarctic Mountains—supreme stipulations for everlasting snow and next formation of ice caps. From there, the ice sheet unfold all of a sudden into the East Antarctic hinterland. Alternatively, it took a while ahead of it reached West Antarctica.
“It wasn’t till about seven million years later that stipulations allowed for advance of an ice sheet to the West Antarctic coast,” explains Hanna Knahl, a paleoclimate modeler on the AWI. “Our effects obviously display how chilly it needed to get ahead of the ice may just advance to hide West Antarctica that, at the moment, used to be already underneath sea degree in lots of portions.”
What the investigations additionally impressively display is how otherwise the 2 areas of the Antarctic ice sheet react to exterior influences and basic climatic adjustments.
“Even a slight warming is sufficient to motive the ice in West Antarctica to soften once more—and that is the reason precisely the place we’re presently,” provides Klages.
The findings of the global analysis crew are important for figuring out the intense local weather transition from the greenhouse local weather to our present icehouse local weather. Importantly, the learn about additionally supplies new perception that permits local weather fashions to simulate extra appropriately how completely glaciated spaces have an effect on world local weather dynamics, this is, the interactions amongst ice, ocean and environment.
That is of the most important significance, as Klages says, “particularly in gentle of the truth that we might be going through this sort of basic local weather trade once more within the close to long run.”
The usage of new generation to achieve distinctive insights
The researchers have been in a position to near this data hole with the assistance of a novel drill core that they retrieved right through the expedition PS104 at the analysis vessel Polarstern in West Antarctica in 2017. The MARUM-MeBo70 drill rig evolved at MARUM in Bremen used to be used for the primary time in Antarctica.
The seabed off the West Antarctic Pine Island and Thwaites glaciers is so onerous that it used to be up to now not possible to achieve deep sediments the usage of typical drilling strategies. The MARUM-MeBo70 has a rotating cutterhead, which made it conceivable to drill about 10 meters into the seabed and retrieve the samples.
Additional information:
J. P. Klages, Ice sheet-free West Antarctica right through height early Oligocene glaciation, Science (2024). DOI: 10.1126/science.adj3931. www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adj3931
Supplied through
Alfred Wegener Institute
Quotation:
Restoration of distinctive geological samples sheds gentle on formation of these days’s Antarctic ice sheet (2024, July 4)
retrieved 5 July 2024
from
This report is topic to copyright. Except for any honest dealing for the aim of personal learn about or analysis, no
phase could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is equipped for info functions simplest.