Scientists at Scripps Analysis have found out that during Caenorhabditis elegans, a molecule produced within the intestine all through fasting travels to the mind and blocks fat-burning alerts. This discovering, which sheds mild at the verbal exchange between the intestine and mind, means that fasting will have advantages past easy calorie restriction. The find out about highlights the opportunity of new therapies focused on metabolic sicknesses via mimicking intestine hormone movements.
Scientists at Scripps Analysis have found out that during Caenorhabditis elegans, a molecule produced within the intestine all through fasting travels to the mind and blocks fat-burning alerts. This discovering, which sheds mild at the verbal exchange between the intestine and mind, means that fasting will have advantages past easy calorie restriction. The find out about highlights the opportunity of new therapies focused on metabolic sicknesses via mimicking intestine hormone movements.
Scientists at Scripps Analysis have recognized a molecule secreted via roundworm intestines that communicates with the mind to scale back the speed of fats loss all through sessions of meals shortage.
In a state of affairs that many dieters can most probably relate to, the fewer a Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) malicious program eats, the slower it sheds fats. Researchers at Scripps Analysis have now exposed the rationale: a small molecule produced within the worms’ intestines all through fasting travels to the mind, the place it blocks a sign accountable for burning fats all through this era.
Even if the precise molecule they recognized within the worms has no longer but been studied in people, the brand new paintings is helping scientists higher perceive the advanced crosstalk between the intestine and the mind. It additionally would possibly make clear why fasting—no longer consuming for set sessions of time—has advantages which can be impartial from the collection of energy an individual eats. The brand new find out about was once revealed in Nature Communications on August 11, 2024.
“We’ve discovered for the primary time that fasting is conveying data to the mind past simply caloric withdrawal,” says Scripps Analysis Professor of Neuroscience Supriya Srinivasan, PhD, the senior writer of the brand new find out about. “Those findings make me wonder if there are molecules made within the guts of different animals, together with mammals, that provide an explanation for probably the most well being results related to fasting.”
Mind-Intestine Communique in Fats Metabolism
Researchers have lengthy recognized that the mind controls the manufacturing and breakdown of fat in people, different mammals, and style organisms corresponding to C. elegans. In 2017, Srinivasan’s workforce recognized FLP-7, a mind hormone that triggers fats burning within the roundworm’s intestine. Alternatively, C. elegans should not have sensory nerves of their intestines, so scientists have struggled to pin down the opposite verbal exchange pathway: How does the intestine sign the mind?
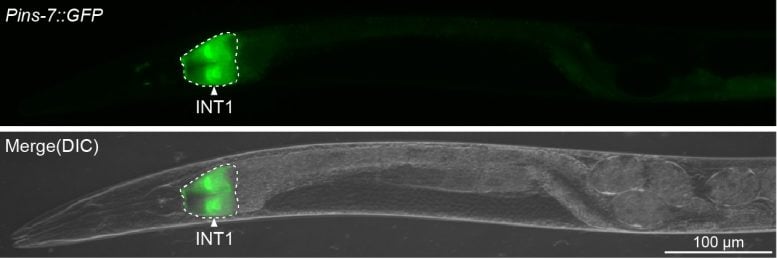 Scripps Analysis scientists found out that specialised gut cells (proven in inexperienced) within the C. elegans malicious program (grey) produce a peptide hormone that travels to the mind to keep an eye on fats metabolism. Credit score: Scripps Analysis
Scripps Analysis scientists found out that specialised gut cells (proven in inexperienced) within the C. elegans malicious program (grey) produce a peptide hormone that travels to the mind to keep an eye on fats metabolism. Credit score: Scripps Analysis
“We knew that changing the metabolic state of the intestine may just alternate the homes of neurons within the mind, nevertheless it was once very mysterious how this in reality took place,” says Srinivasan.
Within the new paintings, Srinivasan and her colleagues got rid of greater than 100 signaling molecules from C. elegans intestines, one after the other, and measured their affect at the mind’s manufacturing of FLP-7. They discovered one molecule that had a big impact on FLP-7: a type of insulin referred to as INS-7. In people, insulin is maximum referred to as the hormone produced via the pancreas that controls blood sugar ranges. However this insulin molecule was once as an alternative being made via intestine cells and in addition impacting fats metabolism by way of the mind.
“After we first discovered that this was once an insulin, we idea it was once paradoxical,” recollects Srinivasan. “Insulin is so neatly studied in mammals, and there was once no precedent for an insulin molecule having this position.”
Discovery of a Distinctive Insulin Serve as
Alternatively, when the gang probed how INS-7 was once impacting FLP-7-producing mind cells, they discovered that it was once no longer activating insulin receptors—as all in the past found out insulin molecules do—however via blocking off the insulin receptor. In flip, this blockade activate a cascade of different molecular occasions that finally made the mind cells prevent generating FLP-7.
“INS-7 is principally a sign coming from the intestines that tells the mind to not burn to any extent further fats shops at this time as a result of there’s no meals coming in,” explains Srinivasan.
Research have in the past proven that sessions of fasting can affect the frame in quite a lot of techniques, however the mechanisms of the ones adjustments were unclear. The brand new find out about issues towards a method that an empty intestine can sign the mind, which might doubtlessly result in quite a lot of well being affects past fats.
The brand new effects, Srinivasan says, assist provide an explanation for how the mind and digestive device keep up a correspondence in each instructions to keep an eye on metabolism in accordance with the supply of meals. Extra analysis is had to discover which particular pathways are interested in new gut-to-brain alerts in mammals.
Compounds that mimic intestine hormones—corresponding to semaglutide, regularly recognized beneath logo names corresponding to Ozempic, Wegovy, and Rybelus—have lately emerged as common techniques to keep an eye on weight problems and diabetes, so new intestine peptides may just upload to this drug elegance. Srinivasan could also be making plans experiments to probe how C. elegans intestine cells are brought on to supply INS-7 all through fasting and which varieties of mind cells are suffering from the molecule.
Reference: “A homeostatic gut-to-brain insulin antagonist restrains neuronally stimulated fats loss” via Chung-Chih Liu, Ayub Khan, Nicolas Seban, Nicole Littlejohn, Aayushi Shah and Supriya Srinivasan, 11 August 2024, Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51077-3
This paintings was once supported via investment from the Nationwide Institutes of Well being (R01 DK124706 and R01 AG056648).
Rethinking Weight-reduction plan: Researchers Uncover Why Fasting Doesn’t At all times Equivalent Fats Loss