People are but to set foot on Mars, however over the years, Mars has come to the people. Chunks of Martian rock ejected from their homeworld via processes reminiscent of violent affects have wended their manner throughout the Sun Device to finally end up – smack! – crashing into Earth.As we gather those samples of our neighboring planet, a curious trend has emerged. Lots of the samples appear to be rocks that shaped at the pink planet relatively not too long ago; a peculiarity, given many of the Martian floor is so outdated.It’s conceivable the measures of age are in large part unsuitable. Other relationship ways have returned other effects, which means that scientists are not absolutely assured in estimates of when those rocks shaped on Mars.A crew of scientists from america and UK has now discovered a option to get to the bottom of this downside. And, to their marvel, many of those rocks are certainly reasonably younger – only some hundred million years outdated, actually. This data may provide clues about how lengthy the meteorites took to get right here, in addition to geological processes on Mars.”We all know from positive chemical traits that those meteorites are indubitably from Mars,” says volcanologist Ben Cohen of the College of Glasgow, who led the analysis.”They have been blasted off the pink planet via large affect occasions, forming huge craters. However there are tens of 1000’s of affect craters on Mars, so we do not know precisely the place on the earth the meteorites are from. One of the crucial very best clues you’ll be able to use to decide their supply crater is the samples’ age.”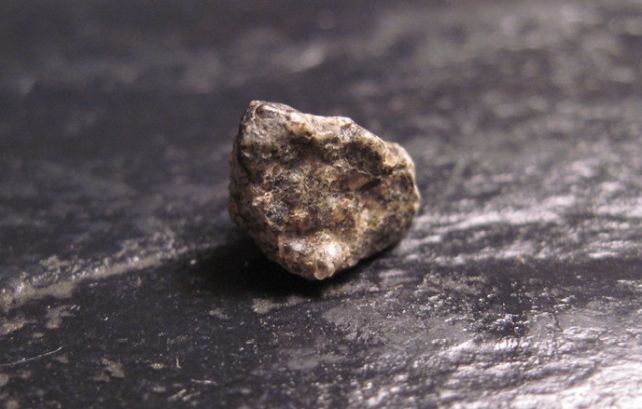 A small piece of shergottite, weighing simply 0.4 grams. (Jon Taylor/Flickr, CC BY-SA 2.0)There are round 360 or so meteorite samples discovered on Earth which have been known as having a Martian starting place. Some 302 of those at time of writing – so, maximum of them – are classed as shergottite, one of those metal-rich Mars rock cast within the warmth of volcanic job.In keeping with how closely cratered Mars’ floor is, scientists have estimated that floor to be lovely outdated. If the skin was once more youthful, refreshed via volcanic job, most of the craters could be erased via volcanic flows. So any rocks that get ejected from the Martian floor must even be outdated.Now not handiest are relationship ways on shergottite right here on Earth difficult via their make-up, however what little we’ve been in a position to glean from them has instructed many are not up to 200 million years outdated. This has led to what’s referred to as the shergottite age paradox, and it is been bugging scientists for many years.Explanations for this strangely younger chance ranged from a unmarried level of starting place for the entire more youthful shergottite, to the concept that the affect match can have heated and smushed the rock to this kind of level that its age was once type of reset. However those theories did not stack as much as the proof – the rocks themselves.The process used to decide the age of shergottite is referred to as argon-argon relationship, which is in response to the decay of radioactive potassium into argon. Since this decay price produces a identified ratio of argon isotopes, scientists can have a look at that ratio to decide how lengthy the radioactive decay has been going down, and thus date the rock pattern.
A small piece of shergottite, weighing simply 0.4 grams. (Jon Taylor/Flickr, CC BY-SA 2.0)There are round 360 or so meteorite samples discovered on Earth which have been known as having a Martian starting place. Some 302 of those at time of writing – so, maximum of them – are classed as shergottite, one of those metal-rich Mars rock cast within the warmth of volcanic job.In keeping with how closely cratered Mars’ floor is, scientists have estimated that floor to be lovely outdated. If the skin was once more youthful, refreshed via volcanic job, most of the craters could be erased via volcanic flows. So any rocks that get ejected from the Martian floor must even be outdated.Now not handiest are relationship ways on shergottite right here on Earth difficult via their make-up, however what little we’ve been in a position to glean from them has instructed many are not up to 200 million years outdated. This has led to what’s referred to as the shergottite age paradox, and it is been bugging scientists for many years.Explanations for this strangely younger chance ranged from a unmarried level of starting place for the entire more youthful shergottite, to the concept that the affect match can have heated and smushed the rock to this kind of level that its age was once type of reset. However those theories did not stack as much as the proof – the rocks themselves.The process used to decide the age of shergottite is referred to as argon-argon relationship, which is in response to the decay of radioactive potassium into argon. Since this decay price produces a identified ratio of argon isotopes, scientists can have a look at that ratio to decide how lengthy the radioactive decay has been going down, and thus date the rock pattern.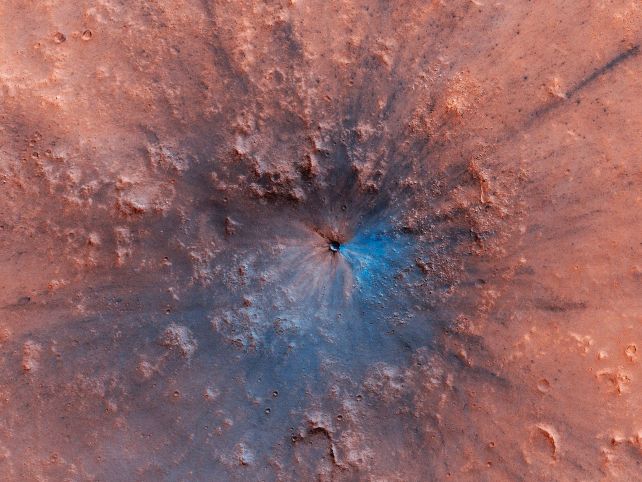 A crater that shaped on Mars someday between September 2016 and February 2019. (NASA/JPL-Caltech/UArizona)The issue is that, right here on Earth, we will be able to simply consider other assets of argon that can make its manner right into a pattern. For shergottite, which began on a complete different planet and spent goodness is aware of how lengthy in area, that is extra difficult. There are 5 attainable assets of argon for shergottite, in comparison to simply 3 for Earth rocks.To catch up on this, Cohen and his colleagues advanced a technique to proper for argon contamination from Earth and area. “When we did that, the argon-argon ages got here out as being younger and coupled completely with different strategies, like Uranium-Lead,” he explains.They dated seven samples of shergottite, returning ages ranging between 161 million and 540 million years in the past. The researchers say that the cause of this may well be the widespread bombardment of Mars has damaged up the older floor, exposing the more youthful rock underneath, that has been replenished via volcanic job. In the end, it turns into much more likely that that more youthful rock is excavated and ejected.Martian volcanic job might nonetheless be ongoing as of late, and Mars is underneath consistent bombardment. Scientists have estimated some 200 affects annually create craters greater than 4 meters in diameter. So it is most certainly now not sudden that more youthful rocks on occasion get flung against Earth, in a roundabout Sun-Device-y type of manner.The analysis has been revealed in Earth and Planetary Science Letters.
A crater that shaped on Mars someday between September 2016 and February 2019. (NASA/JPL-Caltech/UArizona)The issue is that, right here on Earth, we will be able to simply consider other assets of argon that can make its manner right into a pattern. For shergottite, which began on a complete different planet and spent goodness is aware of how lengthy in area, that is extra difficult. There are 5 attainable assets of argon for shergottite, in comparison to simply 3 for Earth rocks.To catch up on this, Cohen and his colleagues advanced a technique to proper for argon contamination from Earth and area. “When we did that, the argon-argon ages got here out as being younger and coupled completely with different strategies, like Uranium-Lead,” he explains.They dated seven samples of shergottite, returning ages ranging between 161 million and 540 million years in the past. The researchers say that the cause of this may well be the widespread bombardment of Mars has damaged up the older floor, exposing the more youthful rock underneath, that has been replenished via volcanic job. In the end, it turns into much more likely that that more youthful rock is excavated and ejected.Martian volcanic job might nonetheless be ongoing as of late, and Mars is underneath consistent bombardment. Scientists have estimated some 200 affects annually create craters greater than 4 meters in diameter. So it is most certainly now not sudden that more youthful rocks on occasion get flung against Earth, in a roundabout Sun-Device-y type of manner.The analysis has been revealed in Earth and Planetary Science Letters.
Rocks From Mars Are Hitting Earth, And One thing Is Strange About Their Age