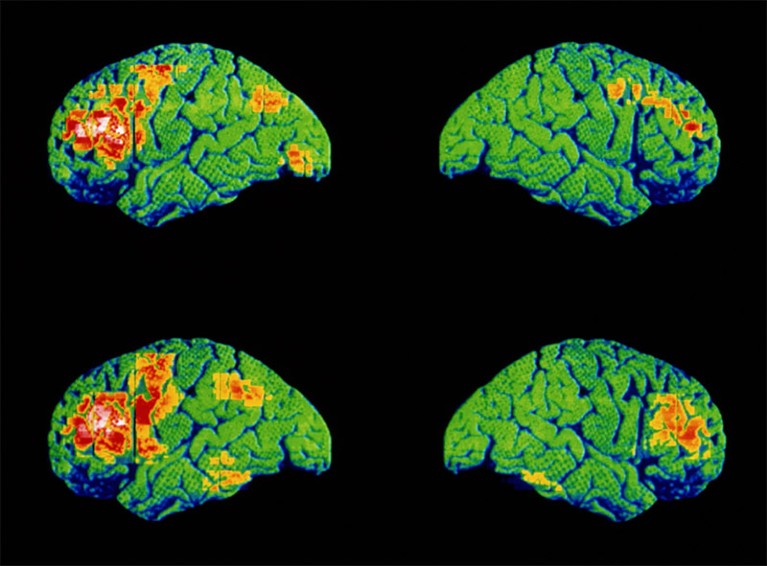
Scans appearing mind task all over speech for an individual with schizophrenia (backside) and one with out (best).Credit score: Wellcome Centre Human Neuroimaging/Science Picture Library
Pc algorithms which are designed to assist docs deal with other folks with schizophrenia don’t adapt smartly to contemporary, unseen information, a find out about has discovered.Such gear — which use synthetic intelligence (AI) to identify patterns in huge information units and expect how folks will reply to a selected remedy — are central to precision medication, wherein health-care pros attempt to tailor remedy to every particular person. In paintings printed on 11 January in Science1, researchers confirmed that AI fashions can expect remedy results with top accuracy for other folks in a pattern that they had been skilled on. However their efficiency drops to little higher than likelihood when implemented to subsets of the preliminary pattern, or to other information units.To be efficient, prediction fashions want to be constantly correct throughout other circumstances, with minimum bias or random results.“It’s an enormous drawback that folks have now not woken as much as,” says find out about co-author Adam Chekroud, a psychiatrist at Yale College in New Haven, Connecticut. “This find out about principally provides the evidence that algorithms want to be examined on a couple of samples.”Set of rules accuracyThe researchers assessed an set of rules this is frequently utilized in psychiatric-prediction fashions. They used information from 5 medical trials of antipsychotic medicine, involving 1,513 contributors throughout North The usa, Asia, Europe and Africa, who have been identified with schizophrenia. The rigors, which have been performed between 2004 and 2009, measured contributors’ signs sooner than and 4 weeks after taking one among 3 antipsychotic medicine (or in comparison the results of various doses of the similar drug).The workforce skilled the set of rules to expect enhancements in signs over 4 weeks of antipsychotic remedy. First, the researchers examined the set of rules’s accuracy within the trials wherein it have been advanced — evaluating its predictions with the real results recorded within the trials — and located that the accuracy used to be top.Then they used a number of approaches to guage how smartly the fashion generalizes to new information. The researchers skilled it on a subset of information from one medical trial after which implemented it to any other subset from the similar trial. Additionally they skilled the set of rules on the entire information from one trial — or a bunch of trials — after which measured its efficiency on a separate trial.The fashion carried out poorly in those exams, producing apparently virtually random predictions when implemented to a knowledge set that it had now not been skilled on. The workforce repeated the experiment the usage of a special prediction set of rules, however were given equivalent effects.Higher testingThe find out about’s authors say that their findings spotlight how medical prediction fashions will have to be examined carefully on huge information units to make certain that they’re dependable. A scientific review2 of 308 clinical-prediction fashions for psychiatric results discovered that best about 20% of fashions underwent validation on samples rather than those on which they had been advanced.“We will have to take into accounts it a lot more like drug building,” says Chekroud. Many medicine display promise in early medical trials, however falter within the later phases, he explains. “We do need to be in point of fact disciplined about how we construct those algorithms and the way we check them. We will be able to’t do exactly it as soon as and suppose it’s actual.”