A coveted study award that includes a $250,000 prize goes to a scientist who helped discover a protein’s function within the human frame’s immune defenses.Biochemist Zhijian “James” Chen, director of the Irritation Analysis Heart and a professor of molecular biology on the College of Texas Southwestern Scientific Heart, has received one in every of this 12 months’s Lasker Awards — biomedical-research prizes frequently known as the “American Nobels.”Chen led paintings that resulted within the discovery of a important enzyme — cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) — that acts like a hearth alarm within the frame. However as a substitute of being tripped by way of smoke, cGAS turns on in line with the DNA of international invaders, equivalent to viruses and micro organism. Previous to the invention of cGAS, scientists did not understand how this DNA prompt the innate immune device, the frame’s first defensive line towards international components.
cGAS: Sounding the alarm on self and international DNA – YouTube
Watch On
Ilya Mechnikov, who received a Nobel in 1908, found out phagocytosis, a phenomenon wherein one cellular gobbles up some other. That is a method that immune cells rid the frame of disease-causing micro organism. In his Nobel lecture, Mechnikov famous that bacterial DNA someway awakens a “protecting military of phagocytes” within the frame — however on the time, nobody knew how.Similar: Avi Wigderson wins $1 million Turing Award for the use of randomness to modify pc scienceLater study, carried out within the early 2000s, published that injecting cells with DNA drove a spike in interferons, immune alerts that assist forestall infections. Scientists then exposed a gaggle of genes that permits the manufacturing of those interferons, which they dubbed “stimulator of interferon genes” (STING). STING does indirectly sense international DNA, however the DNA someway turns on STING however.Beginning with a paper revealed in 2012, Chen and his collaborators in any case began filling within the lacking hyperlinks on this chain of occasions. The primary is cyclic GMP-AMP (cGAMP), a molecule that switches on STING when international DNA lurks in cells. The second one is cGAS, the enzyme that permits the cells of mammals — together with people — to make cGAMP.Get the arena’s most attractive discoveries delivered directly on your inbox.Within the frame’s early caution device, cGAS is the alarm itself, which detects international DNA and calls in reinforcements within the type of cGAMP. In flip, cGAMP recruits the “fireplace brigade” — which on this case is the innate immune device, together with the cells that gobble up invaders.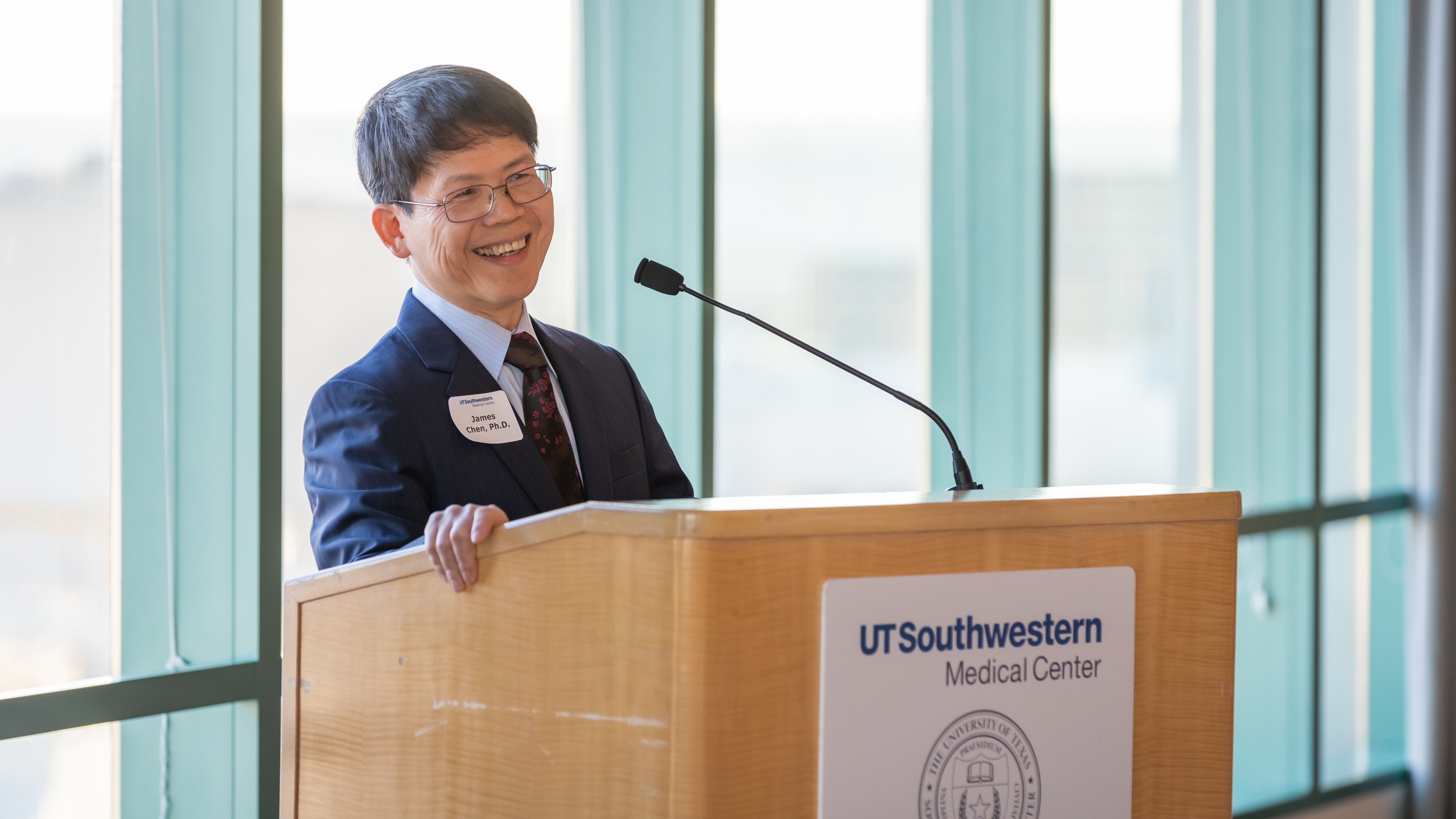 Chen leads a lab that research how cells keep in touch with their setting and inside of themselves. (Symbol credit score: UT Southwestern Scientific Heart)Chen’s crew later discovered that the program detects now not simplest DNA but additionally retroviruses, the crowd of viruses to which HIV belongs. Those viruses include RNA, a genetic cousin to DNA. HIV is a grasp of evasion in the case of dodging the innate immune device — but if the virus is detected, it is cGAS that spots it.Sadly, the cGAS alarm device is not at all times useful; within the context of a few sicknesses, it might probably cross haywire.cGAS performs a task in autoimmune sicknesses, wherein the immune device mistakenly assaults the frame. cGAS detects DNA floating round within the fluid of a cellular, which is normally an indication of an infection. Our personal human DNA is in most cases packaged smartly in compartments known as the nucleus and mitochondria — but if a cellular falls beneath pressure, that DNA can leak out and finally end up in different places within the cellular.Now we have enzymes to assist destroy down that escaped DNA, however in some folks, those enzymes do not paintings smartly. And this deficiency, Chen and co-workers have discovered, can finally end up triggering the cGAS alarm device. This hints that cGAS might be key to reining in those damaging immune responses.”cGAS has been implicated now not simplest in autoimmune stipulations, however in a lot of inflammatory sicknesses, together with age-related macular degeneration and neurological issues equivalent to Parkinson’s illness, Alzheimer illness, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis,” the Lasker Award grantees wrote in a remark. “Calming the cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway may due to this fact supply receive advantages throughout a vast span of diseases.”Chen used to be awarded the 2024 Albert Lasker Fundamental Scientific Analysis Award.Two different Lasker Awards had been awarded this 12 months — one for scientific study and one for public provider. The primary went to Joel Habener, Lotte Bjerre Knudsen and Svetlana Mojsov for his or her discovery and building of gear that mimic the hormone glucagon-like peptide 1, equivalent to Ozempic, for weight problems remedy. The second one went to Quarraisha Abdool Karim and Dr. Salim Abdool Karim, whose paintings has been instrumental in combating and treating HIV.Ever surprise why some folks construct muscle extra simply than others or why freckles pop out within the solar? Ship us your questions on how the human frame works to neighborhood@livescience.com with the topic line “Well being Table Q,” and you may even see your query spoke back at the web page!
Chen leads a lab that research how cells keep in touch with their setting and inside of themselves. (Symbol credit score: UT Southwestern Scientific Heart)Chen’s crew later discovered that the program detects now not simplest DNA but additionally retroviruses, the crowd of viruses to which HIV belongs. Those viruses include RNA, a genetic cousin to DNA. HIV is a grasp of evasion in the case of dodging the innate immune device — but if the virus is detected, it is cGAS that spots it.Sadly, the cGAS alarm device is not at all times useful; within the context of a few sicknesses, it might probably cross haywire.cGAS performs a task in autoimmune sicknesses, wherein the immune device mistakenly assaults the frame. cGAS detects DNA floating round within the fluid of a cellular, which is normally an indication of an infection. Our personal human DNA is in most cases packaged smartly in compartments known as the nucleus and mitochondria — but if a cellular falls beneath pressure, that DNA can leak out and finally end up in different places within the cellular.Now we have enzymes to assist destroy down that escaped DNA, however in some folks, those enzymes do not paintings smartly. And this deficiency, Chen and co-workers have discovered, can finally end up triggering the cGAS alarm device. This hints that cGAS might be key to reining in those damaging immune responses.”cGAS has been implicated now not simplest in autoimmune stipulations, however in a lot of inflammatory sicknesses, together with age-related macular degeneration and neurological issues equivalent to Parkinson’s illness, Alzheimer illness, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis,” the Lasker Award grantees wrote in a remark. “Calming the cGAS-cGAMP-STING pathway may due to this fact supply receive advantages throughout a vast span of diseases.”Chen used to be awarded the 2024 Albert Lasker Fundamental Scientific Analysis Award.Two different Lasker Awards had been awarded this 12 months — one for scientific study and one for public provider. The primary went to Joel Habener, Lotte Bjerre Knudsen and Svetlana Mojsov for his or her discovery and building of gear that mimic the hormone glucagon-like peptide 1, equivalent to Ozempic, for weight problems remedy. The second one went to Quarraisha Abdool Karim and Dr. Salim Abdool Karim, whose paintings has been instrumental in combating and treating HIV.Ever surprise why some folks construct muscle extra simply than others or why freckles pop out within the solar? Ship us your questions on how the human frame works to neighborhood@livescience.com with the topic line “Well being Table Q,” and you may even see your query spoke back at the web page!










/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25416369/STK473_NET_NEUTRALITY_CVIRGINIA_A.jpg)

