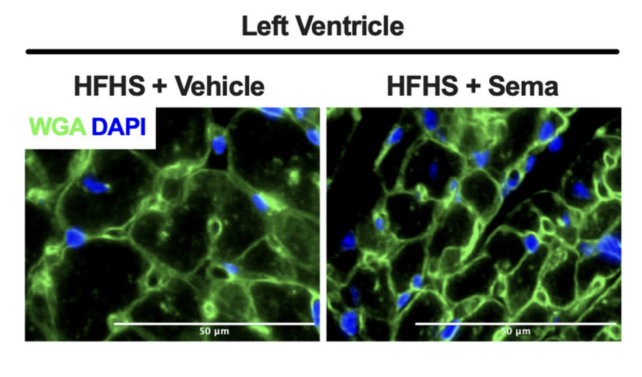
Researchers investigated 3 mysterious gadgets within the early universe. Proven listed below are their colour pictures, composited from 3 NIRCam clear out bands onboard the James Webb Area Telescope. They’re remarkably compact at crimson wavelengths (incomes them the time period “little crimson dots”), with some proof for spatial construction at blue wavelengths. Credit score: Bingjie Wang/Penn StateNASA’s James Webb Area Telescope has published mysterious gadgets within the early universe that problem present theories of galaxy and supermassive black hollow evolution.Those gadgets comprise previous stars and big black holes, a lot greater than anticipated, suggesting a speedy and unconventional type of early galaxy formation. The findings spotlight important discrepancies with current fashions, and the gadgets’ distinctive homes point out a fancy early cosmic historical past.Step forward Discovery in Early UniverseA contemporary discovery by means of NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope (JWST) showed that luminous, very crimson gadgets up to now detected within the early universe problem established concepts concerning the origins and evolution of galaxies and their supermassive black holes.Led by means of researchers from Penn State and using the NIRSpec software on JWST as a part of the RUBIES survey, the global staff known 3 enigmatic gadgets relationship again to 600-800 million years after the Giant Bang, a time when the universe was once simply 5% of its present age. They introduced the invention on June 27 within the magazine Astrophysical Magazine Letters.The scientists analyzed spectral measurements, or depth of various wavelengths of sunshine emitted from the gadgets. Their research discovered signatures of “previous” stars, masses of tens of millions of years previous, a ways older than anticipated in a tender universe.
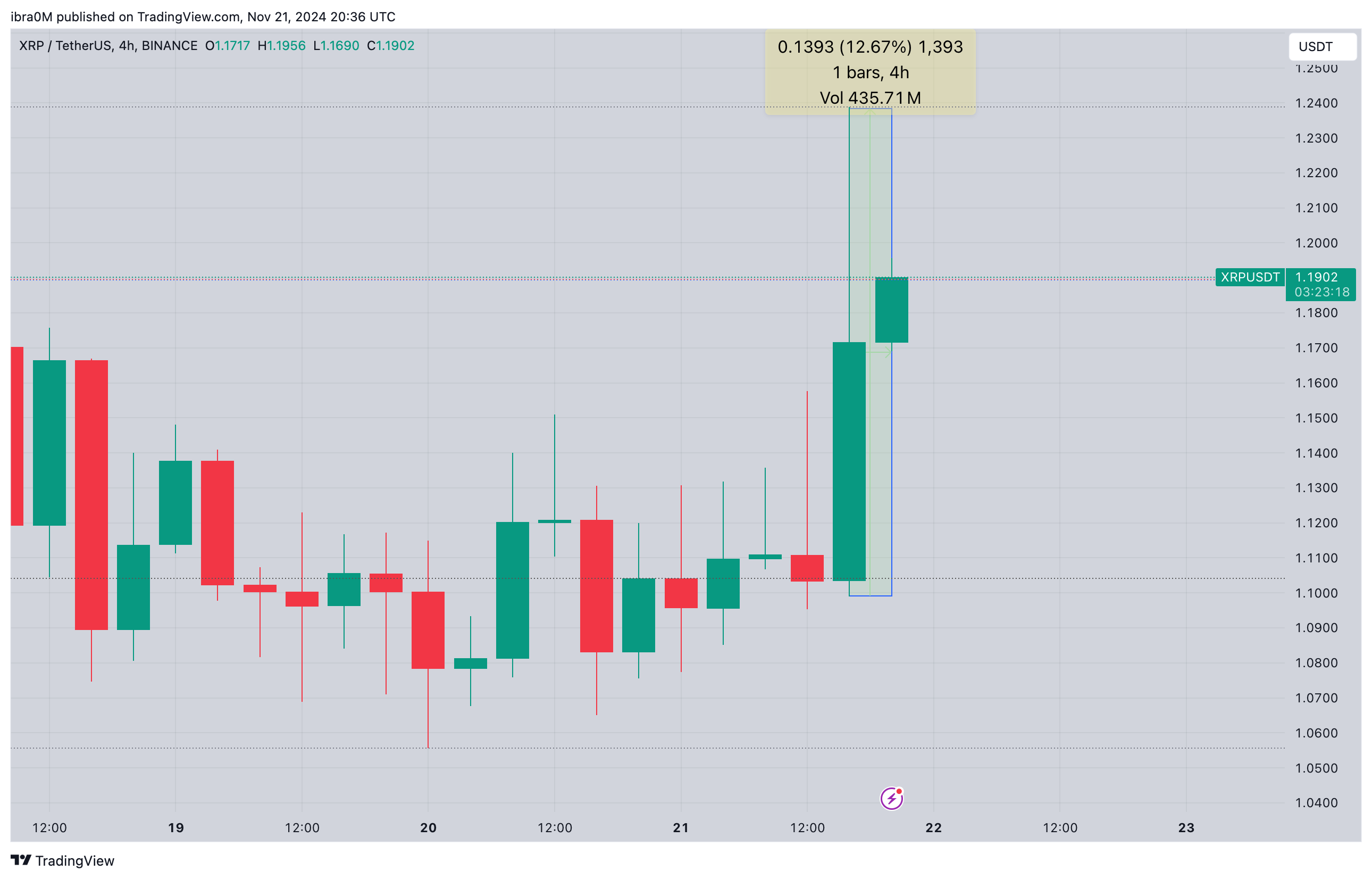
Researchers investigated 3 mysterious gadgets within the early universe. Proven listed below are their colour pictures, composited from 3 NIRCam clear out bands onboard the James Webb Area Telescope. They’re remarkably compact at crimson wavelengths (incomes them the time period “little crimson dots”), with some proof for spatial construction at blue wavelengths. Credit score: Bingjie Wang/Penn StateNASA’s James Webb Area Telescope has published mysterious gadgets within the early universe that problem present theories of galaxy and supermassive black hollow evolution.Those gadgets comprise previous stars and big black holes, a lot greater than anticipated, suggesting a speedy and unconventional type of early galaxy formation. The findings spotlight important discrepancies with current fashions, and the gadgets’ distinctive homes point out a fancy early cosmic historical past.Step forward Discovery in Early UniverseA contemporary discovery by means of NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope (JWST) showed that luminous, very crimson gadgets up to now detected within the early universe problem established concepts concerning the origins and evolution of galaxies and their supermassive black holes.Led by means of researchers from Penn State and using the NIRSpec software on JWST as a part of the RUBIES survey, the global staff known 3 enigmatic gadgets relationship again to 600-800 million years after the Giant Bang, a time when the universe was once simply 5% of its present age. They introduced the invention on June 27 within the magazine Astrophysical Magazine Letters.The scientists analyzed spectral measurements, or depth of various wavelengths of sunshine emitted from the gadgets. Their research discovered signatures of “previous” stars, masses of tens of millions of years previous, a ways older than anticipated in a tender universe. The James Webb Area Telescope (JWST) provides a window into the cosmos’ far away previous, taking pictures pictures of the universe’s first galaxies and stars that shaped over 13.5 billion years in the past. Credit score: NASA-GSFC, Adriana M. Gutierrez (CI Lab)Sudden Findings in Galactic EvolutionThe researchers stated they had been additionally stunned to find signatures of large supermassive black holes in the similar gadgets, estimating that they’re 100 to at least one,000 occasions extra huge than the supermassive black hollow in our personal Milky Manner. Neither of those is anticipated in present fashions of galaxy expansion and supermassive black hollow formation, which be expecting galaxies and their black holes to develop in combination over billions of years of cosmic historical past.“We now have showed that those seem to be full of historical stars — masses of tens of millions of years previous — in a universe this is most effective 600-800 million years previous. Remarkably, those gadgets hang the report for the earliest signatures of previous starlight,” stated Bingjie Wang, a postdoctoral pupil at Penn State and lead writer at the paper. “It was once completely sudden to seek out previous stars in an overly younger universe. The usual fashions of cosmology and galaxy formation were extremely a success, but, those luminous gadgets don’t rather are compatible conveniently into the ones theories.”The researchers first noticed the large gadgets in July of 2022, when the preliminary dataset was once launched from JWST. The staff printed a paper in Nature a number of months later saying the gadgets’ lifestyles.Demanding situations in Cosmic ObservationAt the time, the researchers suspected the gadgets had been galaxies, however adopted up their research by means of taking spectra to raised perceive the actual distances of the gadgets, in addition to the assets powering their immense mild.The researchers then used the brand new knowledge to attract a clearer image of what the galaxies gave the look of and what was once within them. Now not most effective did the staff verify that the gadgets had been certainly galaxies close to the start of time, however in addition they discovered proof of unusually massive supermassive black holes and a shockingly previous inhabitants of stars.“It’s very complicated,” stated Joel Leja, assistant professor of astronomy and astrophysics at Penn State and co-author on each papers. “You’ll be able to make this uncomfortably are compatible in our present fashion of the universe, however provided that we evoke some unique, insanely speedy formation at the start of time. That is, certainly, essentially the most strange and fascinating set of gadgets I’ve noticed in my profession.”
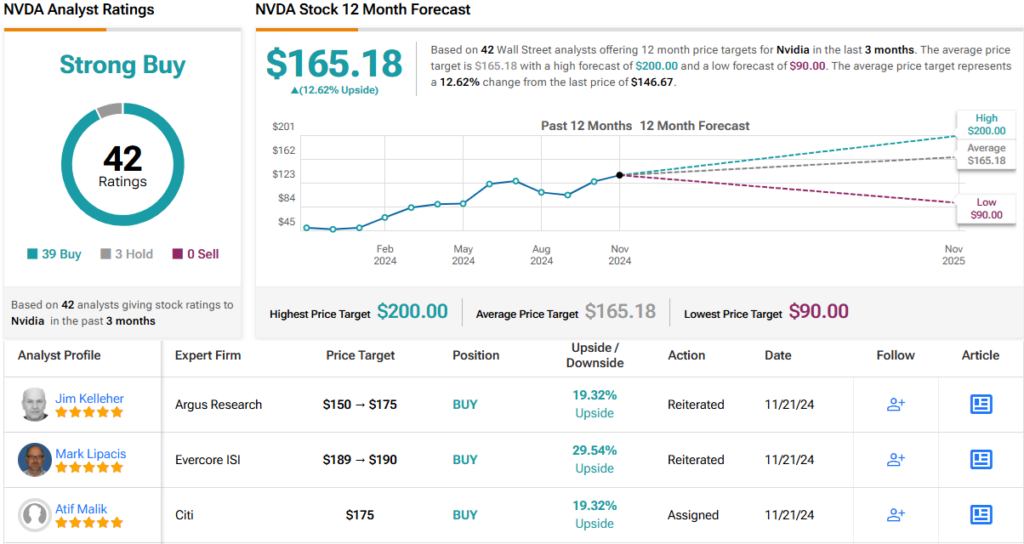
The James Webb Area Telescope (JWST) provides a window into the cosmos’ far away previous, taking pictures pictures of the universe’s first galaxies and stars that shaped over 13.5 billion years in the past. Credit score: NASA-GSFC, Adriana M. Gutierrez (CI Lab)Sudden Findings in Galactic EvolutionThe researchers stated they had been additionally stunned to find signatures of large supermassive black holes in the similar gadgets, estimating that they’re 100 to at least one,000 occasions extra huge than the supermassive black hollow in our personal Milky Manner. Neither of those is anticipated in present fashions of galaxy expansion and supermassive black hollow formation, which be expecting galaxies and their black holes to develop in combination over billions of years of cosmic historical past.“We now have showed that those seem to be full of historical stars — masses of tens of millions of years previous — in a universe this is most effective 600-800 million years previous. Remarkably, those gadgets hang the report for the earliest signatures of previous starlight,” stated Bingjie Wang, a postdoctoral pupil at Penn State and lead writer at the paper. “It was once completely sudden to seek out previous stars in an overly younger universe. The usual fashions of cosmology and galaxy formation were extremely a success, but, those luminous gadgets don’t rather are compatible conveniently into the ones theories.”The researchers first noticed the large gadgets in July of 2022, when the preliminary dataset was once launched from JWST. The staff printed a paper in Nature a number of months later saying the gadgets’ lifestyles.Demanding situations in Cosmic ObservationAt the time, the researchers suspected the gadgets had been galaxies, however adopted up their research by means of taking spectra to raised perceive the actual distances of the gadgets, in addition to the assets powering their immense mild.The researchers then used the brand new knowledge to attract a clearer image of what the galaxies gave the look of and what was once within them. Now not most effective did the staff verify that the gadgets had been certainly galaxies close to the start of time, however in addition they discovered proof of unusually massive supermassive black holes and a shockingly previous inhabitants of stars.“It’s very complicated,” stated Joel Leja, assistant professor of astronomy and astrophysics at Penn State and co-author on each papers. “You’ll be able to make this uncomfortably are compatible in our present fashion of the universe, however provided that we evoke some unique, insanely speedy formation at the start of time. That is, certainly, essentially the most strange and fascinating set of gadgets I’ve noticed in my profession.” JWST is designed to watch phenomena that came about simply after the Giant Bang, the usage of its complex infrared functions to look via cosmic mud and discover hidden buildings in area. Credit score: Northrop GrummanMysteries of Historic Galactic StructuresThe JWST is provided with infrared-sensing tools able to detecting mild that was once emitted by means of essentially the most historical stars and galaxies. Necessarily, the telescope permits scientists to look again in time more or less 13.5 billion years, close to the start of the universe as we realize it, Leja stated.One problem to examining historical mild is that it may be laborious to tell apart between the sorts of gadgets that may have emitted the sunshine. On the subject of those early gadgets, they have got transparent traits of each supermassive black holes and previous stars. On the other hand, Wang defined, it’s now not but transparent how a lot of the seen mild comes from each and every – that means those might be early galaxies which can be impulsively previous and extra huge even than our personal Milky Manner, forming a ways previous than fashions expect, or they might be extra normal-mass galaxies with “overmassive” black holes, more or less 100 to at least one,000 occasions extra huge than the sort of galaxy would have lately.“Distinguishing between mild from subject material falling right into a black hollow and lightweight emitted from stars in those tiny, far away gadgets is difficult,” Wang stated. “That incapacity to inform the variation within the present dataset leaves abundant room for interpretation of those intriguing gadgets. In truth, it’s exciting to have such a lot of this thriller left to determine.”Excluding their unexplainable mass and age, if a part of the sunshine is certainly from supermassive black holes, then in addition they aren’t standard supermassive black holes. They produce way more ultraviolet photons than anticipated, and equivalent gadgets studied with different tools lack the feature signatures of supermassive black holes, corresponding to scorching mud and brilliant X-ray emission. However perhaps essentially the most unexpected factor, the researchers stated, is how huge they appear to be.“In most cases supermassive black holes are paired with galaxies,” Leja stated. “They develop up in combination and undergo all their main existence studies in combination. However right here, now we have a completely shaped grownup black hollow residing within what must be a child galaxy. That doesn’t actually make sense, as a result of these items must develop in combination, or no less than that’s what we concept.”The researchers had been additionally puzzled by means of the extremely small sizes of those programs, just a few hundred mild years throughout, more or less 1,000 occasions smaller than our personal Milky Manner. The celebs are roughly as a large number of as in our personal Milky Manner galaxy — with someplace between 10 billion and 1 trillion stars — however contained inside of a quantity 1,000 occasions smaller than the Milky Manner.Leja defined that for those who took the Milky Manner and compressed it to the dimensions of the galaxies they discovered, the closest celebrity would virtually be in our sun gadget. The supermassive black hollow within the middle of the Milky Manner, about 26,000 mild years away, would most effective be about 26 mild years clear of Earth and visual within the sky as a large pillar of sunshine.“Those early galaxies can be so dense with stars — stars that should have shaped in some way we’ve by no means noticed, underneath prerequisites we’d by no means be expecting right through a duration during which we’d by no means be expecting to look them,” Leja stated. “And for no matter reason why, the universe stopped making gadgets like those after simply a few billion years. They’re distinctive to the early universe.”The researchers are hoping to practice up with extra observations, which they stated may lend a hand provide an explanation for one of the most gadgets’ mysteries. They plan to take deeper spectra by means of pointing the telescope on the gadgets for extended sessions of time, which can lend a hand disentangle emission from stars and the prospective supermassive black hollow by means of figuring out the particular absorption signatures that will be found in each and every.“There’s otherwise that we may have a leap forward, and that’s simply the fitting thought,” Leja stated. “We now have a majority of these puzzle items and so they most effective are compatible if we forget about the truth that a few of them are breaking. This downside is amenable to a stroke of genius that has to this point eluded us, all of our collaborators and all of the medical neighborhood.”Reference: “RUBIES: Developed Stellar Populations with Prolonged Formation Histories at z ∼ 7–8 in Candidate Large Galaxies Recognized with JWST/NIRSpec” by means of Bingjie Wang, 冰洁 王, Joel Leja, Anna de Graaff, Gabriel B. Brammer, Andrea Weibel, Pieter van Dokkum, Josephine F. W. Baggen, Katherine A. Suess, Jenny E. Greene, Rachel Bezanson, Nikko J. Cleri, Michaela Hirschmann, Ivo Labbé, Jorryt Matthee, Ian McConachie, Rohan P. Naidu, Erica Nelson, Pascal A. Oesch, David J. Setton and Christina C. Williams, 26 June 2024, The Astrophysical Magazine Letters.
JWST is designed to watch phenomena that came about simply after the Giant Bang, the usage of its complex infrared functions to look via cosmic mud and discover hidden buildings in area. Credit score: Northrop GrummanMysteries of Historic Galactic StructuresThe JWST is provided with infrared-sensing tools able to detecting mild that was once emitted by means of essentially the most historical stars and galaxies. Necessarily, the telescope permits scientists to look again in time more or less 13.5 billion years, close to the start of the universe as we realize it, Leja stated.One problem to examining historical mild is that it may be laborious to tell apart between the sorts of gadgets that may have emitted the sunshine. On the subject of those early gadgets, they have got transparent traits of each supermassive black holes and previous stars. On the other hand, Wang defined, it’s now not but transparent how a lot of the seen mild comes from each and every – that means those might be early galaxies which can be impulsively previous and extra huge even than our personal Milky Manner, forming a ways previous than fashions expect, or they might be extra normal-mass galaxies with “overmassive” black holes, more or less 100 to at least one,000 occasions extra huge than the sort of galaxy would have lately.“Distinguishing between mild from subject material falling right into a black hollow and lightweight emitted from stars in those tiny, far away gadgets is difficult,” Wang stated. “That incapacity to inform the variation within the present dataset leaves abundant room for interpretation of those intriguing gadgets. In truth, it’s exciting to have such a lot of this thriller left to determine.”Excluding their unexplainable mass and age, if a part of the sunshine is certainly from supermassive black holes, then in addition they aren’t standard supermassive black holes. They produce way more ultraviolet photons than anticipated, and equivalent gadgets studied with different tools lack the feature signatures of supermassive black holes, corresponding to scorching mud and brilliant X-ray emission. However perhaps essentially the most unexpected factor, the researchers stated, is how huge they appear to be.“In most cases supermassive black holes are paired with galaxies,” Leja stated. “They develop up in combination and undergo all their main existence studies in combination. However right here, now we have a completely shaped grownup black hollow residing within what must be a child galaxy. That doesn’t actually make sense, as a result of these items must develop in combination, or no less than that’s what we concept.”The researchers had been additionally puzzled by means of the extremely small sizes of those programs, just a few hundred mild years throughout, more or less 1,000 occasions smaller than our personal Milky Manner. The celebs are roughly as a large number of as in our personal Milky Manner galaxy — with someplace between 10 billion and 1 trillion stars — however contained inside of a quantity 1,000 occasions smaller than the Milky Manner.Leja defined that for those who took the Milky Manner and compressed it to the dimensions of the galaxies they discovered, the closest celebrity would virtually be in our sun gadget. The supermassive black hollow within the middle of the Milky Manner, about 26,000 mild years away, would most effective be about 26 mild years clear of Earth and visual within the sky as a large pillar of sunshine.“Those early galaxies can be so dense with stars — stars that should have shaped in some way we’ve by no means noticed, underneath prerequisites we’d by no means be expecting right through a duration during which we’d by no means be expecting to look them,” Leja stated. “And for no matter reason why, the universe stopped making gadgets like those after simply a few billion years. They’re distinctive to the early universe.”The researchers are hoping to practice up with extra observations, which they stated may lend a hand provide an explanation for one of the most gadgets’ mysteries. They plan to take deeper spectra by means of pointing the telescope on the gadgets for extended sessions of time, which can lend a hand disentangle emission from stars and the prospective supermassive black hollow by means of figuring out the particular absorption signatures that will be found in each and every.“There’s otherwise that we may have a leap forward, and that’s simply the fitting thought,” Leja stated. “We now have a majority of these puzzle items and so they most effective are compatible if we forget about the truth that a few of them are breaking. This downside is amenable to a stroke of genius that has to this point eluded us, all of our collaborators and all of the medical neighborhood.”Reference: “RUBIES: Developed Stellar Populations with Prolonged Formation Histories at z ∼ 7–8 in Candidate Large Galaxies Recognized with JWST/NIRSpec” by means of Bingjie Wang, 冰洁 王, Joel Leja, Anna de Graaff, Gabriel B. Brammer, Andrea Weibel, Pieter van Dokkum, Josephine F. W. Baggen, Katherine A. Suess, Jenny E. Greene, Rachel Bezanson, Nikko J. Cleri, Michaela Hirschmann, Ivo Labbé, Jorryt Matthee, Ian McConachie, Rohan P. Naidu, Erica Nelson, Pascal A. Oesch, David J. Setton and Christina C. Williams, 26 June 2024, The Astrophysical Magazine Letters.
DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/ad55f7Wang and Leja won investment from NASA’s Normal Observers program. The analysis was once additionally supported by means of the World Area Science Institute in Bern. The paintings is based totally partially on observations made with the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Area Telescope. Computations for the analysis had been carried out on Penn State’s Institute for Computational and Information Sciences’ Roar supercomputer.Different co-authors at the paper are Anna de Graaff of the Max-Planck-Institut für Astronomie in Germany; Gabriel Brammer of the Cosmic Crack of dawn Heart and Niels Bohr Institute; Andrea Weibel and Pascal Oesch of the College of Geneva; Nikko Cleri, Michaela Hirschmann, Pieter van Dokkum and Rohan Naidu of Yale College; Ivo Labbé of Stanford College; Jorryt Matthee and Jenny Greene of Princeton College; Ian McConachie and Rachel Bezanson of the College of Pittsburgh; Josephine Baggen of Texas A&M College; Katherine Suess of the Observatoire de Sauverny in Switzerland; David Setton of Massachusetts Institute of Generation’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Area Analysis; Erica Nelson of the College of Colorado; Christina Williams of the U.S. Nationwide Science Basis’s Nationwide Optical-Infrared Astronomy Analysis Laboratory and the College of Arizona.
Scientists Baffled: Webb Uncovers Historic Galaxies That Defy Clarification