Scientists have used a brand new approach to synthesize diamonds at standard, atmospheric strain and with no starter gem, which might make the valuable gems a lot more straightforward to develop within the lab. Herbal diamonds shape in Earth’s mantle, the molten zone buried loads of miles underneath the planet’s floor. The method takes position beneath super pressures of a number of gigapascals and sizzling temperatures exceeding 2,700 levels Fahrenheit (1,500 levels Celsius).Identical stipulations are hired within the means these days used to synthesize 99% of all artificially created diamonds. Referred to as high-pressure and high-temperature (HPHT) enlargement, this technique makes use of those excessive settings to coax carbon dissolved in liquid metals, like iron, to transform it to diamond round a small seed, or starter diamond. On the other hand, the excessive pressures and temperatures are tough to provide and deal with. Plus, the elements concerned have an effect on the diamonds’ measurement, with the biggest being a few cubic centimeter, or about as large as a blueberry. But even so, HPHT takes a slightly very long time — per week or two — to provide even those tiny gemstones. Any other means, known as chemical vapor deposition, removes some necessities of HPHT, like excessive pressures. However others persist, like the will for seeds.The brand new methodology removes some drawbacks of each synthesis processes. A group led by way of Rodney Ruoff, a bodily chemist on the Institute for Fundamental Science in South Korea, printed their findings April 24 within the magazine Nature. Similar: Scientists can have pinpointed the actual beginning of the Hope Diamond and different pristine gemstonesThe diamond crucibleThe novel means was once a very long time within the making. “For over a decade I’ve been enthusiastic about new techniques to develop diamonds, as I believed it could be imaginable to succeed in this in what could be sudden (in line with ‘standard’ pondering) techniques,” Ruoff instructed Are living Science by way of electronic mail.Get the sector’s most attractive discoveries delivered directly in your inbox.To begin out, the researchers used electrically heated gallium with somewhat of silicon in a graphite crucible. Gallium might appear to be an esoteric part, nevertheless it was once decided on as a result of a prior, unrelated learn about confirmed that it would catalyze the formation of graphene from methane. Graphene, like diamond, is natural carbon, nevertheless it comprises the atoms in a single layer moderately than within the gemstone’s tetrahedral orientation. The researchers housed the crucible in a home-built chamber maintained at sea-level atmospheric strain, wherein superhot, carbon-rich methane gasoline might be flushed. Designed by way of co-author Received Kyung Seong, additionally of the Institute for Fundamental Science, this 2.4-gallon (9 liters) chamber might be readied for experimentation in simply quarter-hour, permitting the group to all of a sudden adopt runs with other concentrations of metals and gases. Via such tweaking, the researchers figured {that a} gallium-nickel-iron combination — coupled with a pinch of silicon — was once optimum for catalyzing the expansion of diamonds. Certainly, with this mix, the group received diamonds from the crucible’s base after simply quarter-hour. Inside of two and a part hours, a extra whole diamond movie shaped. Spectroscopic analyses confirmed that this movie was once in large part natural however contained a couple of silicon atoms.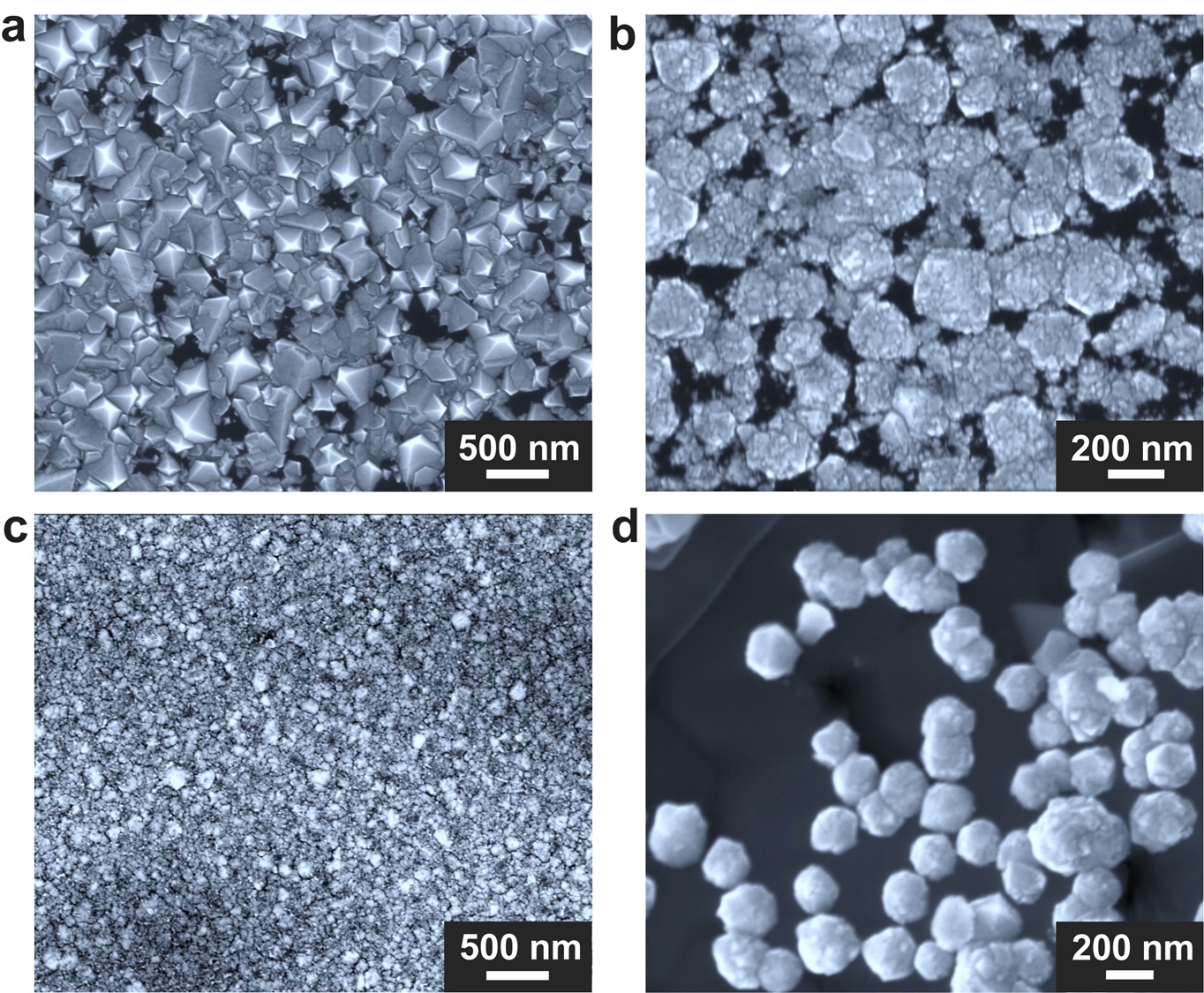 Diamonds made with the brand new methodology are most commonly natural — however they are too tiny to suit to your finger. (Symbol credit score: Institute for Fundamental Science)The trivialities of the mechanism that shaped the diamonds are nonetheless in large part murky, however the researchers suppose a temperature drop drives carbon from the methane towards the crucible’s middle, the place it coalesces into diamond. Plus, with out silicon, no diamonds shape, so the researchers suppose it is going to act as a seed for the carbon to crystallize round. On the other hand, the brand new means has its personal demanding situations. One drawback is that the diamonds grown with this method are tiny; the biggest ones are loads of hundreds of occasions smaller than those grown with HPHT. That makes them too small for use as jewels.Different doable makes use of — for instance, in additional technological packages like sharpening and drilling — for the diamonds synthesized with the brand new methodology are unclear. On the other hand, for the reason that procedure comes to low strain, Ruoff mentioned, it would considerably scale up diamond synthesis. “In a few yr or two, the sector may have a clearer image of such things as imaginable industrial affect,” he added.
Diamonds made with the brand new methodology are most commonly natural — however they are too tiny to suit to your finger. (Symbol credit score: Institute for Fundamental Science)The trivialities of the mechanism that shaped the diamonds are nonetheless in large part murky, however the researchers suppose a temperature drop drives carbon from the methane towards the crucible’s middle, the place it coalesces into diamond. Plus, with out silicon, no diamonds shape, so the researchers suppose it is going to act as a seed for the carbon to crystallize round. On the other hand, the brand new means has its personal demanding situations. One drawback is that the diamonds grown with this method are tiny; the biggest ones are loads of hundreds of occasions smaller than those grown with HPHT. That makes them too small for use as jewels.Different doable makes use of — for instance, in additional technological packages like sharpening and drilling — for the diamonds synthesized with the brand new methodology are unclear. On the other hand, for the reason that procedure comes to low strain, Ruoff mentioned, it would considerably scale up diamond synthesis. “In a few yr or two, the sector may have a clearer image of such things as imaginable industrial affect,” he added.












