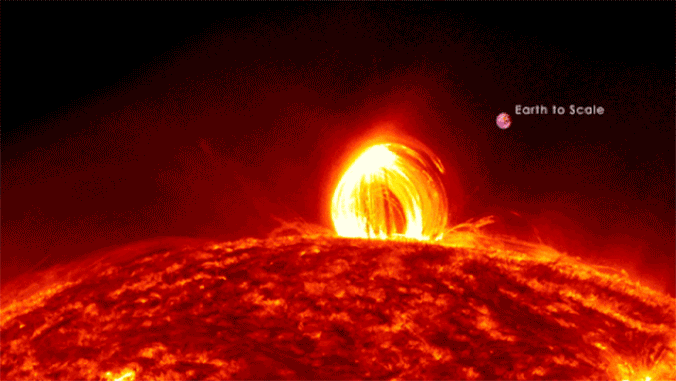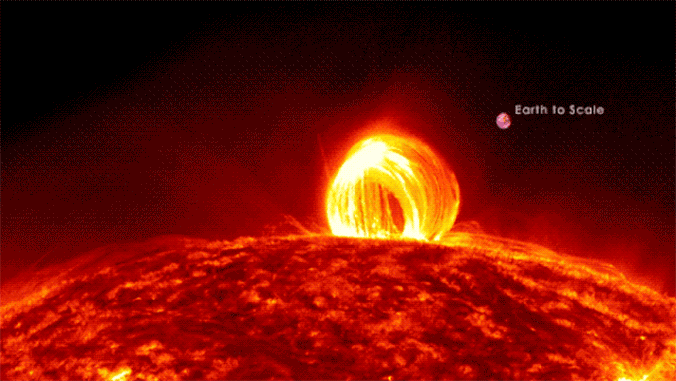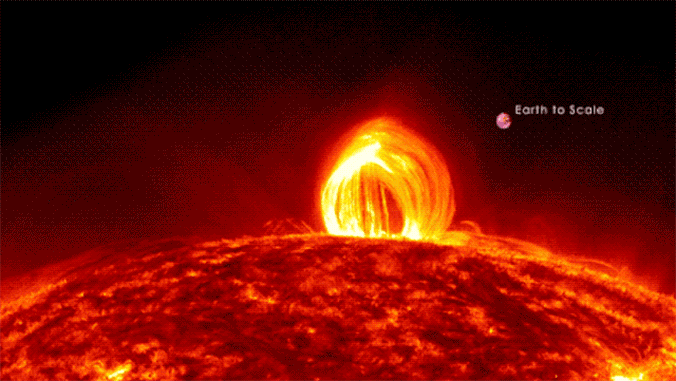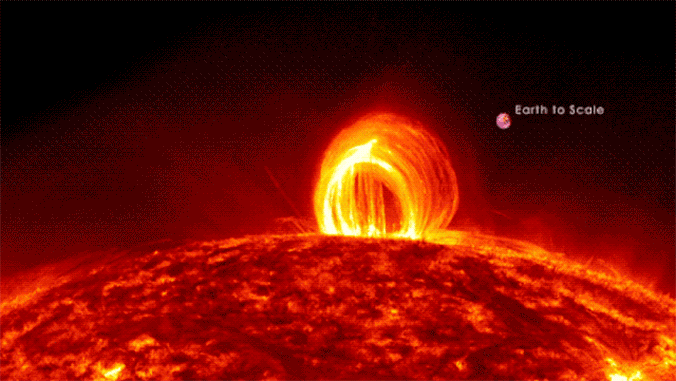
Scientists could have solved the physics in the back of large and violent “superflares” that rip unfastened from stars hundreds of instances as vivid because the solar.Our host megastar steadily erupts with sun flares that may affect Earth and, if sturdy sufficient, disrupt communications and tool infrastructure on a world scale. However those sun flares are mere kid’s tantrums in comparison to the hundreds of “superflares” that NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite tv for pc (TESS) and now defunct Kepler house telescopes have observed blasting from stars between 100 and 10,000 instances brighter than the solar. Superflaring stars have more potent magnetic fields than the solar, resulting in brighter flares, and those stars additionally appear to show an preliminary, short-lived spice up in brightness enhancement, adopted through a secondary, longer-lasting (however much less intense) flare.But regardless of this disparity in scale and tool, the superflares of vivid, far-off stars and the sun flares of the solar are believed to percentage the similar underlying bodily mechanisms, rising from the unexpected free up of magnetic power. Thus, a group of scientists led through College of Hawaii Institute for Astronomy Postdoctoral Researcher Kai Yang and Affiliate Professor Xudong Solar used sun flares as a proxy for superflares to fashion those large eruptions of plasma.Comparable: Gigantic ‘hollow’ within the solar wider than 60 Earths is spewing superfast sun wind proper at us”Via making use of what we’ve got realized concerning the solar to different, cooler stars, we had been in a position to spot the physics using those flares, although shall we by no means see them immediately,” group co-leader and College of Hawaii Institute for Astronomy Postdoctoral Researcher Kai Yang stated in a commentary. “The converting brightness of those stars over the years in fact helped us ‘see’ those flares which might be truly some distance too small to watch immediately.” Protecting scientists within the loopScientists have theorized that coronal loops, which can be large hoops of plasma that observe the trajectory of magnetic box strains observed at the solar, could also be found in superflares as smartly. In the event that they exist, alternatively, those loops would want to be extremely dense at the superflaring stars; as of but, astrophysicists had been not able to check this concept. From our vantage level on Earth, we will handiest witness coronal loops at the solar.However any other function may just trace on the presence of those far-off stars’ coronal loops, the group says.Particularly, Kepler and TESS have noticed some stars with a bizarre “bump” in related gentle curves. This “top bump,” as it is referred to as, turns out to constitute a leap in brightness and lead to a gentle curve that resembles a phenomenon observed at the solar when an preliminary burst of sunshine is adopted through a 2d, extra slow peaking of the sunshine — a phenomenon referred to as “sun late-phase flares.”Solar, Yang and fellow colleagues sought after to grasp if those presumed late-phase brightness improvements in visual gentle on far-off stars might be led to through large stellar loops just like the solar’s coronal loops motive our megastar to change in brightness. To check this principle, the group became to pc simulations of fluids that mimicked coronal loops, periodically upping the period of the loops and extending the magnetic power in the back of.The group discovered that giant flare energies would pump extra mass into those loops on brighter stars, expanding their density simply as predicted. This could certainly permit dense stellar loops to give a contribution to visual gentle emissions. And, the scientists concluded, with an extended evolutionary timescale, the loops would certainly produce a definite, secondary emission top — simply as observed in gentle curves accrued through TESS and Kepler. The group additional discovered that the overdue time “bump” flaring of sunshine observed within the gentle spectrums of far-off, flaring stars will be the results of super-hot plasma on the best issues of related coronal loops at the stars cooling down, then falling again to the megastar as sparkling subject material. In flip, that entire procedure would result in the ambience heating up.The group believes this discovering helps their fashion as a result of it’s analogous to the coronal rains observed falling from coronal loops that motive the solar’s personal surroundings to warmth up.The group’s analysis used to be revealed on Dec. 6 in The Astrophysical Magazine.
Scientists find out about violent ‘superflares’ on stars hundreds of instances brighter than the solar