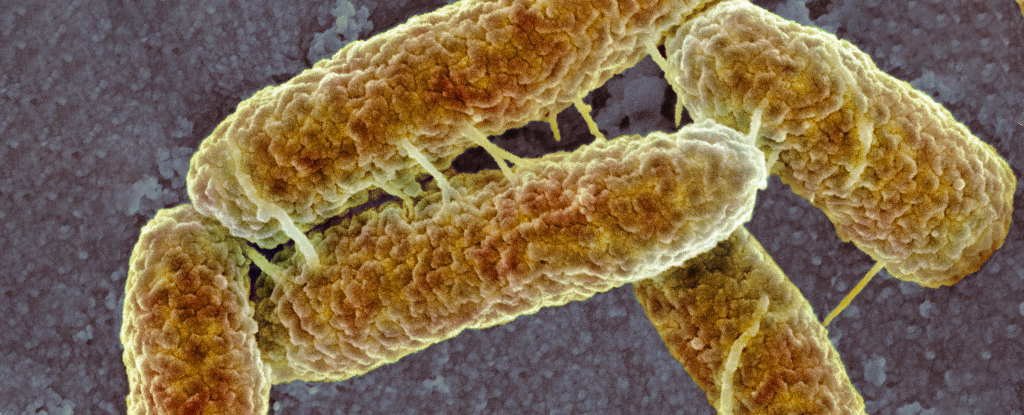
Micro organism can broaden a heightened new sensitivity to acid ranges when uncovered to other environmental extremes within the laboratory, a brand new find out about displays.This feeling triggers a cascade of various gene expression, permitting the microbes to reconfigure themselves to the repeatedly converting extremes.
From the smallest cells to the most important whales, all existence faces the problem of ever-shifting and biking environmental prerequisites.
To raised know the way we will physiologically bend to such extremes, microbiologist Sarah Worthan from Vanderbilt College in Nashville and her workforce driven Escherichia coli micro organism to the extraordinary.
One of the most micro organism populations have been ready to briefly evolve genetic mutations that helped them thrive. Cancers employ the ensuing mutations too, to create themselves a extra favorable surroundings.
“Our effects recommend [these mutations] would possibly serve to hastily coordinate advanced physiological responses thru pH sensing and make clear how cell populations use environmental cues to coordinate fast responses to advanced, fluctuating environments,” the researchers write of their paper.
Worthan and co-workers created their intense experimental model of environmental shifts by way of exposing 16 populations of E. coli to bouts of utmost, long-term hunger prior to moving them right into a contemporary nutrient-rich surroundings and repeating the method.
Because the microbes starved, metabolic waste accrued, inflicting drastic adjustments of their environmental pH. The micro organism have been then given a contemporary get started with new sources each and every 100 days, replicating the ceremonial dinner and famine cycle existence regularly faces in the true international.
A unmarried protein development block exchange sprung up and unfold in seven of the micro organism populations, most commonly inside of handiest the primary 300 days of the experiment. This amino acid exchange from an arginine to a histidine took place within the Rho protein – a molecule fascinated about telling the micro organism’s protein-making equipment when to stop manufacturing.
“This mutation in rho many times arose in our laboratory evolution cultures,” explains Vanderbilt College microbiologist Megan Behringer.
“We returned to our genomic information and spotted that each and every mutation in rho co-occurred with a mutation in a gene named ‘ydcI.’ No longer a lot is understood about this gene, however very fresh research advised that it is going to have a task in pH homeostasis.”
The traditional Rho protein is helping the micro organism cells to do higher in ceremonial dinner situation, however is a hindrance when its proprietor faces famine. Worthan and workforce discovered mutated ydcI allowed cells to higher tolerate adjustments within the Rho protein.
The ydcI mutation seems to be responding to adjustments in pH. So it acts as a transfer grew to become on by way of adjustments within the surroundings to cause adjustments inside of particular person cells.
“Even if micro organism have interaction with each and every different thru their extracellular surroundings, particular person cells have some keep an eye on over their intracellular environments,” says Bratton.
Those genes paintings in combination to permit the cells to extra simply bend physiologically to the repeatedly moving environmental prerequisites. The workforce discovered a number of examples of the similar mechanism in nature.
“We discovered it on this disregarded pathogen, Bartonella bacilliformis, which reasons Carrion’s Illness within the Andean valleys of South The us,” says Behringer.
“This species of micro organism was once already recognized to pH sense because it will have to hastily modify from the top pH insect intestine to the impartial pH of human blood when it is transmitted by way of its sand fly vector.”
Being just right at adapting like this is helping cells outcompete others, as we see with most cancers. Cancers seem to use a identical mechanism to extend their inside pH too, making a cascade of various gene expression which can be then used to reshape the cell surroundings round them.
Those effects illustrate “the facility of experimental evolution for figuring out functionally vital mutations related to herbal environments,” Worthan and workforce conclude.This analysis was once revealed in PNAS.
Scientists Grew Microbes in a Lab Experiment, And They Developed a New Sense