The best way we take into consideration lightning has a tendency to be rather directional. It arcs down from the sky in cracking streams of electrical energy, the very image of the may of the typhoon.However downward is not all the time how lightning is going, and scientists have simply made a primary size that may assist us perceive the best way this tough drive of nature bureaucracy.
In a undeniable form of lightning that moves upward in opposition to the sky known as upward sure flashes, a staff led through astrophysicist Toma Oregel-Chaumont of the Swiss Federal Institute of Era (EPFL) has at once detected and measured the emission of X-rays.
Upward sure flashes are one of those lightning that begins with negatively charged leaders at some extent of excessive altitude, and ascends stepwise into the sky to connect to a thundercloud sooner than moving a favorable rate to the bottom. And the detection of X-radiation may assist mitigate the wear and tear led to through lightning around the globe.
“At sea stage, upward flashes are uncommon, however may change into the dominant sort at excessive altitudes,” Oregel-Chaumont says. “Additionally they have the prospective to be extra harmful, as a result of in an upward flash, lightning stays involved with a construction for longer than it does all the way through a downward flash, giving it extra time to switch electric rate.”
X-rays are a recognized accompaniment to lightning. We’ve got detected them in downward, cloud-to-ground lightning, and in lightning precipitated through rockets, in each instances all the way through the downward detrimental dart-leader segment. And it is been detected within the dart chief segment of upward detrimental lightning.
However the detection of X-rays within the dart chief segment of 4 flashes of upward sure lightning erupting from the Säntis Tower in Switzerland, Oregel-Chaumont and their staff say, is a brand new device for working out lightning.
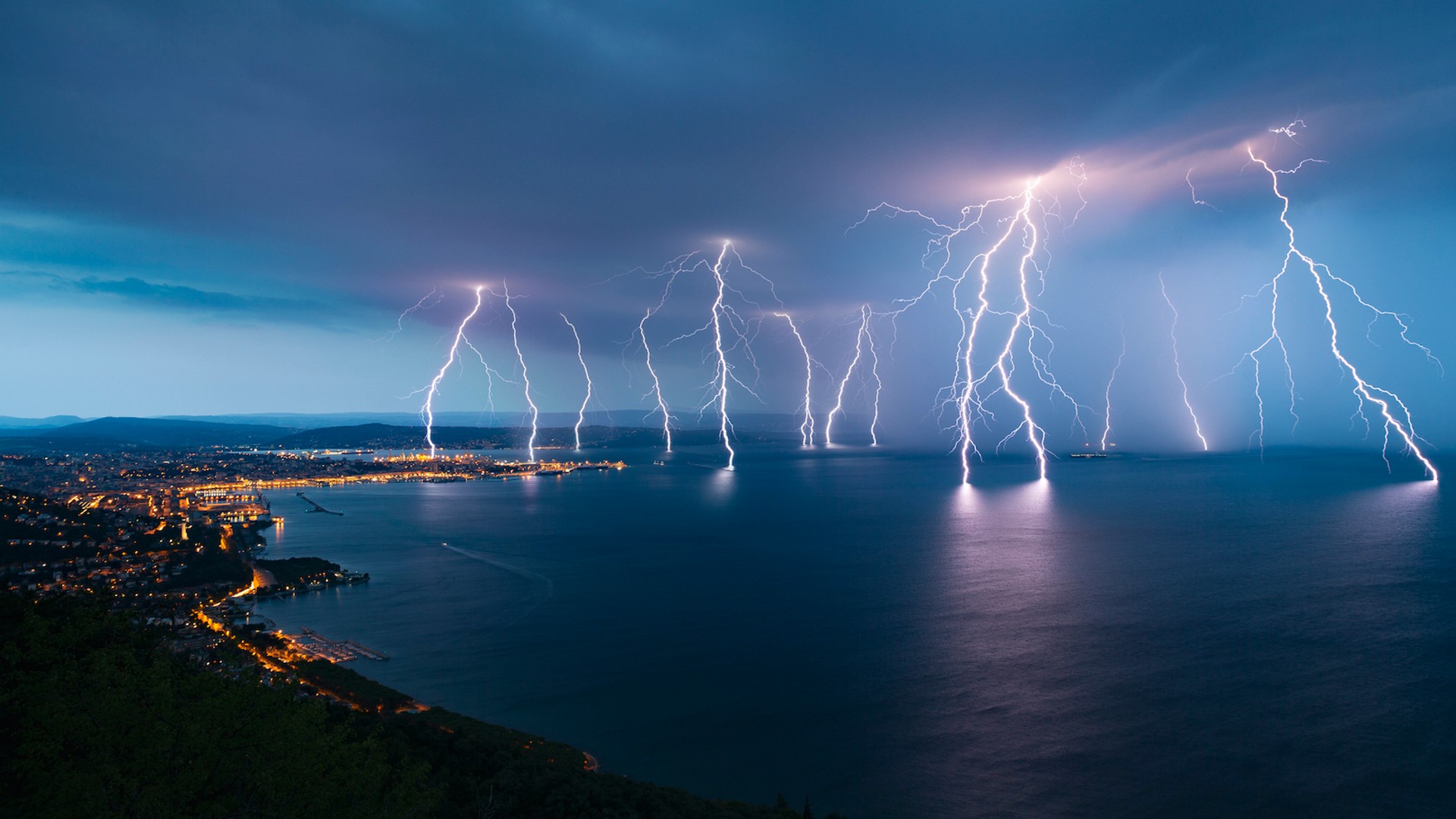
“The real mechanism during which lightning initiates and propagates continues to be a thriller,” they give an explanation for. “The commentary of upward lightning from tall constructions just like the Säntis tower makes it conceivable to correlate X-ray measurements with different concurrently measured amounts, like high-speed video observations and electrical currents.” Säntis Tower within the Appenzell Alps. (EPFL)Säntis Tower is remarkably located for the find out about of lightning. Designed and used as a telecommunications tower and climate tracking station, the 124-meter-high (407-foot) construction sits atop the two,502-meter (8,209-foot) Mount Säntis within the Appenzell Alps.
Säntis Tower within the Appenzell Alps. (EPFL)Säntis Tower is remarkably located for the find out about of lightning. Designed and used as a telecommunications tower and climate tracking station, the 124-meter-high (407-foot) construction sits atop the two,502-meter (8,209-foot) Mount Säntis within the Appenzell Alps.
Jutting like a finger into the sky, it is a top goal for lightning; certainly, bolts of electrical energy strike it round 100 occasions a yr.
As a result of it is so excessive, and there are transparent perspectives from mountains within sight, it is a great spot for recording and inspecting the conduct of lightning. The researchers stuck their 4 upward flashes the usage of high-speed cameras; one flash was once even recorded at a jaw-dropping 24,000 frames according to 2nd.
Those cameras allowed the researchers to determine the variation between upward sure flashes that emit X-rays and the ones that do not. X-ray emission could be very temporary, disappearing throughout the first millisecond of chief formation, and correlating with very fast adjustments within the electrical box, in addition to the velocity at which the present adjustments.
This, the researchers say, has implications for mitigating the quantity of destruction wrought through lightning on human constructions.
“As a physicist, I love so as to perceive the speculation in the back of observations, however this knowledge may be vital for working out lightning from an engineering standpoint,” Oregel-Chaumont says.
“An increasing number of high-altitude constructions, like wind generators and airplane, are being constructed from composite fabrics. Those are much less conductive than metals like aluminum, in order that they warmth up extra, making them at risk of harm from upward lightning.”The staff’s analysis has been printed in Clinical Reviews.
Scientists Measure X-Rays From Specifically Bad Upward Lightning For First Time