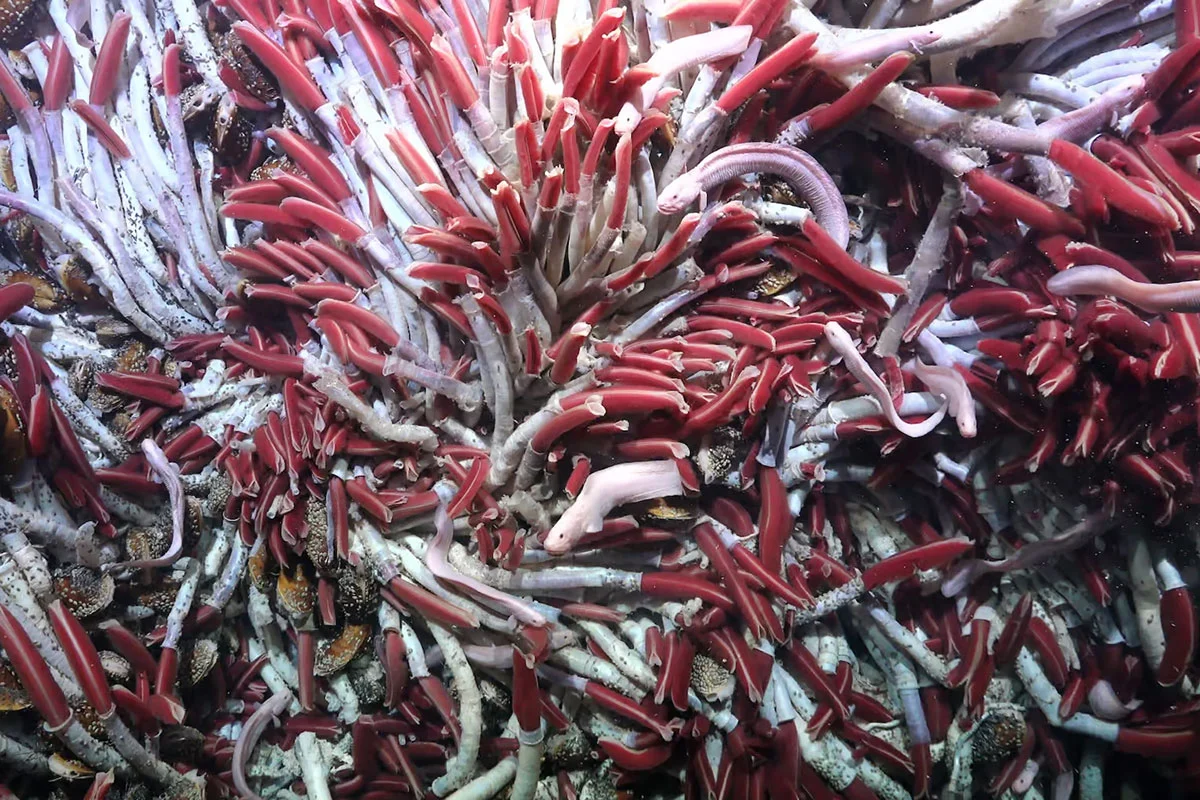
Researchers aboard the Schmidt Ocean Institute’s analysis vessel Falkor (too) made an surprising discovery whilst exploring the East Pacific Upward push, an lively volcanic ridge situated 2,500 meters underneath the sea floor. Their preliminary objective used to be to assemble rock samples from hydrothermal vents to check tubeworm larvae agreement. On the other hand, what they discovered used to be way more odd.
Because the remotely operated car SuBastian lifted plates of oceanic crust, it published cavities stuffed with hydrothermal fluid about 10 centimeters deep. Those cavities, recognized to geologists, maintained a at ease temperature of 25°C. However the actual marvel got here when the researchers tested the photographs extra carefully.
Hidden inside those subterranean chambers used to be a thriving ecosystem, together with :
Snails
Mussels
Massive tubeworms (Riftia pachyptila)
The invention of those complicated existence paperwork in such an surprising location has shocked the clinical neighborhood. It demanding situations earlier assumptions in regards to the barriers of existence in excessive environments and hints at the opportunity of equivalent ecosystems present somewhere else in our sun machine.
In @NatureComms, Vivid et al. provide findings from the #VentUnderworld expedition that turn into clinical figuring out of ecology and the evolution of animal existence at and underneath hydrothermal vents within the deep sea. Learn the whole paper right here: %.twitter.com/Vrl3asqpxq— Schmidt Ocean (@SchmidtOcean) October 16, 2024
The giants of the deep : Riftia pachyptila
A few of the most attractive population of those subterranean cavities are the enormous tubeworms, often referred to as large beard worms. Those outstanding creatures can develop as much as 3 meters in duration, making them true giants of the deep sea.
Riftia pachyptila has lengthy been recognized to thrive round hydrothermal vents at the ocean flooring, however their presence underneath the seafloor used to be totally surprising. Those worms have tailored to live on in one of the excessive environments on Earth, devoid of daylight and matter to crushing drive.
The invention of those worms in subsurface cavities raises intriguing questions on their existence cycle and adaptation methods. Researchers recommend that larvae residing at the ocean flooring is also transported into the subsurface by way of hydrothermal fluids, setting up a dynamic connection between oceanic, seafloor, and subsurface ecosystems.
CharacteristicDescriptionMaximum length3 metersHabitatHydrothermal vents, subsurface cavitiesAdaptationSymbiotic courting with chemosynthetic micro organism
Implications for astrobiology and environmental coverage
The invention of a fancy ecosystem underneath the sea flooring has far-reaching implications for our figuring out of existence on Earth and doubtlessly past. It highlights the interconnectedness of marine ecosystems and underscores the significance of defending those fragile environments.
This discovering may just additionally tell the seek for existence somewhere else in our sun machine. For instance, Jupiter’s moon Europa, which is assumed to have a subsurface ocean and volcanic job, may harbor equivalent prerequisites to these discovered round Earth’s hydrothermal vents. The new release of NASA’s Europa Clipper undertaking objectives to discover this intriguing moon and seek for doable biosignatures.
On the other hand, the newly came upon “biomass layer” underneath the sea flooring is already underneath danger from deep-sea mining tasks. Scientists are calling for pressing protecting measures to safeguard those distinctive ecosystems prior to they’re irreparably broken.
The invention of huge worms in deep-sea cavities serves as a reminder of ways little we learn about our planet’s oceans. It additionally emphasizes the will for persevered exploration and analysis to discover the secrets and techniques hidden within the depths. As we proceed to analyze those excessive environments, we might achieve treasured insights into the prospective risks and alternatives offered by way of underwater volcanic job and its affect on marine existence.
As we delve deeper into the mysteries of the sea flooring, it turns into increasingly more transparent that our planet nonetheless holds many surprises. The invention of huge worms in subsurface cavities is just the start of what guarantees to be a thrilling new bankruptcy in marine biology and astrobiology analysis.