Scientists have came upon the neural headquarters for REM sleep – that dreamy mind state the place the eyes are the one a part of the frame actively transferring.When this circuit on the best of the brainstem is caused in mice, researchers could make animals slip into REM (fast eye motion) sleep, although they’re conscious initially.
If the findings prolong to people, we will be able to be one large step nearer to figuring out the biology of sleep and why it could cross awry.
The data may even lend a hand us manipulate REM sleep for the easier in people with sleep apnea, narcolepsy, widespread distressing nightmares, or REM problems, which motive other people to behave out their goals with motion or vocalizations – equivalent to speaking of their sleep.
Mysteries round REM sleep abound, and analysis is made all of the tougher by means of the truth that scientists nonetheless do not know the place the keep watch over middle for REM sleep sits within the mind, or although there is a keep watch over middle in any respect.
For many years now, some researchers have suspected that neurons within the mammal brainstem play a crucial position within the onset of REM. If the brainstem is minimize out of the image in cats, for example, correct REM sleep can’t be generated and the animals start to act out their goals.
In people with recognized brainstem degeneration, like that observed in Parkinson’s illness, REM sleep will also be disordered in identical techniques.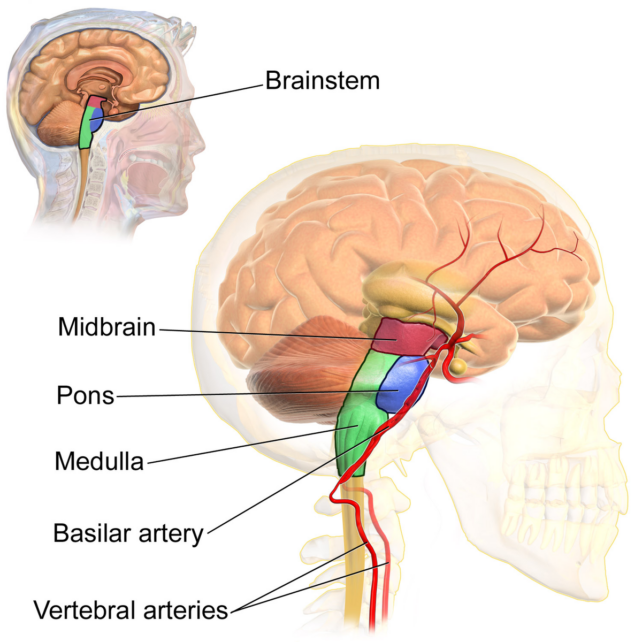 The human brainstem and its portions. (BruceBlaus/Wikimedia Commons)Over time, additional experiments on rodents have discovered proof it’s the pons, on the best of the brainstem, that’s the ‘keep watch over middle’ for the standard lack of muscle pressure that limits motion all through REM sleep.
The human brainstem and its portions. (BruceBlaus/Wikimedia Commons)Over time, additional experiments on rodents have discovered proof it’s the pons, on the best of the brainstem, that’s the ‘keep watch over middle’ for the standard lack of muscle pressure that limits motion all through REM sleep.
However since the neurons that advertise wakefulness on this a part of the mind are intermingled with those who advertise sleep, pinpointing the precise pathways chargeable for this an important segment of sleep has proved difficult.
Neuroscientist Mitsuaki Kashiwagi from the College of Tsukuba and the College of Tokyo has now led a group in Japan and France to a cluster of REM-related neurons within the dorsal a part of the pons.
In mice, those neurons categorical a corticotropin-releasing hormone-binding protein, so they’re known as Crhbp+ neurons.
Those cells undertaking from the pons to neurons within the medulla oblongata, the area of the brainstem simply beneath. Those are known as Nos1+ neurons as a result of they categorical nitric oxide synthase 1. NOs1+ neurons then attach again to the Crhbp+ neurons and directly to neurons within the forebrain.
This loop from the pons to the medulla and again once more may perform as a core circuit of REM sleep, Kashiwagi and his colleagues argue.
When the group deleted pons neurons from the sure comments loop, the mice confirmed diminished sleep and impaired muscle rest all through REM sleep.
When the pons neurons that stretch to the medulla had been activated, then again, mice slipped into REM sleep sooner, and the quantity and duration of REM episodes all through their sleep higher on the expense of wakefulness.
Within the medulla, Nos1+ neurons strongly promoted REMS, projecting to a couple of spaces fascinated by REM process.
In truth, activating those neurons in mice led to direct transitions from wakefulness to REM sleep. Even if non-REM sleep got here first, it was once extremely shortened, with the mice slipping into REM sleep sooner. Neurons that stretch to the forebrain appear to inhibit wakefulness.
People who be afflicted by narcolepsy are recognized to head from wakefulness instantly to REM sleep, however another way this leap is very strange.
“Having established Crhbp as a marker for sleep-regulating neurons, we tested whether or not those neurons are affected in Parkinson’s sufferers with REMS conduct dysfunction,” the authors give an explanation for.
Positive sufficient, the group discovered Crhbp-immunoreactive neurons are in large part diminished on this cohort, “offering perception into the mechanisms underlying the sleep deficits characterizing this illness.”
In a mouse fashion of Parkinson’s illness, the researchers confirmed activation of Crhbp+ neurons within the pons can opposite the noticed sleep abnormalities.
The next move, Kashiwagi and his colleagues say, is to file the process of those neurons at a single-cell solution to determine what they’re truly doing, and why.The find out about was once revealed in Mobile.
Scientists One Step Nearer to Discovering Cause in Mind For REM Sleep