Antibiotics found out within the soil of a Cameroon volcano part a century in the past have in spite of everything been reverse-engineered through Jap researchers, giving clinical scientists a brand new attainable drug within the struggle towards an infection.
In 1974, German chemist Axel Zeeck and his Turkish colleague Mithat Mardin confirmed pink pigments produced through the bacterium Streptomyces arenae have antimicrobial houses, making them a ravishing subject material for pharmacologists to tinker with.
Synthesizing the possibly helpful compounds referred to as β- and γ-naphthocyclinone in helpful amounts proved to be a problem. Some trial and mistake is ceaselessly required to determine the essential chemical reactions, despite the fact that complexity of the naphthocyclinones cause them to tricky to create with out introducing all kinds of byproducts alongside the way in which.
Best now have researchers from the Institute of Science Tokyo been ready to get the process executed, the usage of an means referred to as retrosynthetic research.
As you could wager from the title, it comes to running backwards from a goal molecule to determine its fundamental development blocks. It is a bit like breaking down a posh gadget into its element portions – portions which might be more straightforward to know and compile.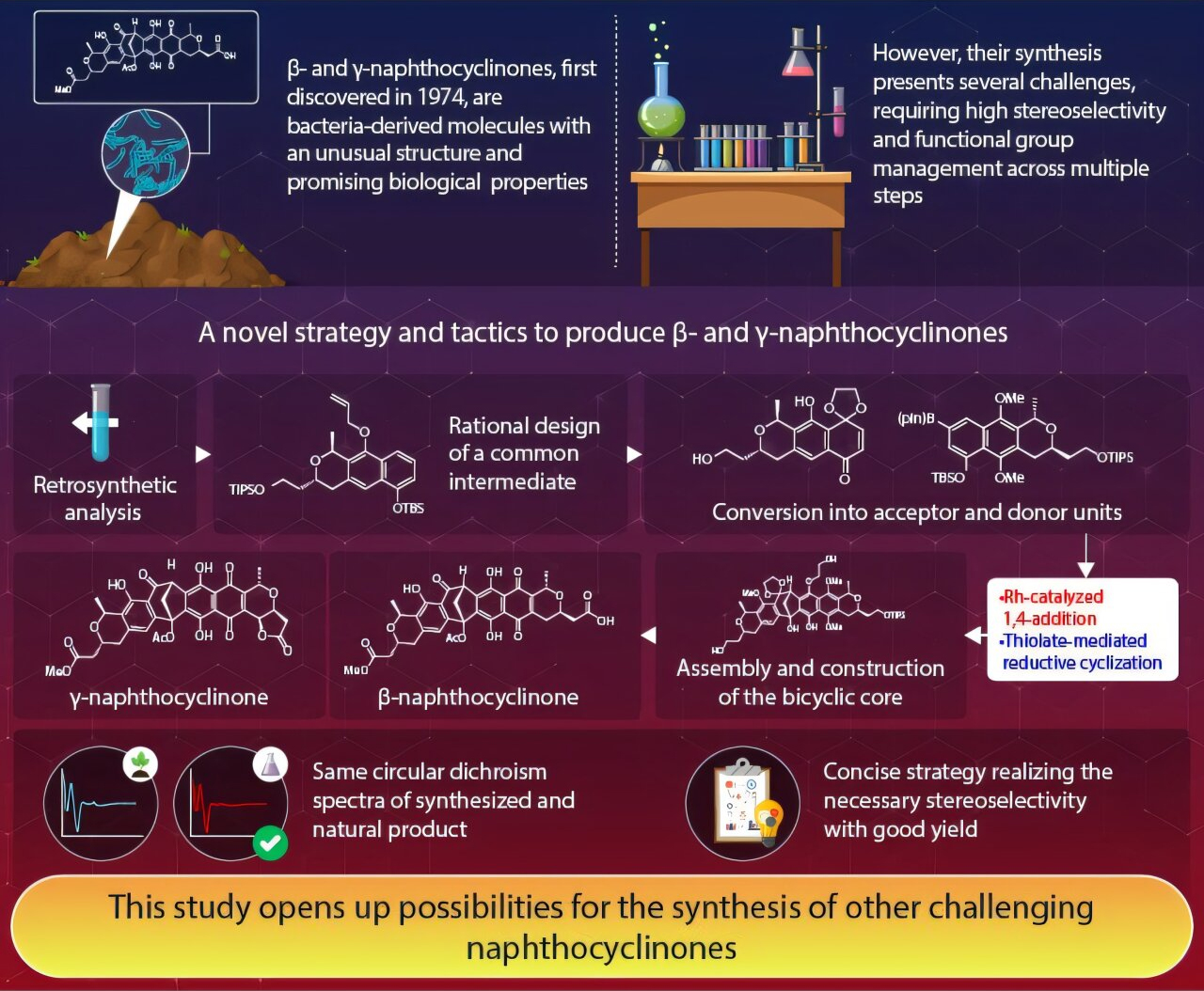 The researchers did some opposite engineering to synthesize the compounds. (Institute of Science Tokyo)The workforce began with β-naphthocyclinone, as γ-naphthocyclinone can also be regarded as a variation. Like many massive molecules, a mix of more effective molecular devices served as a place to begin for the compound’s development.
The researchers did some opposite engineering to synthesize the compounds. (Institute of Science Tokyo)The workforce began with β-naphthocyclinone, as γ-naphthocyclinone can also be regarded as a variation. Like many massive molecules, a mix of more effective molecular devices served as a place to begin for the compound’s development.
Bridging the 2 devices is a posh molecule referred to as bicyclo[3.2.1]octadienone, despite the fact that getting the chemical into the easiest place with out converting the opposite parts or developing a wholly other product is more straightforward mentioned than executed.
Guided through their retrosynthetic recipe and making use of quite a few complicated chemistry strategies, the researchers discovered a trail that allowed them to place the items with precision and bond them in some way that did not have an effect on their serve as.
The instant of fact got here in evaluating the precise three-D atom preparations – or in clinical phrases, the round dichroism spectra – of the synthesized compounds with the ones created through nature within the volcano.
“The round dichroism spectra of our synthesized compounds had been just like the ones of naturally going on ones, implying that absolutely the configuration of artificial and herbal molecules was once the similar,” says chemist Yoshio Ando from the Institute of Science Tokyo.
Those strategies in spite of everything enabled the researchers to synthesize β-naphthocyclinone with a yield of a minimum of 70 p.c (so 70 p.c of the utmost quantity anticipated given the beginning fabrics).
They then used any other chemical procedure, oxidative lactonization, to provide γ-naphthocyclinone with a yield of 87 p.c. The 2 compounds are equivalent, however γ-naphthocyclinone has some added extras.
Synthesizing the antibiotics in a lab may see them produced in better amounts for clinical and analysis use: there is no wish to take common journeys again to a volcano, for instance. What is extra, the researchers suppose the moderately calibrated approaches they used right here can be utilized in long run research as neatly – specifically in synthesizing different compounds with equivalent constructions.
“Additional efforts alongside those strains are already in development in our laboratory,” says Ando.The analysis has been printed in Angewandte Chemie World Version.
Scientists Recreated an Antibiotic Molecule Present in a Volcanic Crater