After greater than a decade of labor, researchers have reached a big milestone of their efforts to re-engineer lifestyles within the lab, placing in combination the general chromosome in a man-made yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) genome.
The researchers, led by means of a staff from Macquarie College in Australia, selected yeast with the intention to show the potential of generating foodstuffs that might live on the trials of a converting local weather or common illness.
It is the first time a man-made eukaryotic genome has been built in complete, following on from successes with more practical micro organism organisms. It is a proof-of-concept for a way extra complicated organisms, like meals vegetation, may well be synthesized by means of scientists.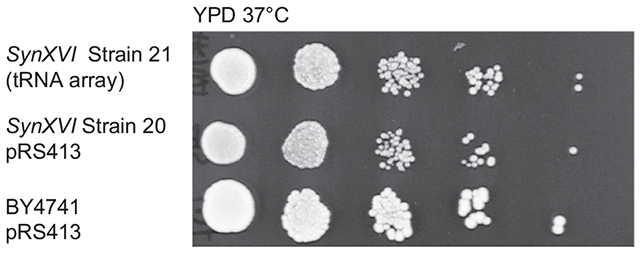 Scientists manipulated SynXVI to get yeast rising at increased temperatures. (Goold et al., Nature Communications, 2025)”This can be a landmark second in artificial biology,” says molecular microbiologist Sakkie Pretorius, from Macquarie College. “It’s the ultimate piece of a puzzle that has occupied artificial biology researchers for a few years now.”
Scientists manipulated SynXVI to get yeast rising at increased temperatures. (Goold et al., Nature Communications, 2025)”This can be a landmark second in artificial biology,” says molecular microbiologist Sakkie Pretorius, from Macquarie College. “It’s the ultimate piece of a puzzle that has occupied artificial biology researchers for a few years now.”
This doesn’t suggest we will get started rising utterly synthetic yeast from scratch, however it does imply dwelling yeast cells can doubtlessly be completely recoded – regardless that so much extra paintings is needed to get this procedure delicate and scaled up sooner than that may occur.
And the coding analogy is a superb one, since the researchers needed to spend quite a lot of effort and time debugging the sixteenth and ultimate artificial yeast chromosome (known as SynXVI) sooner than the genome functioned as desired.
A number of gene-editing gear, comparable to one according to CRISPR, had been deployed to identify and connect issues within the chromosome. As an example, they had to get the yeast to correctly use glycerol as an power supply at upper temperatures, which is one thing that scientists may need to do to beef up yeast resilience.
Some other factor the staff overcame used to be with genetic markers, used to spot and observe DNA within the genome. The hanging of those markers issues, it seems – getting it flawed can intrude with mobile habits.
“Considered one of our key findings used to be how the site of genetic markers may disrupt the expression of crucial genes,” says artificial biologist Hugh Goold, from Macquarie College.
The Sc2.0 venture, of which this analysis is part, is not only about enhancing vegetation. The similar rules may be implemented to medications and sustainable fabrics, with alternatives to hurry up their manufacturing or cause them to harder.
Our efforts in genetic engineering proceed to get extra bold and extra complete, and that is every other vital step down that street. The enhancements are partly all the way down to advances in generation and strategies, with the robotics to be had on the Australian Genome Foundry a very powerful on this explicit find out about.
“The factitious yeast genome represents a quantum soar in our skill to engineer biology,” says artificial biologist Briardo Llorente, from Macquarie College. “This success opens up thrilling probabilities for growing extra environment friendly and sustainable biomanufacturing processes, from generating prescribed drugs to making new fabrics.”The analysis has been printed in Nature Communications.
Scientists Simply Completed a Primary Milestone in Developing Artificial Lifestyles













