Desolate tract-dwelling micro organism that feed on daylight, slurp up carbon dioxide, and emit oxygen may well be integrated into paint that dietary supplements the air in a habitat on Mars.It is referred to as Chroococcidiopsis cubana, and scientists have evolved a biocoating that emits measurable quantities of oxygen each day whilst decreasing the quantity of carbon dioxide within the air round it. This has implications, no longer only for house commute however right here at house on Earth, too, in step with a workforce led by way of microbiologist Simone Krings of the College of Surrey in the United Kingdom.”With the rise in greenhouse gasses, specifically CO2, within the environment and issues about water shortages because of emerging international temperatures, we’d like leading edge, environmentally pleasant, and sustainable fabrics,” says bacteriologist Suzie Hingley-Wilson of the College of Surrey.”Automatically tough, ready-to-use biocoatings, or ‘dwelling paints,’ may just assist meet those demanding situations by way of decreasing water intake in generally water-intensive bioreactor-based processes.”Chroococcidiopsis is a unusual little genus of beasties. If there is a position on Earth you suppose no lifestyles may be able to to find acquire, you might be prone to discover a species of this bacterium there. It harnesses a peculiar roughly photosynthesis that may benefit from extraordinarily low-light stipulations, with a back-up survival mechanism for even darker puts. It is been discovered within the pitch blackness of ultra-deep caves, and in Earth’s decrease crust underneath the sea flooring.Chroococcidiopsis cubana once in a while lives in deserts, in stipulations no longer dissimilar to these on Mars. And, like different cyanobacteria, its metabolism has some fascinating houses. The bacterium takes in CO2, which it fixes to turn out to be by means of photosynthesis into natural compounds, freeing oxygen as a part of the method.Krings and her workforce sought after to broaden a biocoating that harnesses those houses. Those are coatings, like paint, into which dwelling micro organism are integrated in layers. They need to be sturdy, with out containing elements that would hurt the micro organism therein.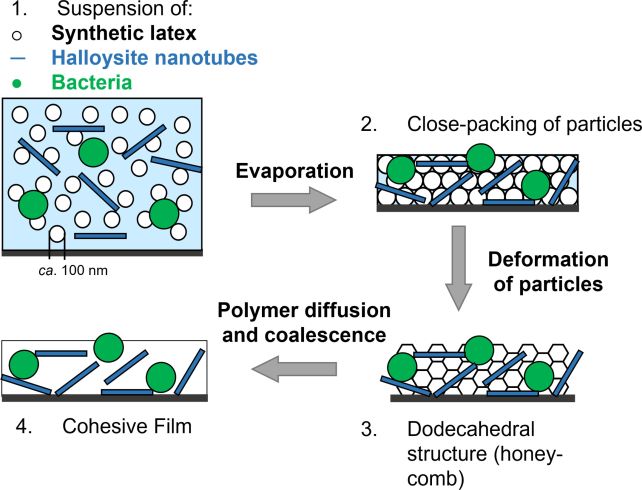 Diagram illustrating how the biopaint is made. (Krings et al., Microbiol. Spectr., 2023)This is more difficult than it would appear: the biocoating matrix must be porous, to permit for hydration and mobile delivery, however automatically tough, and difficult. The workforce evolved one way of blending latex with nanoclay debris that accomplished those houses, safely encapsulating their micro organism.Your next step was once to be sure that the paint was once running as supposed, and that the tiny microbes inside of it have been proceeding to are living satisfied, tiny lives. The workforce noticed their coating for 30 days, appearing measurements of oxygen output, and CO2 enter.They discovered the paint persistently launched oxygen at a fee of as much as 0.4 grams of oxygen according to gram of biomass according to day, and that this remained stable for all of the month. That is as much as 400 grams (14 oz) of oxygen for each kilogram (35 oz) of paint. As well as, the paint absorbed CO2. The researchers have referred to as their invention Inexperienced Residing Paint.That output would almost certainly no longer be enough by itself for a Mars habitat; a workforce of astronauts dwelling on Mars for a 12 months will want an estimated 500 metric lots of oxygen; however each little little bit of oxygen that may be eked in situ at the pink planet will cut back the quantity of oxygen house missions are going to wish to send there on a spacecraft.”The photosynthetic Chroococcidiopsis have an unusual talent to live to tell the tale in excessive environments, like droughts and after top ranges of UV radiation publicity,” Krings says. “This makes them attainable applicants for Mars colonization.”The analysis has been printed in Microbiology Spectrum.
Diagram illustrating how the biopaint is made. (Krings et al., Microbiol. Spectr., 2023)This is more difficult than it would appear: the biocoating matrix must be porous, to permit for hydration and mobile delivery, however automatically tough, and difficult. The workforce evolved one way of blending latex with nanoclay debris that accomplished those houses, safely encapsulating their micro organism.Your next step was once to be sure that the paint was once running as supposed, and that the tiny microbes inside of it have been proceeding to are living satisfied, tiny lives. The workforce noticed their coating for 30 days, appearing measurements of oxygen output, and CO2 enter.They discovered the paint persistently launched oxygen at a fee of as much as 0.4 grams of oxygen according to gram of biomass according to day, and that this remained stable for all of the month. That is as much as 400 grams (14 oz) of oxygen for each kilogram (35 oz) of paint. As well as, the paint absorbed CO2. The researchers have referred to as their invention Inexperienced Residing Paint.That output would almost certainly no longer be enough by itself for a Mars habitat; a workforce of astronauts dwelling on Mars for a 12 months will want an estimated 500 metric lots of oxygen; however each little little bit of oxygen that may be eked in situ at the pink planet will cut back the quantity of oxygen house missions are going to wish to send there on a spacecraft.”The photosynthetic Chroococcidiopsis have an unusual talent to live to tell the tale in excessive environments, like droughts and after top ranges of UV radiation publicity,” Krings says. “This makes them attainable applicants for Mars colonization.”The analysis has been printed in Microbiology Spectrum.
Scientists Simply Got here Up With a Wild Thought For Making Oxygen on Mars