“Hearst Magazines and Yahoo might earn fee or income on some pieces via those hyperlinks.”
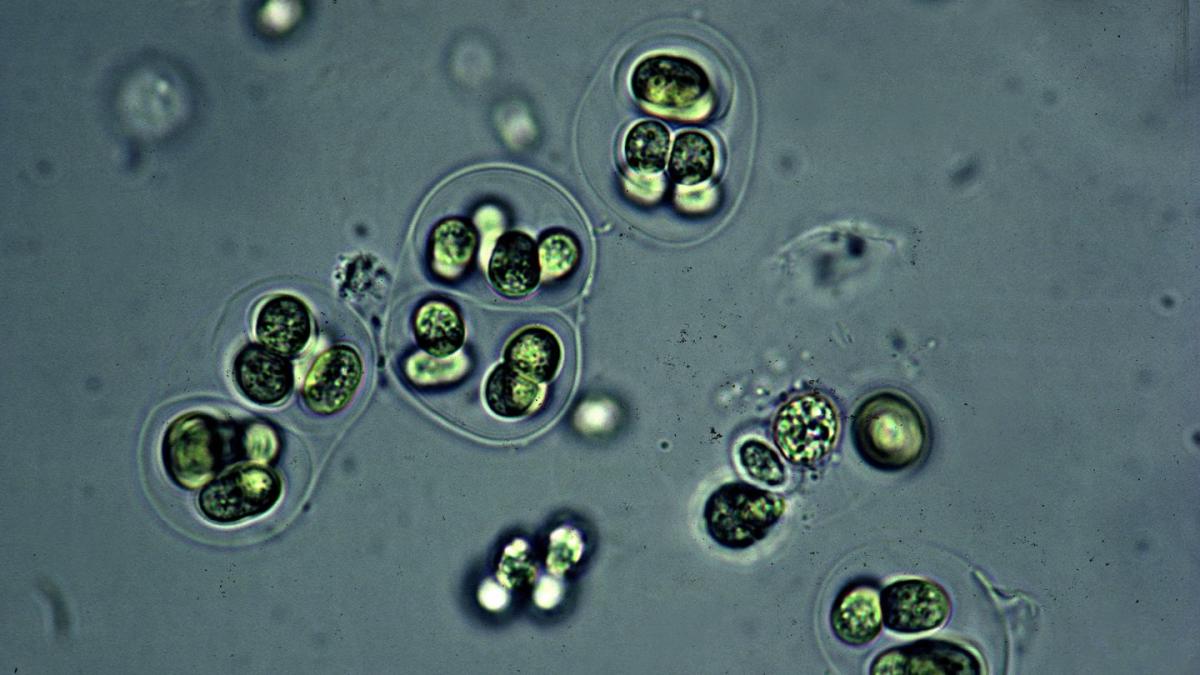
Fossils preserved inside historic rock might turn out that photosynthesis began manner previous than we concept.If accurately dated to one.75 billion years in the past, the brand new to find supplies further perception into early Earth ecosystems.Scientists consider the learn about of extra fossils may just yield extra clues in regards to the origins of lifestyles.Researchers on a quest to grasp the origins of lifestyles simply realized a bit of lesson about photosynthesis from 1.75 billion years in the past.In a brand new learn about printed in Nature, a group of researchers declare that microfossils discovered within the desolate tract of north Australia blow their own horns the earliest identified indicators of photosynthesis. And that would approach a greater working out of ways all of lifestyles can have begun.Those microfossils are remnants of a kind of organism known as cyanobacteria, which mavens consider were round for so long as 3.5 billion years (despite the fact that the oldest showed fossil examples are from about 2 billion years in the past). Someday of their evolution, some sorts of those organisms advanced thylakoids—constructions inside cells wherein photosynthesis happens—which can have allowed them to give a contribution massive quantities of oxygen to Earth’s surroundings via photosynthesis in what has change into referred to as the Nice Oxidation Tournament.Those new findings be offering up the oldest proof of photosynthesis discovered thus far. The researchers declare that their discovery extends the fossil report by way of no less than 1.2 billion years, and that those first actual photosynthesizing cells gave the impression more or less 1.75 billion years in the past.“[This discovery] permits the unambiguous identity of early oxygenic photosynthesizers and a brand new redox proxy for probing early Earth ecosystems,” the authors wrote within the paper, “highlighting the significance of inspecting the ultrastructure of fossil cells to decipher their paleobiology and early evolution.”Those thrilling fossils have been found out in historic rocks—positioned within the McDermott Formation in northern Australia—and have the pigment chlorophyll, which permits organisms to take in the daylight all over photosynthesis. The presences of chlorophyll used to be sufficient for researchers to resolve that photosynthesis had took place in those little compartments, which might imply that the method advanced a lot previous than used to be in the past demonstrable.And that might most likely lend a hand provide an explanation for the Nice Oxidation Tournament. Proof within the fossil report displays us that there used to be an enormous soar in atmospheric oxygen ranges round 2.4 billion years in the past. It used to be vital to the life of lifestyles on Earth as we realize it, and whilst scientists aren’t certain what brought about it, one concept is that that is across the time that photosynthetic organisms advanced into being and started to exist in massive numbers. Via courting fossilized cells with the essential elements for photosynthesis to as with regards to that oxygen-flourishing tournament as conceivable, researchers are ready to transport one step nearer to working out the position of oxygen—and the cells serving to create it—within the origins of lifestyles on Earth.In fact, your next step is extra analysis. In particular, the group intends to inspect fossil cells internationally to peer simply how properly they fit up with this new timeline.“We expect,” the authors wrote, “that identical ultrastructural analyses of well-preserved microfossils would possibly amplify the geological report of oxygenic photosynthesizers and of early, weakly oxygenated ecosystems wherein advanced cells advanced.”Take a deep breath, and dive on into the science.You Would possibly Additionally Like
Scientists Solved a 1.75-Billion-12 months Thriller About How Existence Materialized on Earth