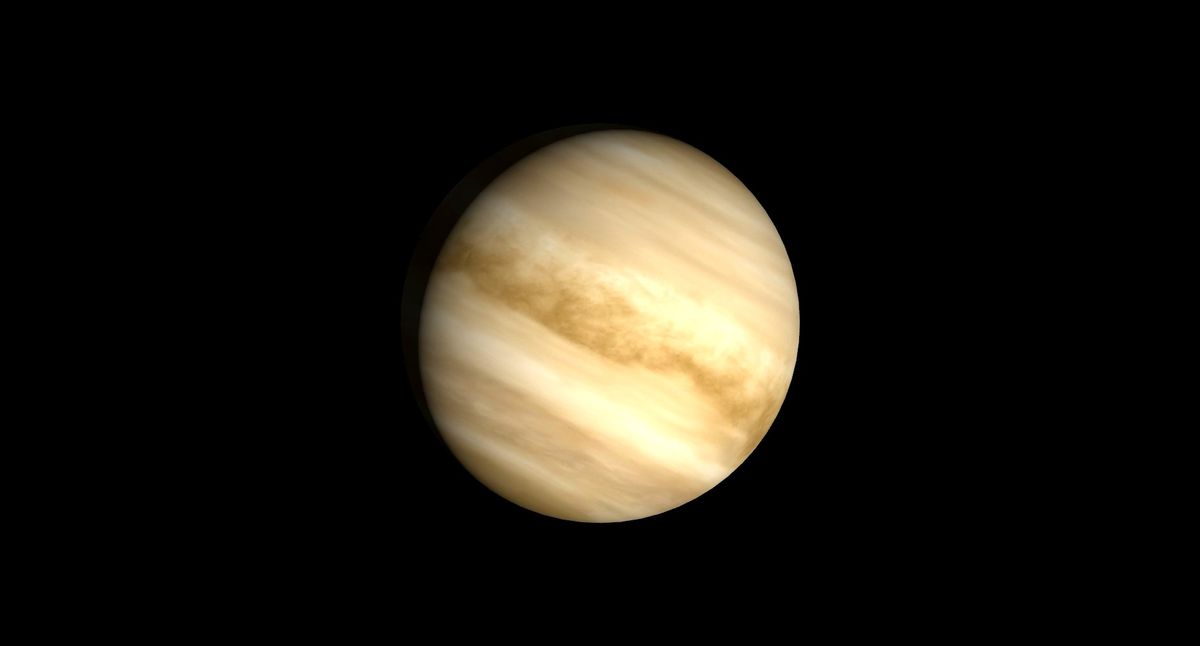
Scientists have seen one thing sudden in Venus’ surroundings — an building up within the degree of deuterium relative to hydrogen. K, positive, that does not sound like probably the most thrilling observation. On the other hand, the effects of this discovery may just in reality upend our present figuring out of the amber global.Because it seems, it could impact our assumption that Venus is a eternally barren, inhospitable planet. Here is how.”Venus is frequently referred to as Earth’s dual because of its identical measurement,” stated Hiroki Karyu, a researcher at Tohoku College and probably the most find out about’s scientists, in a observation. “Regardless of the similarities between the 2 planets, it has advanced in a different way. Not like Earth, Venus has excessive floor prerequisites.”Liquid water is not able to exist in important sufficient amounts because of the extraordinary temperatures and pressures underneath Venus’ thick cloud layers. “To position this into standpoint, those altitudes have 150,000 instances much less water than related altitudes on Earth,” wrote the scientists of their find out about.However that is not to mention this used to be at all times the case.Deuterium and hydrogen are isotopes of each other, that means they are other sorts of the similar component, containing equivalent numbers of protons however other numbers of neutrons of their nuclei. This ends up in them having other atomic lots, however their chemical houses stay fairly the similar.Comparable: Venus might be able to make stronger lifestyles, new atmospheric proof suggestsBreaking house information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!So much can also be gleaned from isotopic ratios. Take carbon relationship, as an example, which is an impressive device scientists use to glean the age of natural subject the use of relative proportions of the isotopes carbon-12 and carbon-14. The ratio of those isotopes in a subject material adjustments through the years as carbon-14 radioactively decays and isn’t changed. Venus and Earth are believed to have had identical HDO/H2O ratios as soon as upon a time, as each planets shaped in a sizzling area of the early sun machine the place water could not condense. Later, water is assumed to were dropped at the worlds through water-rich asteroids most likely from the outer asteroid belt, which will have to have ended in identical deuterium-to-hydrogen (D/H) ratios on each planets. This speculation is additional supported through the related ranges of different risky parts, like carbon and nitrogen, between Venus and Earth.However after poring thru knowledge from the Sun Occultation within the Infrared (SOIR) device at the Venus Categorical house probe (which used to be operational from 2006 to 2014) has positioned a blip on this tale. Scientists discovered that the ratio of HDO is now 120 instances upper in comparison to H2O in Venus’ surroundings. “This enrichment is basically because of sun radiation breaking down water isotopologues within the higher surroundings, generating hydrogen (H) and deuterium (D) atoms,” wrote the ESA scientists. “Since H atoms break out into house extra readily because of their decrease mass, the HDO/H2O ratio step by step will increase.”Additionally they made up our minds that the focus of water molecules, each H2O and HDO, will increase with altitude, in particular between 70 and 110 kilometers (43 and 68 miles) above Venus’ floor. Additional, they discovered that the ratio of HDO to H2O turns into extraordinarily increased at those altitudes, greater than 1,500 instances upper than what is located in Earth’s oceans. This means that Venus’ surroundings incorporates a lot more deuterium-rich water in comparison to Earth, pointing to important variations within the atmospheric processes of the 2 planets.The group speculates that those processes could be managed through local weather mechanisms involving sulfuric acid (H2SO4) aerosols, which make up a majority of Venus’ clouds. “Those aerosols shape simply above the clouds, the place temperatures drop under the sulphurated water dew level, resulting in the formation of deuterium-enriched aerosols,” defined the scientists. “Those debris upward thrust to better altitudes, the place greater temperatures make them evaporate, liberating extra important fraction of HDO in comparison to H2O. The vapour then is transported downwards, restarting the cycle.”As to how the findings could have broader implications for our figuring out of the planet? First, the group hopes long run research will imagine how the ratio of deuterium to hydrogen (D/H) adjustments with altitude when calculating the entire quantities of those gases in Venus’ surroundings. 2nd, the way in which D/H adjustments with altitude impacts how temporarily hydrogen and deuterium break out into house. As an example, prime within the surroundings, a lot more deuterium is launched than anticipated, which will have an effect on the total D/H ratio if a few of this deuterium escapes.Which means that, to appropriately know how Venus’ surroundings has advanced and what kind of water it would have misplaced through the years, scientists want to use detailed fashions that account for those altitude adjustments.
Scientists to find sudden clue about Venus’ previous in its surroundings