Abstract: Researchers have recognized a molecular mechanism in human cells that mimics embryonic diapause, a procedure some mammals use to pause building. Via inhibiting the mTOR signaling pathway in stem cell-derived blastoids, scientists caused a dormant state very similar to that present in different mammals. This reversible state provides new insights into early human building and can have doable packages in in vitro fertilization (IVF). The findings recommend that people may retain this evolutionary talent, which may well be harnessed to reinforce reproductive well being.Key Details:Inhibiting the mTOR pathway can cause a reversible dormant state in human cells.Embryonic diapause is a herbal reproductive technique utilized by some mammals to increase being pregnant.This discovery might result in advances in IVF by means of bettering embryo timing and implantation luck.Supply: IMBAIn some mammals, the timing of the typically steady embryonic building can also be altered to toughen the possibilities of survival for each the embryo and the mummy. This mechanism to briefly gradual building, referred to as embryonic diapause, ceaselessly occurs on the blastocyst degree, simply prior to the embryo implants within the uterus. All the way through diapause, the embryo stays free-floating and being pregnant is prolonged. This dormant state can also be maintained for weeks or months prior to building is resumed, when prerequisites are favorable.Even supposing now not all mammals use this reproductive technique, the power to pause building can also be brought about experimentally. Whether or not human cells can reply to diapause triggers remained an open query. 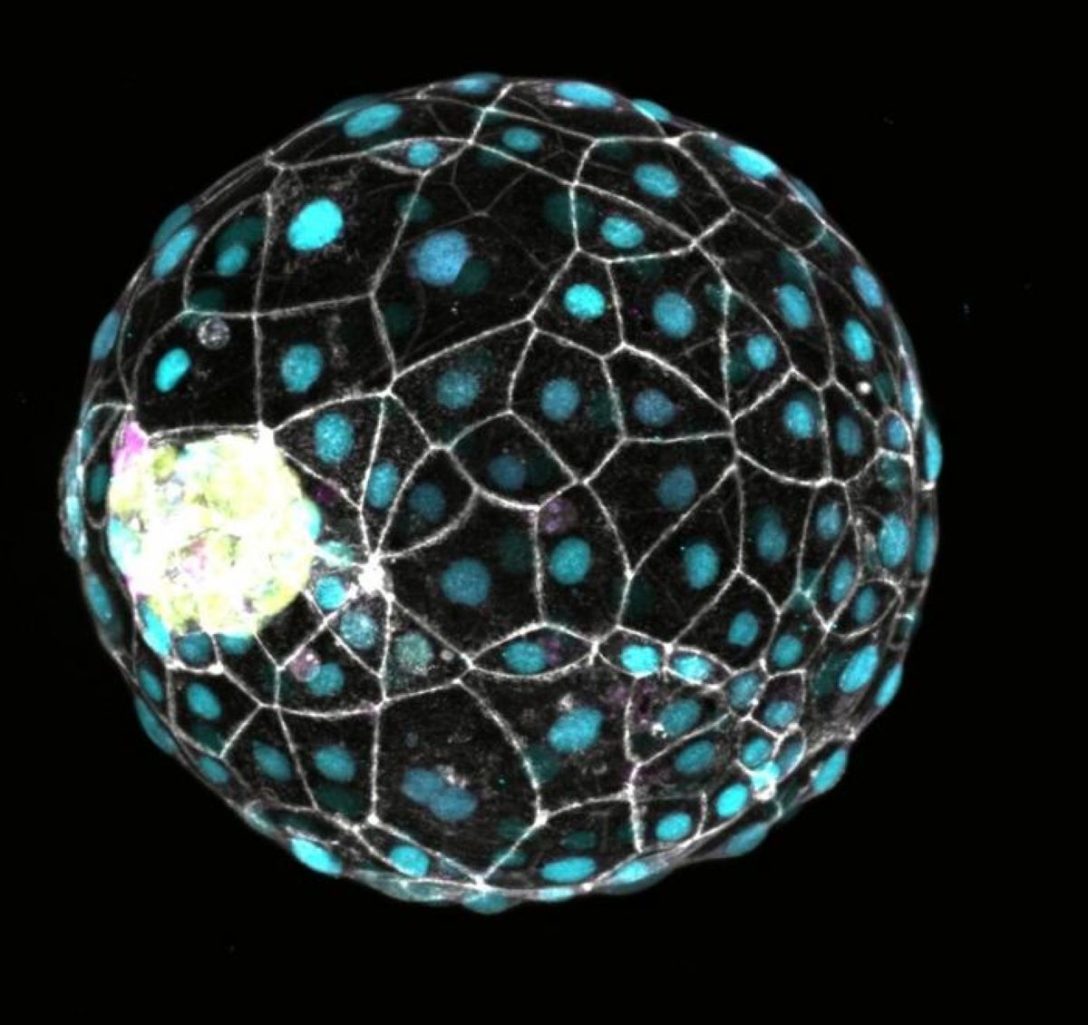 A dormant human blastoid. Credit score: Heidar Heidari Khoei/IMBANow, a learn about by means of the labs of Aydan Bulut-Karslıoğlu on the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics in Berlin and Nicolas Rivron on the Institute of Molecular Biotechnology (IMBA) of the Austrian Academy of Sciences in Vienna, an ERC grantee, has recognized that the molecular mechanisms that keep watch over embryonic diapause additionally appear to be actionable in human cells.Their effects had been printed on September twenty sixth within the magazine Cellular. Stem cell-derived fashions to check embryonic diapause in people Of their analysis, the scientists didn’t perform experiments on human embryos and as a substitute used human stem cells and stem cell-based blastocyst fashions referred to as blastoids.Those blastoids are a systematic and moral choice to the use of embryos for analysis. The researchers came upon that modulation of a particular molecular cascade, the mTOR signaling pathway, in those stem cellular fashions induces a dormant state remarkably corresponding to diapause.“The mTOR pathway is a big regulator of expansion and developmental development in mouse embryos”, says Aydan Bulut-Karslioglu.“After we handled human stem cells and blastoids with an mTOR inhibitor we seen a developmental extend, because of this that human cells can deploy the molecular equipment to elicit a diapause-like reaction.” This dormant state is characterised by means of decreased cellular department, slower building and a reduced talent to connect to the uterine lining. Importantly, the capability to go into this dormant degree appears to be limited to a temporary developmental length.“The developmental timing of blastoids can also be stretched across the blastocyst degree, which is strictly the degree the place diapause works in maximum mammals”, says shared first creator Dhanur P. Iyer. Additionally, this dormancy is reversible, and blastoids resume standard building when the mTOR pathway is reactivated. The power to change the timing of embryonic building has implications for IVF The authors concluded that people, like different mammals, may possess an inherent mechanism to briefly decelerate their building, even if this mechanism might not be used all through being pregnant.“This doable could also be a vestige of the evolutionary procedure that we now not employ,” says Nicolas Rivron.“Even supposing we have now misplaced the power to naturally input dormancy, those experiments recommend that we’ve got however retained this interior talent and may just in the end unharness it.”For elementary analysis, the query arises as as to whether human and different mammalian cells input the dormant state by way of identical or choice pathways and use it for a similar functions, for instance both pausing or timing their building and implantation. The workforce’s discoveries will have implications for reproductive drugs: “At the one hand, present process quicker building is understood to extend the luck price of in vitro fertilization (IVF), and adorning mTOR process may just accomplish that,” Nicolas Rivron explains.“Alternatively, triggering a dormant state all through an IVF process may provide a bigger time window to evaluate embryo well being and to synchronize it with the mummy for higher implantation within the uterus.” General, the brand new findings supply unexpected insights into the processes governing our earliest building, which may open new avenues for reinforcing reproductive well being.“This thrilling collaboration is an affidavit to how complicated organic questions can also be tackled by means of bringing in combination respective experience,” says Heidar Heidari Khoei, postdoctoral fellow within the lab of Nicolas Rivron and the learn about’s co-first creator.“I imagine this paintings now not simplest underscores the significance of collaboration in advancing science but additionally opens up additional chances for figuring out how more than a few alerts are perceived by means of cells as they get ready for his or her developmental adventure.” Investment: Nicolas Rivron is a bunch chief at IMBA and funded by means of an ERC Consolidator Grant. About this embryonic building and genetics analysis newsAuthor: Manel Llado
A dormant human blastoid. Credit score: Heidar Heidari Khoei/IMBANow, a learn about by means of the labs of Aydan Bulut-Karslıoğlu on the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Genetics in Berlin and Nicolas Rivron on the Institute of Molecular Biotechnology (IMBA) of the Austrian Academy of Sciences in Vienna, an ERC grantee, has recognized that the molecular mechanisms that keep watch over embryonic diapause additionally appear to be actionable in human cells.Their effects had been printed on September twenty sixth within the magazine Cellular. Stem cell-derived fashions to check embryonic diapause in people Of their analysis, the scientists didn’t perform experiments on human embryos and as a substitute used human stem cells and stem cell-based blastocyst fashions referred to as blastoids.Those blastoids are a systematic and moral choice to the use of embryos for analysis. The researchers came upon that modulation of a particular molecular cascade, the mTOR signaling pathway, in those stem cellular fashions induces a dormant state remarkably corresponding to diapause.“The mTOR pathway is a big regulator of expansion and developmental development in mouse embryos”, says Aydan Bulut-Karslioglu.“After we handled human stem cells and blastoids with an mTOR inhibitor we seen a developmental extend, because of this that human cells can deploy the molecular equipment to elicit a diapause-like reaction.” This dormant state is characterised by means of decreased cellular department, slower building and a reduced talent to connect to the uterine lining. Importantly, the capability to go into this dormant degree appears to be limited to a temporary developmental length.“The developmental timing of blastoids can also be stretched across the blastocyst degree, which is strictly the degree the place diapause works in maximum mammals”, says shared first creator Dhanur P. Iyer. Additionally, this dormancy is reversible, and blastoids resume standard building when the mTOR pathway is reactivated. The power to change the timing of embryonic building has implications for IVF The authors concluded that people, like different mammals, may possess an inherent mechanism to briefly decelerate their building, even if this mechanism might not be used all through being pregnant.“This doable could also be a vestige of the evolutionary procedure that we now not employ,” says Nicolas Rivron.“Even supposing we have now misplaced the power to naturally input dormancy, those experiments recommend that we’ve got however retained this interior talent and may just in the end unharness it.”For elementary analysis, the query arises as as to whether human and different mammalian cells input the dormant state by way of identical or choice pathways and use it for a similar functions, for instance both pausing or timing their building and implantation. The workforce’s discoveries will have implications for reproductive drugs: “At the one hand, present process quicker building is understood to extend the luck price of in vitro fertilization (IVF), and adorning mTOR process may just accomplish that,” Nicolas Rivron explains.“Alternatively, triggering a dormant state all through an IVF process may provide a bigger time window to evaluate embryo well being and to synchronize it with the mummy for higher implantation within the uterus.” General, the brand new findings supply unexpected insights into the processes governing our earliest building, which may open new avenues for reinforcing reproductive well being.“This thrilling collaboration is an affidavit to how complicated organic questions can also be tackled by means of bringing in combination respective experience,” says Heidar Heidari Khoei, postdoctoral fellow within the lab of Nicolas Rivron and the learn about’s co-first creator.“I imagine this paintings now not simplest underscores the significance of collaboration in advancing science but additionally opens up additional chances for figuring out how more than a few alerts are perceived by means of cells as they get ready for his or her developmental adventure.” Investment: Nicolas Rivron is a bunch chief at IMBA and funded by means of an ERC Consolidator Grant. About this embryonic building and genetics analysis newsAuthor: Manel Llado
Supply: IMBA
Touch: Manel Llado – IMBA
Symbol: The picture is credited to Heidar Heidari Khoei/IMBAOriginal Analysis: The findings will seem in Cellular
Scientists Uncover Attainable to Pause Human Embryo Construction – Neuroscience Information